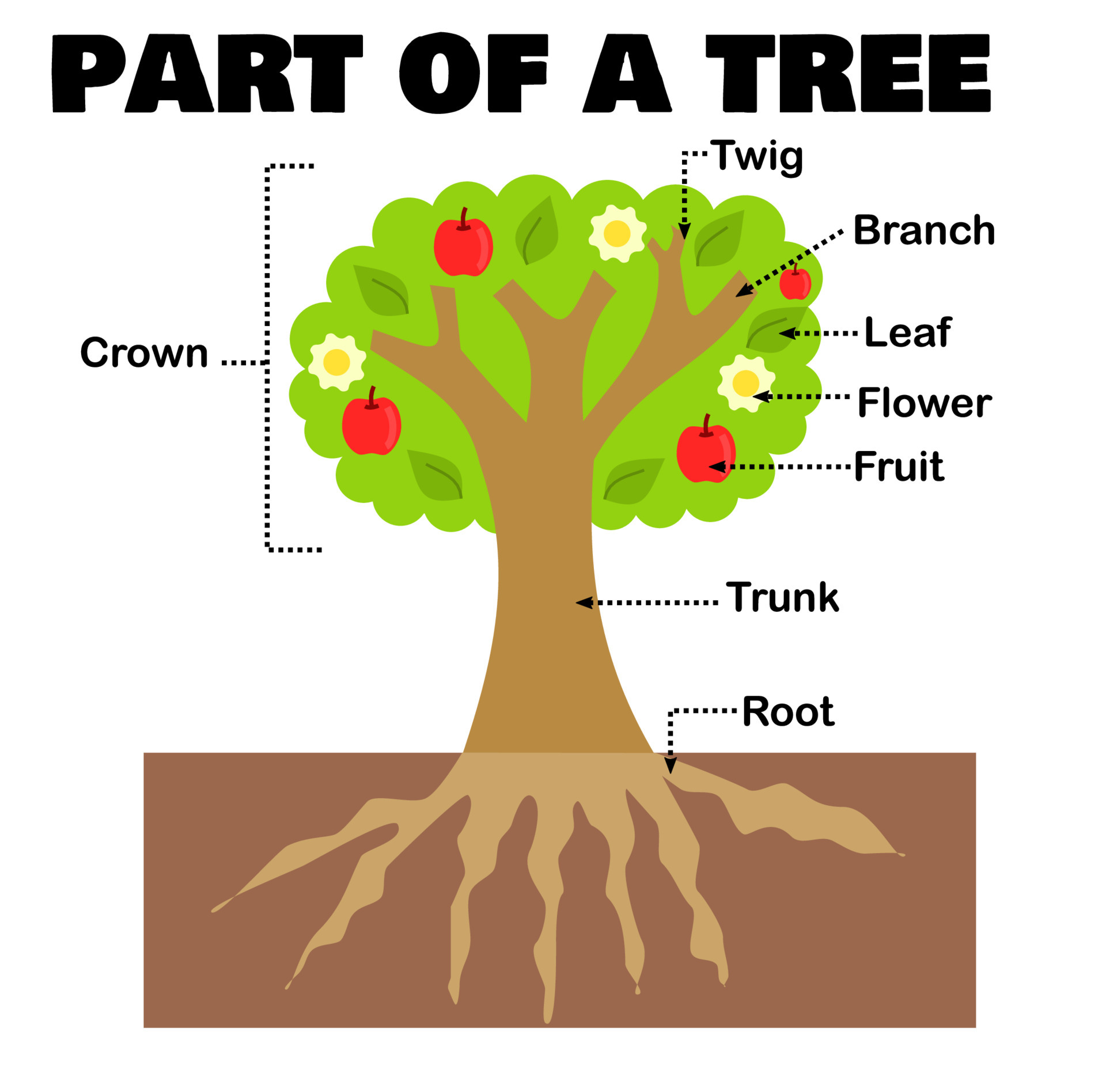
Part of a tree or plant for science and education.Worksheet for kids.Morphology or botany.Tree
A tree contains the following parts: Root: is the part of the tree that remains underground. Its main function is to hold the tree and absorb water and minerals from the soil. Most trees have one main root from which secondary roots emerge. Some trees have special roots with a different purpose such as adventitious roots, which may arise from.
