
Absorbance (optical density) of the different solgel photoelectrodes.... Download Scientific
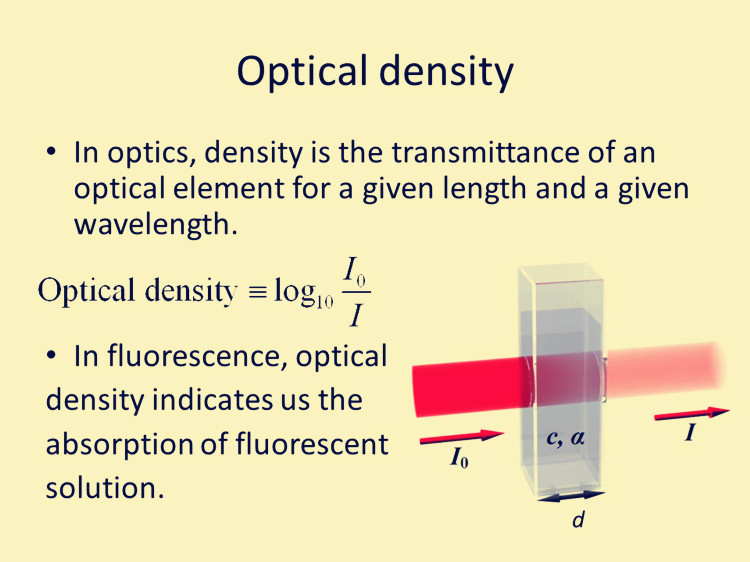
It is defined as the logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted light intensity through a medium. Let Io be the intensity of the incident light and I be the intensity of the transmitted light. Then absorbance A of the medium is mathematically given as, Rewriting the equation, we get Transmittance value in (%) is given as T x 100% So,

Optical density values in terms of the absorbance of the aqueous... Download Scientific Diagram
Optical density measures how much a substance hinders the passage of light, while absorbance quantifies the light absorbed by a substance. Key Differences Optical density refers to the degree to which a material impedes the transmission of light, considering factors like reflection and scattering.

