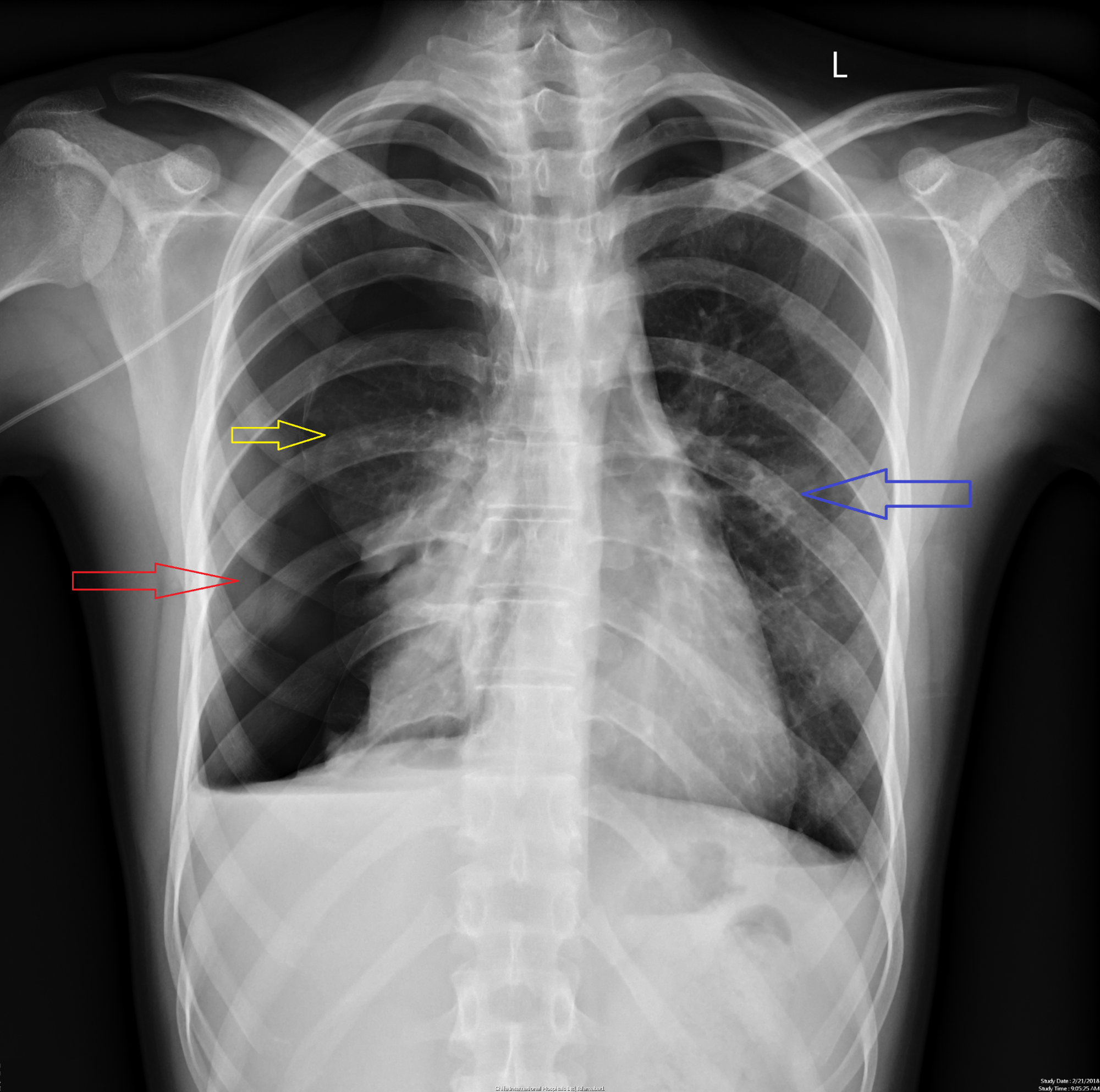
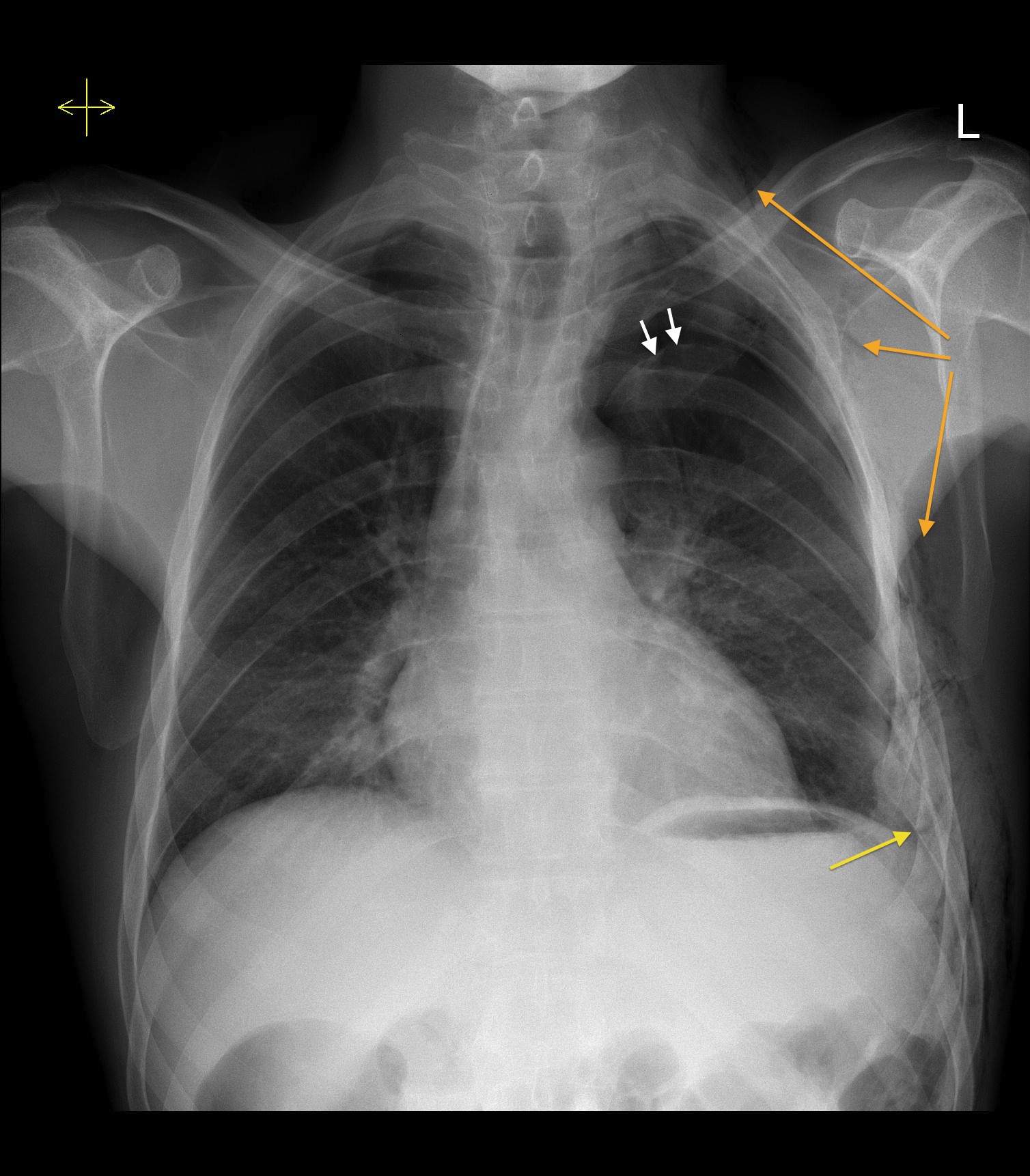
Cureus Simultaneous Bilateral Spontaneous Pneumothorax A Rare Complication of
In this video, you'll learn to identify when radiological pleura is abnormal and the key signs to look out for when trying to diagnose a pneumothorax. Want to master chest x-ray interpretation? Take our Chest X-ray Essentials course and learn how to interpret chest x-rays like a pro. Your instructor, Dr Julian Dobrowski-an award-winning.