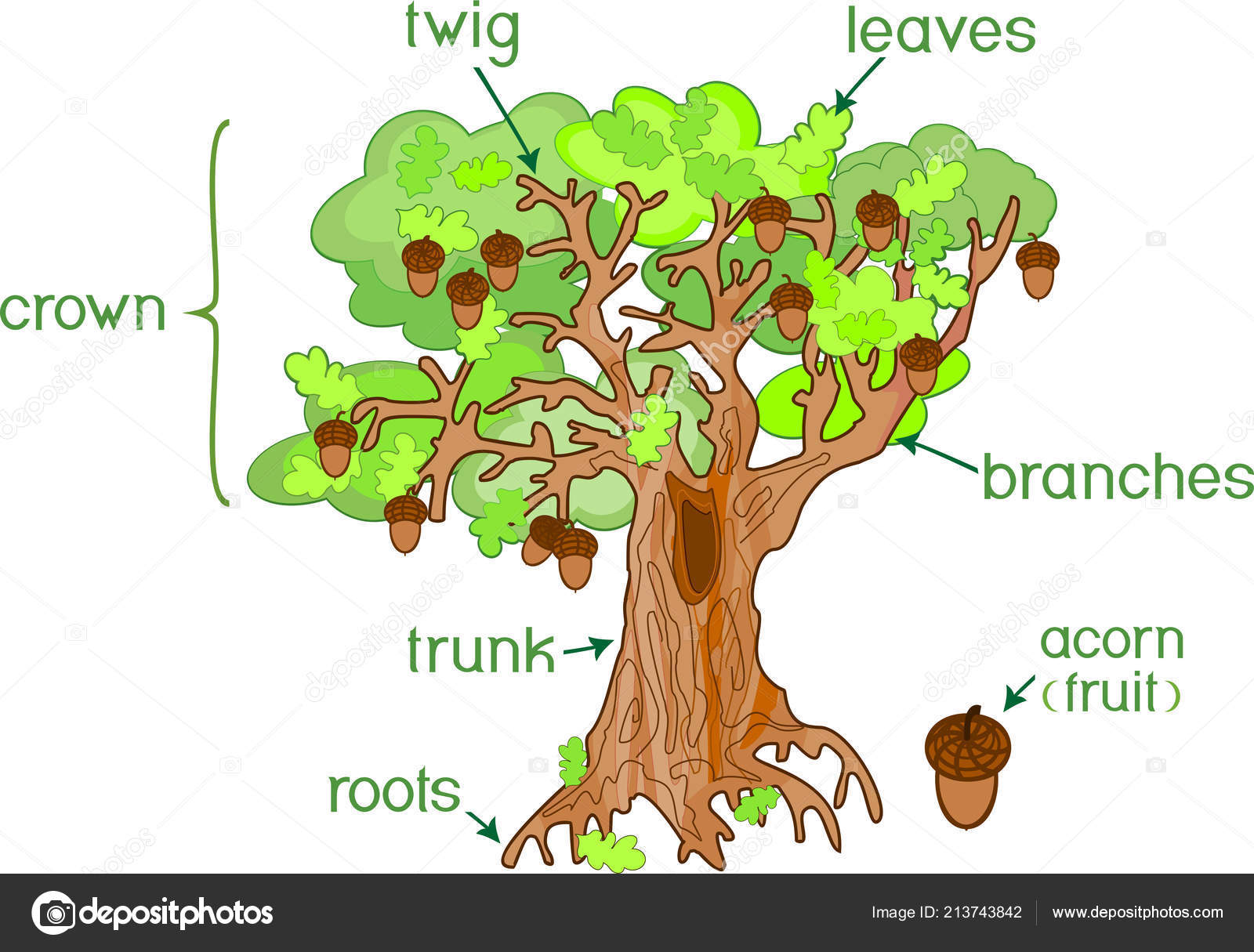
Parts Plant Morphology Oak Tree Acorns Green Leaves Root System Stock Vector Image by
The three key parts of a tree and their functions are: The roots anchor the trunk and crown of the tree and make them stable. They also take up water and nutrients from the soil and serve as a store for carbohydrates. The trunk, branches and stems of the tree give the tree height so the leaves can capture as much light energy as possible.