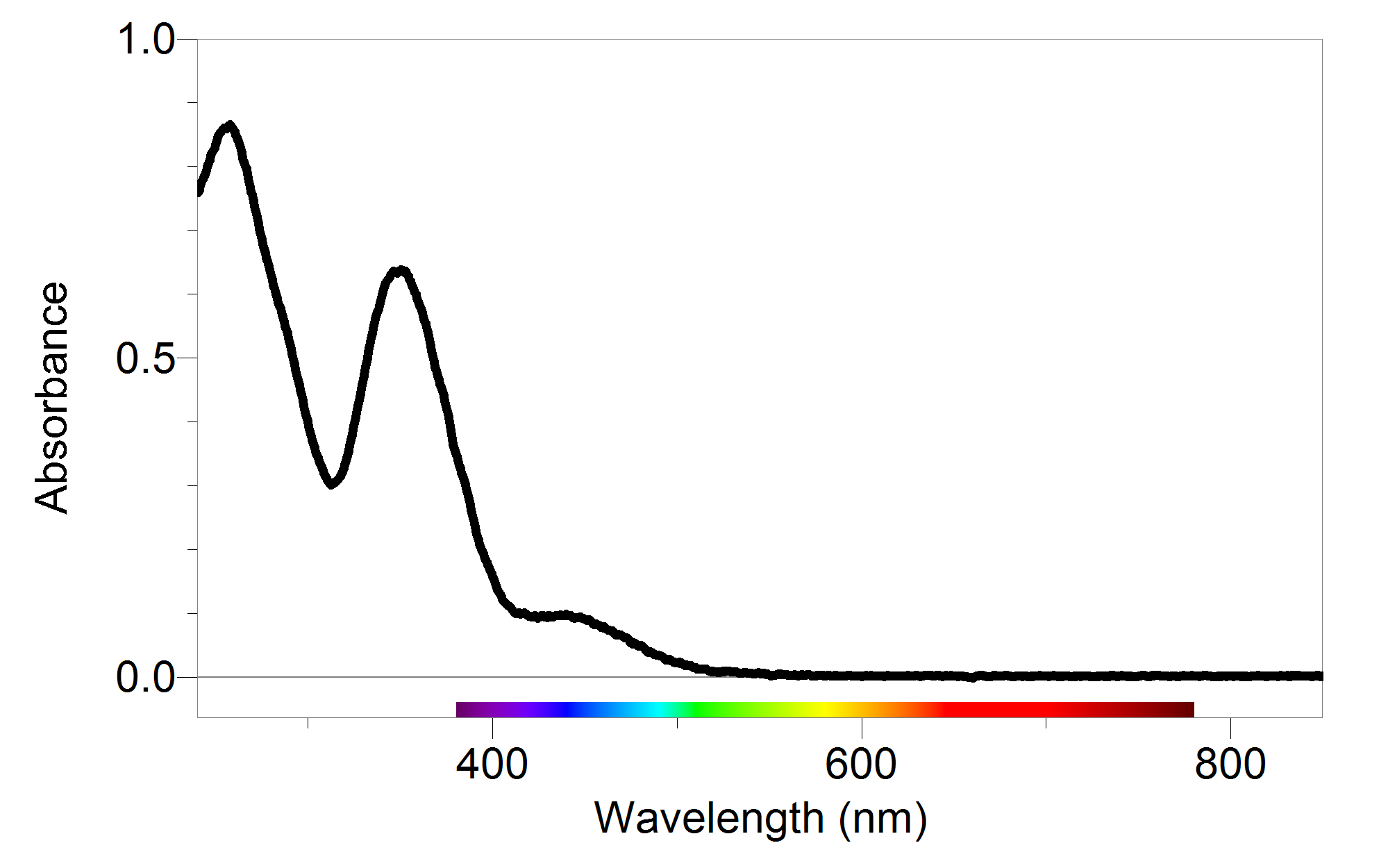
Bisphenol A UVVIS absorbance spectrum in water (OD optical density). Download Scientific Diagram
Because the principles used to measure light scattering and absorbance are different, the amount of light scattered by a solution is referred to as its "optical density" rather than its "absorbance." The optical density of a sample analyzed at 600 nm is abbreviated OD 600, with the subscript indicating the wavelength used for the.

Graphical presentation of the absorbance value (optical density (OD))... Download Scientific
The optical density or absorbance of a material is a logarithmic intensity ratio of the light falling upon the material, to the light transmitted through the material: (5.76) where I0 and I1 are the intensities of the incident and transmitted lights, respectively.

e Calibration curves of optical density (595 nm) versus bacterial... Download Scientific Diagram
Absorbance (A), also known as optical density (OD), is the quantity of light absorbed by a solution. Transmittance is the quantity of light that passes through a solution. Absorbance and % transmittance are often used in spectrophotometry and can be expressed by the following: Absorbance equation A = Log 10 (I 0 /I)

UVvisible optical density (OD) spectra of asprepared (a) n CdS and n... Download Scientific
Absorbance is defined as "the logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted radiant power through a sample (excluding the effects on cell walls)". [1] Alternatively, for samples which scatter light, absorbance may be defined as "the negative logarithm of one minus absorptance, as measured on a uniform sample". [2]

Difference Between Optical Density & Absorbance Sciencing
Optical density (OD) is widely used to estimate the density of cells in liquid culture, but cannot be compared between instruments without a standardized calibration protocol and is.
(a) Absorbance (optical density) spectra of Au nanorods (AR = 3.7) in... Download Scientific
The absorbance e.g. of an optical filter or saturable absorber is the logarithm with base 10 of its inverse power transmission factor ( transmittance ): A = lg ( P i n / P o u t) For example, an absorbance of 3 means that the optical power is attenuated by the factor 10 3 = 1000. That would correspond to an attenuation by 30 decibels and a.