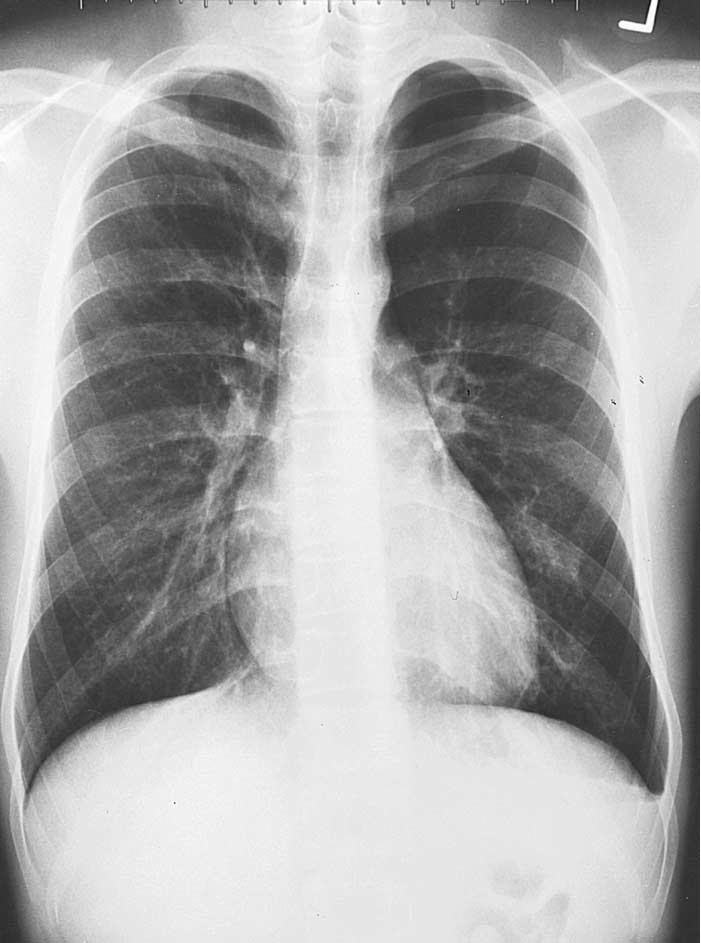
Study Medical Photos Primary Spontaneous Pneumothorax Chest X ray
In contrast, tension pneumothorax is a medical emergency and may be treated before imaging - especially if there is severe hypoxia, very low blood pressure, or an impaired level of consciousness. In tension pneumothorax, X-rays are sometimes required if there is doubt about the anatomical location of the pneumothorax. Chest X-ray
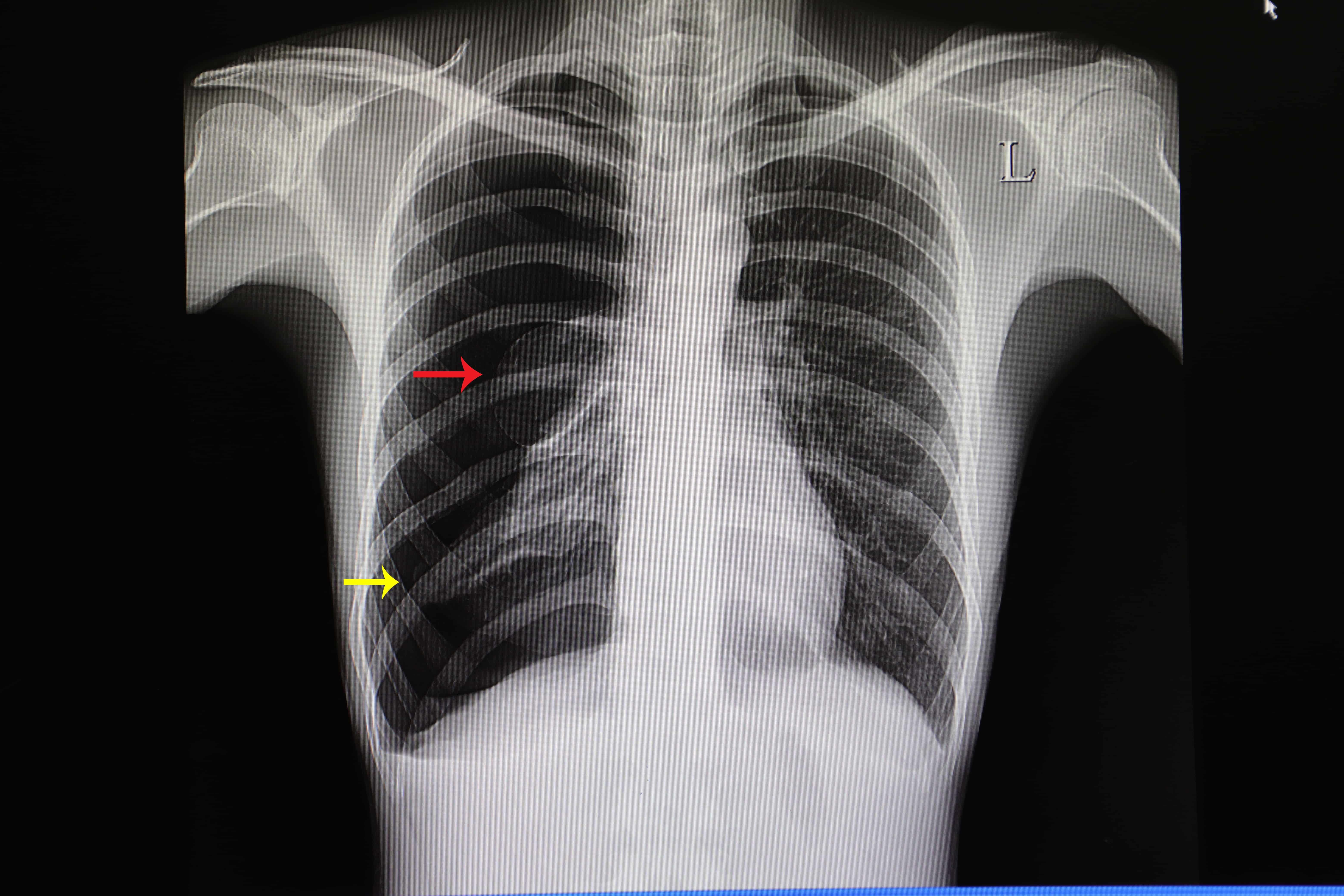
Pneumothorax Hello Doktor
Key Points. Pneumothorax is air in the pleural space causing partial or complete lung collapse. Pneumothorax can occur spontaneously or result from trauma or medical procedures. Diagnosis is based on clinical criteria and chest x-ray. Most pneumothoraces require transcatheter aspiration or tube thoracostomy.