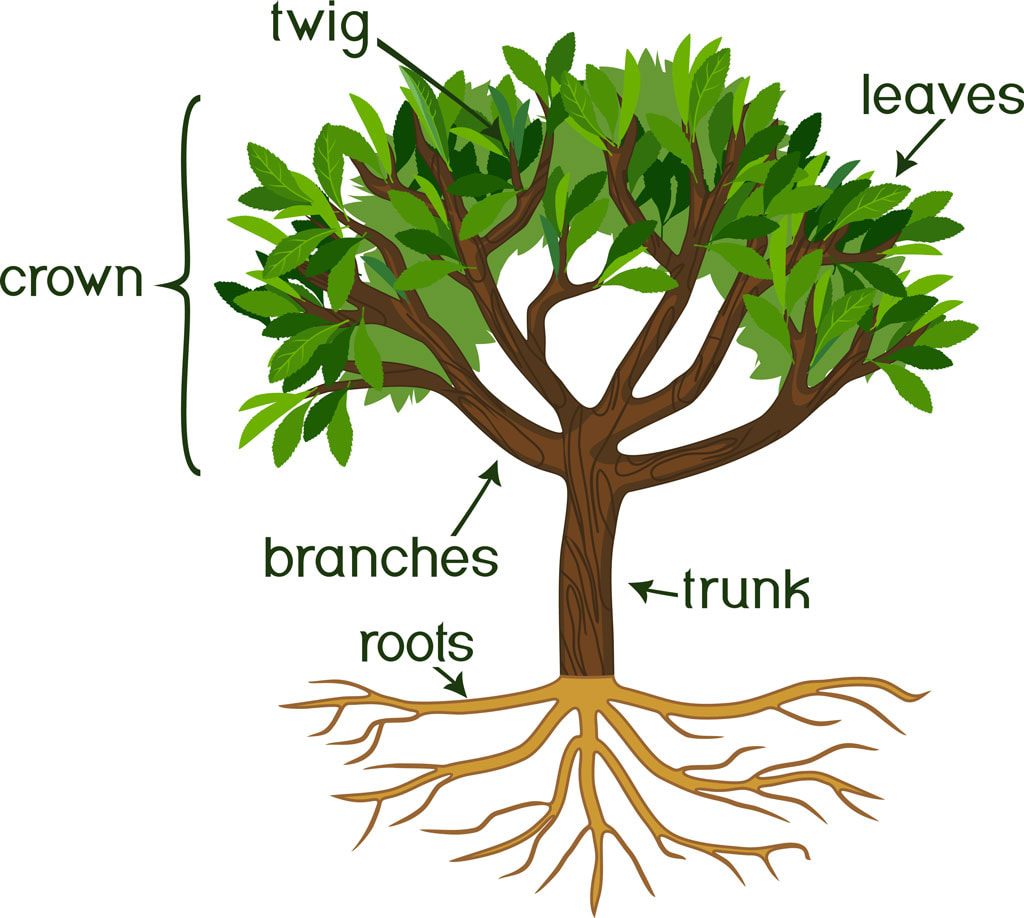
Basic Tree Anatomy The parts of a tree, and their function Snohomish Tree Co.
Crown. Above the trunk is the crown. The crown is all the branches and leaves on the tree. The crown is the powerhouse of the tree. The leaves take in sunlight which reacts with the green chlorophyll to transform light into sugars. The process is called photosynthesis and the byproduct is oxygen released into the air.

Parts of a Tree Ellii (formerly ESL Library)
The woody stems and trunk are just the beginning: Trunk: The most recognizable part of the tree and its support structure. Roots: Provide stability, water, and a food retrieval service, healthy roots are crucial for a tree's survival. 1. Canopy: This is the collective name for the twigs, branches, and leaves on a tree.