Biomass vs. Absorbance. Relation between Optical Density (Absorbance at... Download Scientific
Optical density is an older term that, in the context of absorption spectroscopy, is synonymous with absorbance; however, the use of optical density in place of absorbance is discouraged by the IUPAC. 1. What is the Beer-Lambert Law? The Beer-Lambert law is a linear relationship between the absorbance and the concentration, molar absorption.
Difference Between Optical Density and Absorbance Compare the Difference Between Similar Terms
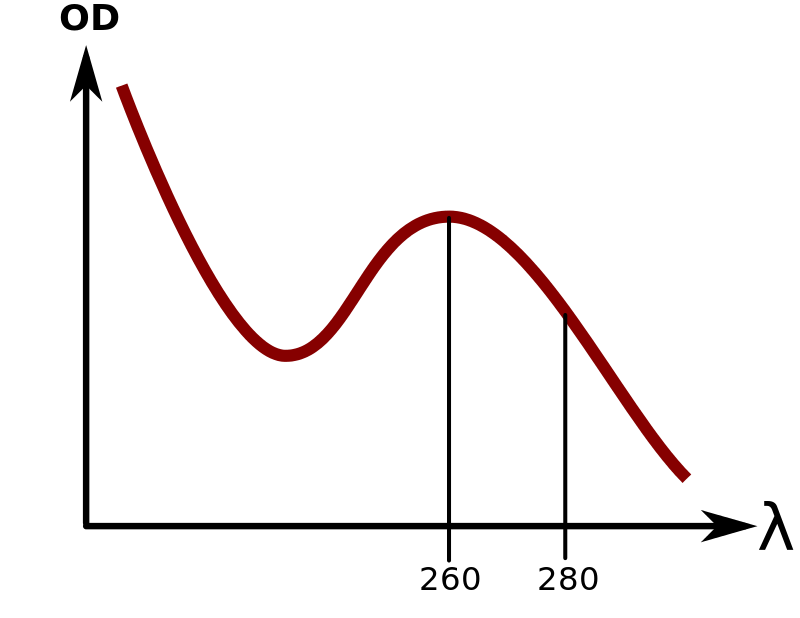
October 22, 2021 For absorbance measurements, the optical density (O.D.) is a logarithmic measurement of the percent transmission (%T) and it can be represented by the equation, A = log10 100 / %T. Dr EJ Dell (8) Here is a graphical scale that represents this: Fig. 1: Graphic representation of the relation between absorbance and transmittance
Decoding Your Absorbance Readings Vernier
The optical density is a property of a transparent material that measures the speed of the light through the material. The extent to which any optically dense medium bends transmitted light rays towards or away from the normal is called the optical density.

Measured optical density (OD should be considered as absorbance) for... Download Scientific
Optical density is a measure of how effectively a medium, such as a material or a solution, absorbs or transmits light. It is a property that describes the degree to which light is attenuated as it passes through the medium. The term "optical density" is also known as "absorbance," which is used interchangeably in many scientific.

Transient absorption spectroscopy (TAS) optical density ΔOD vs.... Download Scientific Diagram
Significant colour-density in some samples can also result in increased absorbance or scattering of certain wavelengths 17, meaning that wavelength-selection and channel-splitting prior to.

Absorbance measurements (in absorbance units, A.U.) vs. optical path... Download Scientific
Optical density (OD) acts as a useful tool to describe the transmission of light through a highly blocking optical filter at a time when the transmission is extremely small. A higher optical density indicates how much slower the wave travels through that material.
What Is Optical Density?
Absorbance In contrast to optical density, absorbance measures the ability of a refractive medium or optical component to absorb light. This sounds incredibly similar but is not quite the same.
Optical absorbance spectrum of the SWCNT layer. (a) The average... Download Scientific Diagram
Optical density is a property of the material that ideally describes its ability to absorb the power (radiant power) of given light transmitting through the material.