Pneumothorax. Causes, symptoms, treatment Pneumothorax
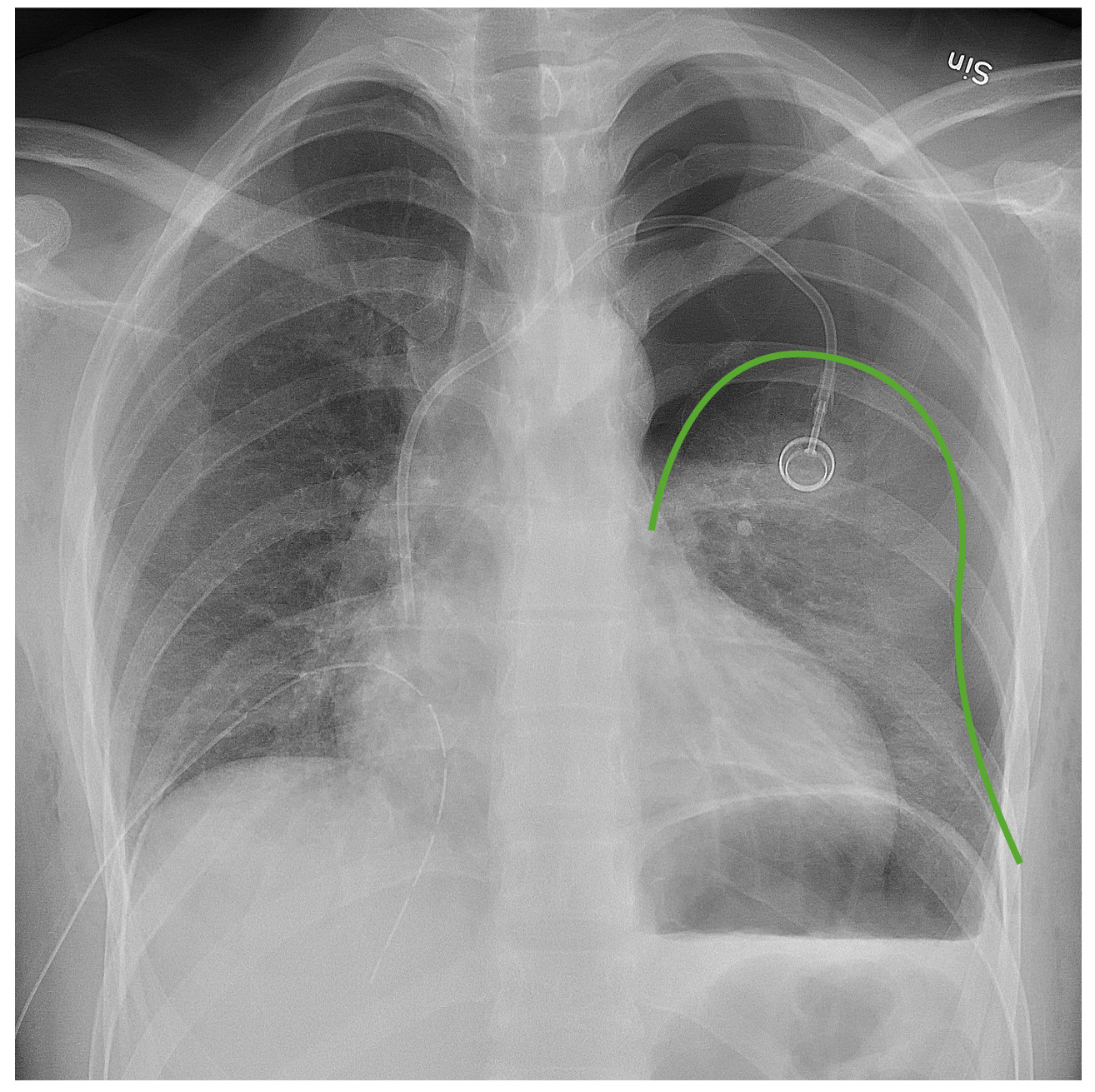
Chest X-ray to tell whether there is air outside the lung; Arterial blood gases; Treatment. Small pneumothoraces may go away on their own. For larger pneumothoraces, the air must be removed from around the lung. A chest tube placed between the ribs into the space around the lungs helps drain the air and allows the lung to re-expand.