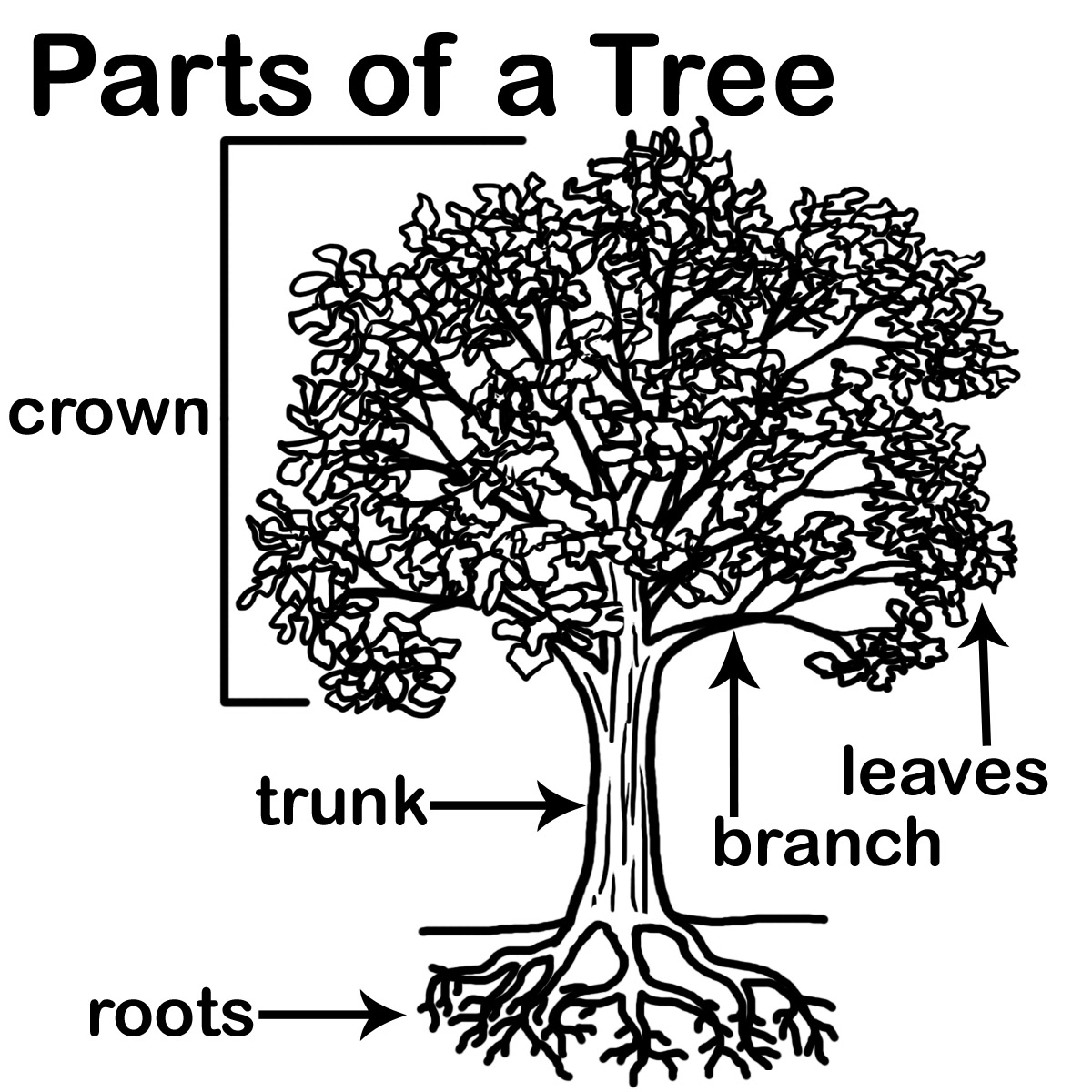
9 Label The Parts Of A Tree Worksheets Kindergarten /
In short, trees help to maintain the balance of nature. Parts of a Tree Diagram. A mature tree has three basic parts: 1) roots, 2) crown, and 3) trunk or bole. Although the structure of these parts may vary based on the altitude and geographical position of the tree, each of them performs distinct functions.