Radiographical Findings in Spontaneous Pneumothorax GrepMed
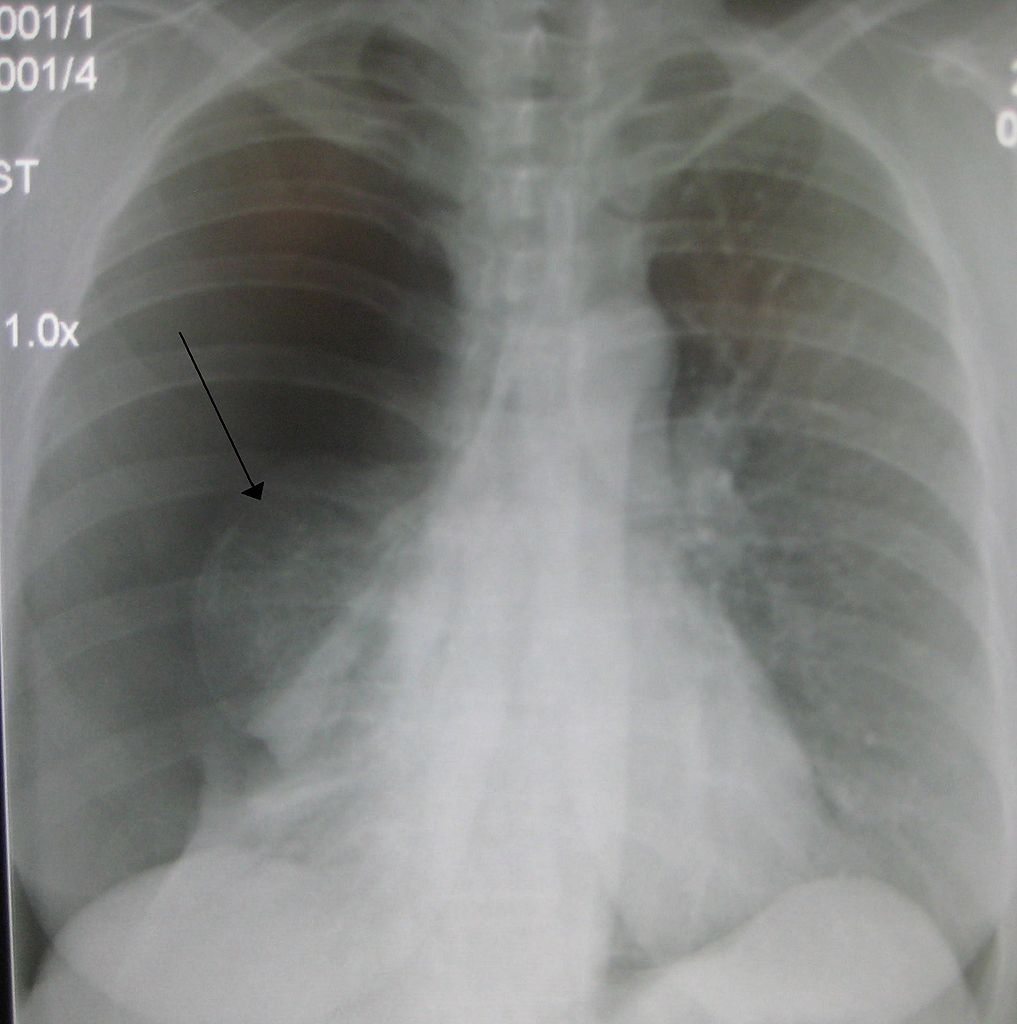
Chest X-ray (Figures 2 and 3): visible rim between the lung margin and chest wall, with an absence of lung markings. The size of the pneumothorax is measured at the level of the hilum: >2cm is classified as a "large" pneumothorax. 17; CT chest (Figure 4): may be used to identify small pneumothoraces missed by chest X-ray.
Pneumothorax Concise Medical Knowledge
Pneumothorax. Pneumothorax is the presence of air between the parietal and visceral pleura in the pleural cavity. It is caused most frequently by trauma or blunt or penetrating injury, which may be accidental or iatrogenic. If it is not caused by trauma, it is referred to as spontaneous; this may be primary (not associated with an underlying.
Tension pneumothorax due to rib fracture Radiology at St. Vincent's University Hospital
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data. Getting a film with a pneumothorax in the exam is one of the many exam set-pieces that can be prepared for. It is unlikely that they will give you a simple pneumothorax - so, it is worthwhile considering the likely causes and whether it is under tension. Miss it at your peril (both in real life and.

Image
A large pneumothorax is radiographically defined as one with > 2 cm from pleural surface to lung edge; this is an objective indication for drainage. chest drain bottle is not placed on the trolley above the level of the patient's thorax during the trip to the x ray department. This may result in accumulation of air and fluid in the pleural.
'pneumothorax, Xray' Photograph by Du Cane Medical Imaging Ltd
Unlike in pneumothorax, the inner margins of bullae or cysts usually are concave rather than convex and do not conform exactly to the contours of the costophrenic sulcus. A pneumothorax with a pleural adhesion also may simulate bullae or lung cysts.. American Roentgen Ray Society, Canadian Association of Radiologists, Canadian Medical.

Cureus Simultaneous Bilateral Spontaneous Pneumothorax A Rare Complication of
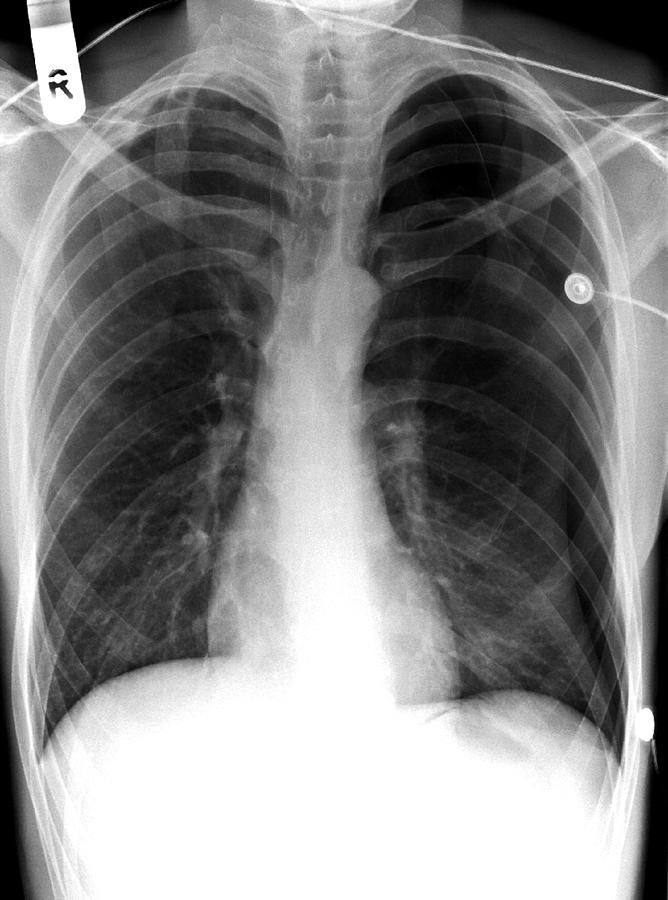
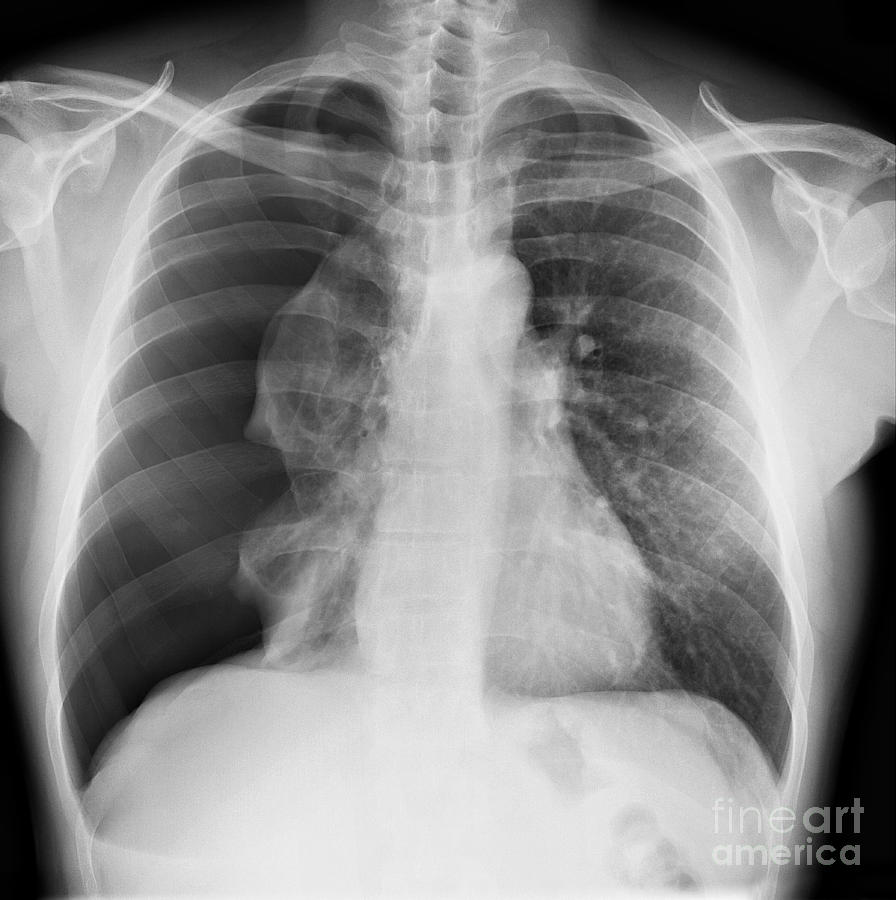
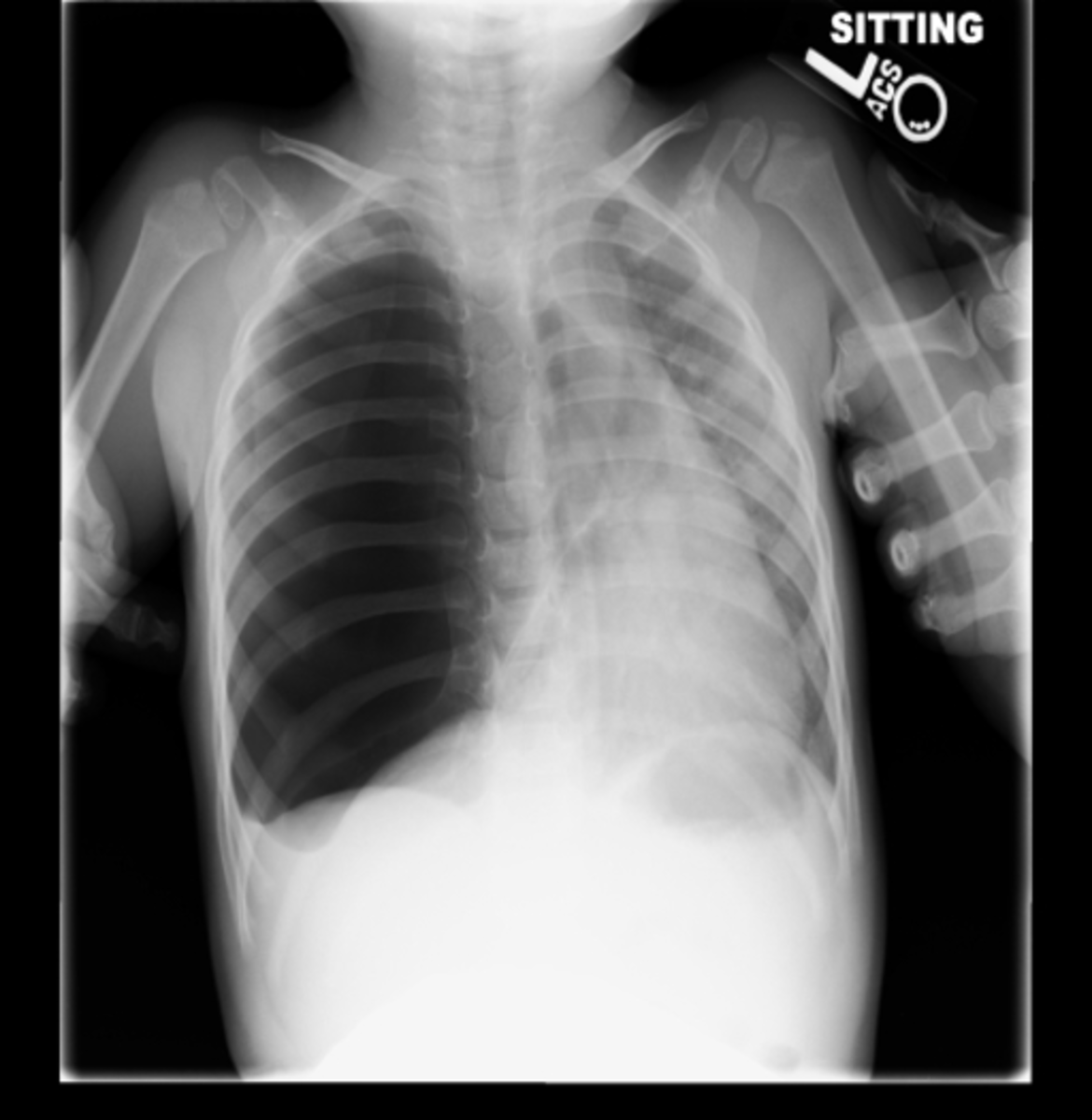
A pneumothorax is, when looked for, usually easily appreciated on erect chest radiographs. Typically they demonstrate: visible visceral pleural edge is seen as a very thin, sharp white line. no lung markings are seen peripheral to this line. peripheral space is radiolucent compared to the adjacent lung.

Pneumothorax Causes, Signs, Symptoms, Treatment
Traumatic pneumothorax must be a suspected diagnosis in any blunt or penetrating chest trauma. Adequate history, physical exam and chest X-rays are the mainstays of the diagnosis. However, small pneumothoraces are often missed on physical exam and chest X-ray and may be present on CT chest during a diagnostic workup for other injuries.