parts of tree English For Life
Use the tree parts to teach functions/ purposes of the different tree parts (for example, the roots take in water and hold tree in place, the bark protects the tree, etc.). Bring students outside to examine these parts in a live tree and challenge them to determine why each part is important to the tree.
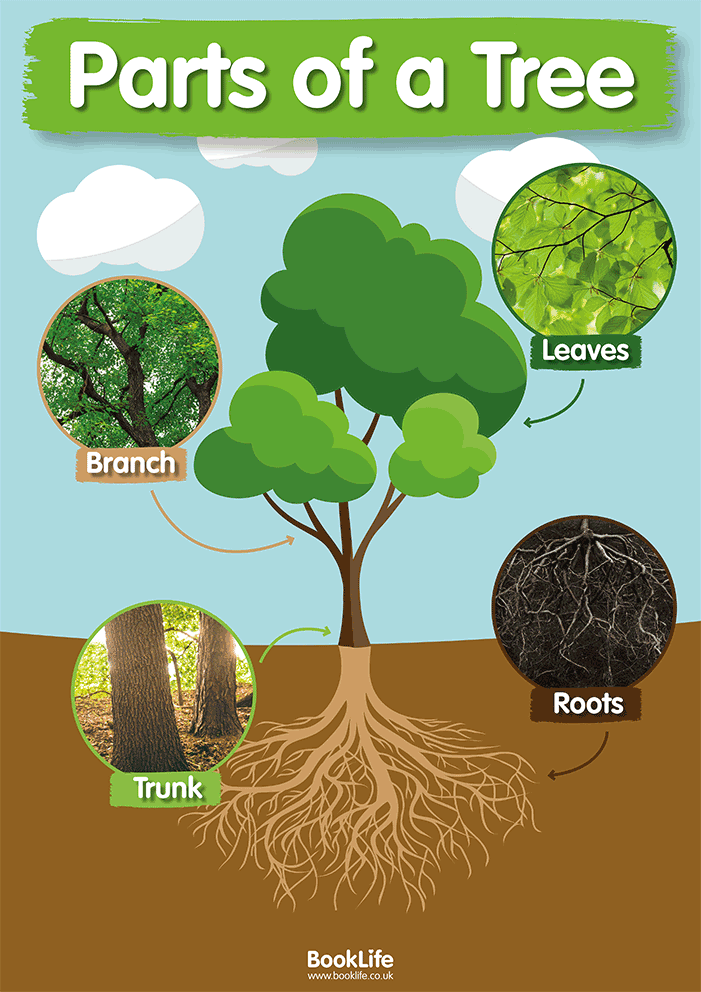
Parts of a Tree Poster BookLife
All trees have three main parts; the crown, trunk, and roots. Each of these parts plays its role in keeping the tree healthy and supporting the ecosystem. The crown is the most visible part of the tree holding the branches while the trunk sits below it. The roots are the bottom anchoring the tree to the soil.

Parts of the Tree Things from Trees Learn parts of the Tree for kindergarten Kids Entry
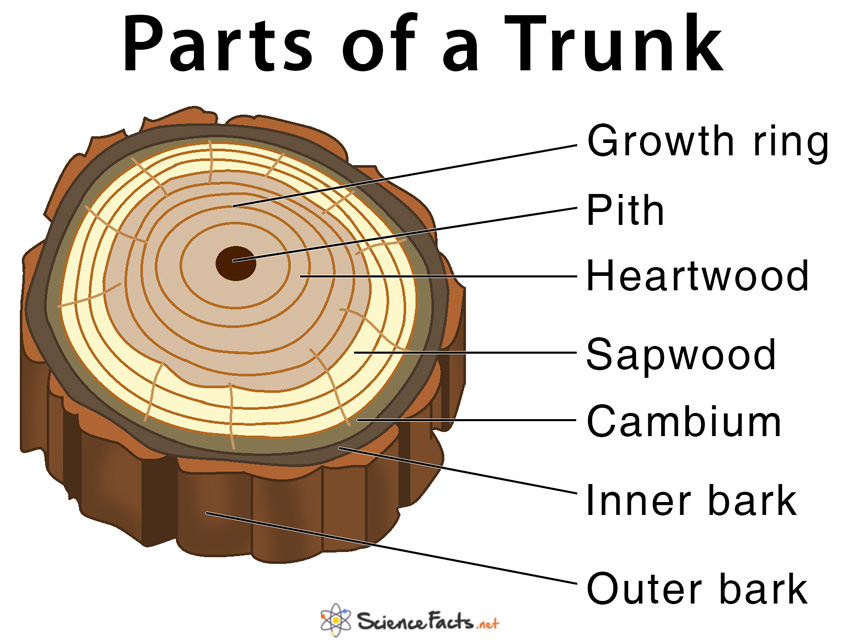
Sapwood is the tree's pipeline for water moving up to the leaves. Sapwood is new wood. As newer rings of sapwood are laid down, inner cells lose their vitality and turn to heartwood. Heartwood is the central, supporting pillar of the tree. Although dead, it will not decay or lose strength while the outer layers are intact.

Parts of a tree CLIL Science Pinterest
Heartwood: The heartwood of a tree is the dead sapwood and xylem cells that are found closer to the centre of the trunk itself. These are often filled with stored sugars, dyes, and oils. The function is simply to store helpful biochemicals as a long-term solution. Pith: The pith of a tree is the thin dark spot that is present at the very centre.

Parts of a Tree and Their Functions Science Facts
Trees are made up from several parts, each with its own purpose. From the supporting trunk to the leaves that aid in photosynthesis, every part of a tree is important. Crown. It sounds rather regal and the crown of a tree is pretty majestic; this is the mass of branches and leaves that make up the bulk of the structure.
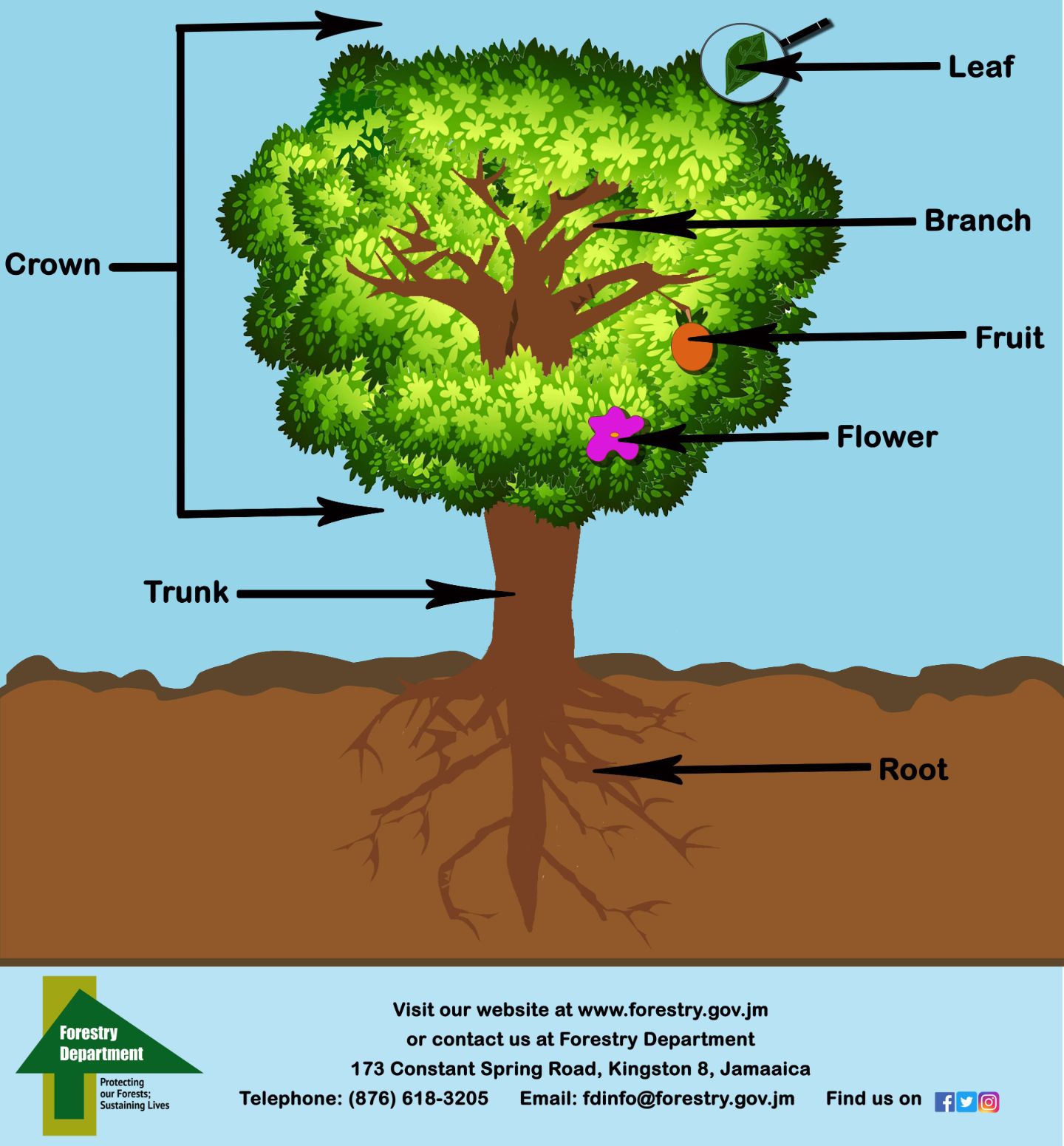
ForestryDepartment Early Childhood
Leaves. First, they are the food factories of the tree, using the sun's energy to convert the carbon dioxide in the air into sugar and oxygen. The green material in leaves is called chlorophyll and is essential in photosynthesis. The sugar provides food for the tree, allowing it to grow. Leaves release water and oxygen into the atmosphere.

CIUDAD DE CÓRDOBA 3º SCIENCE BLOG PARTS OF A TREE
Here are the different tree parts and the functions each one of them serves: 1. Leaves. Leaves belong to the crown of the tree, which is the top part of the tree that grows out of the trunk and includes the branches and stems. While each tree has its unique biological makeup, the average tree consists of 5% leaves. The remaining 95% comprises.

FuN wITh EngLisH The parts of a tree
1. Crown. Crown part of the trees | image by Dietmar Rabich via Wikimedia Commons | CC BY-SA 4.0. The top of the tree which contains the most of its leaves and canopy. Most of the photosynthesis of the tree happens here in the crown. The crown of a deciduous tree is usually shaped like an oval or a partial circle.
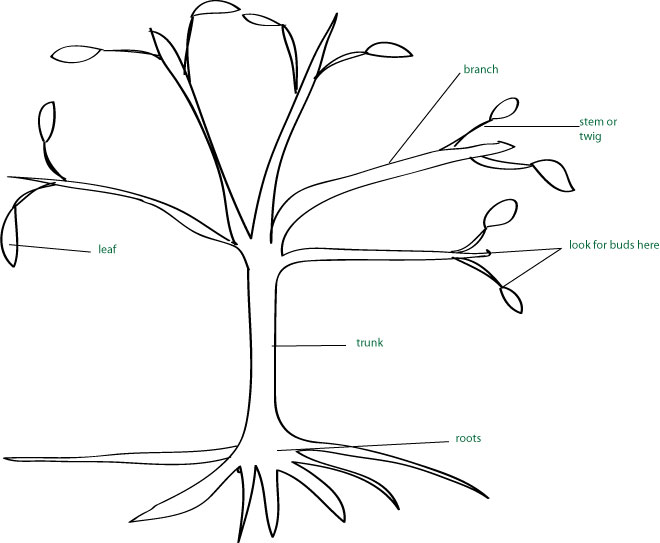
Tree Science for Children Growing With Science Blog
The trunk of a tree serves two purposes. The initial function of a tree trunk is to provide size and form. It is the pillar of strength that gives structural support for the tree's branches and leaves to grow upward and outward. The second function of a tree trunk is to serve as the transport system's centre.
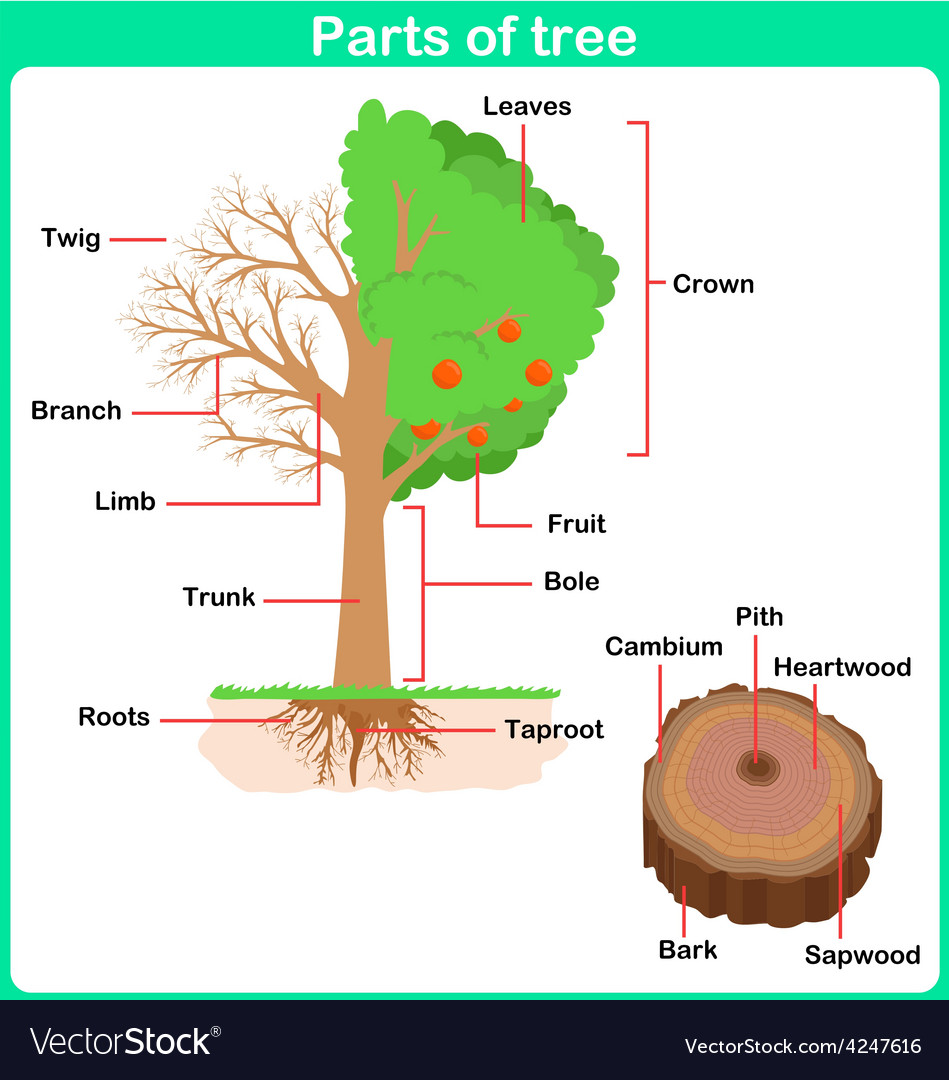
Leaning parts of tree for kids worksheet Vector Image
Parts Of A Tree. The roots, the trunk and branches, the blooms and fruit, and the leaves make up the primary components of a tree. Leaves. To put it simply, leaves are made up of sheets (or sticks) of spongy living cells that are connected to the "plumbing system" of the tree by means of tubular conducting cells. They are protected from.
Parts of a Tree and Their Functions Science Facts
A tree is a vascular plant of a woody substance that exhibits both primary and secondary growth. The basic sections of a tree are the root system, the trunk, the branches and the foliage. The function and description of each part are detailed below. Vascular plants are plants with tissues that specialize in moving resources through the organism.