Pneumothorax, Xray Stock Image C017/7966 Science Photo Library
An erect chest radiograph has a sensitivity as high as 92% for detection of a pneumothorax, whilst a supine projection may only detect 50% 6. Instead, the pneumothorax may be demonstrated by looking for the following signs: relative lucency of the involved hemithorax. deep, sometimes tongue-like, costophrenic sulcus: deep sulcus sign 2.
Chest Xray Interpretation A Structured Approach Radiology OSCE
A tension pneumothorax occurs when there is progressive accumulation of gas within the pleural cavity. This is usually caused by a ball-valve effect with progressive increases in intrapleural air during each expiration. The thoracic cavity has a relatively fixed volume and therefore, as the volume of gas increases, the pressure rises.
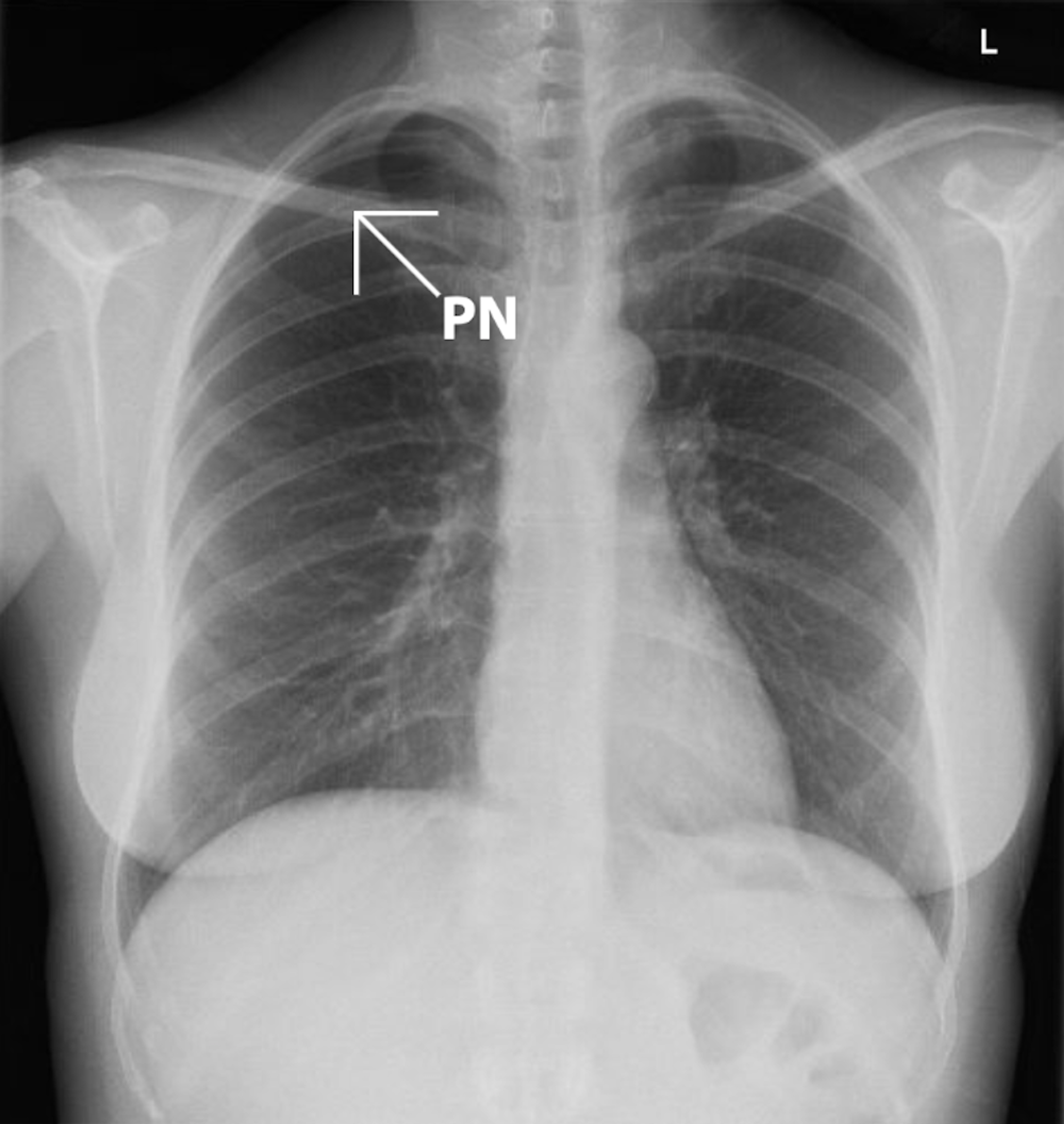
Cureus Pneumothorax Following Acupuncture
erect chest x-ray. will show most pneumothoraces; CT chest. will show tiny pneumothoraces not shown on chest x-ray. these are often incidental and asymptomatic; not used for assessment of pneumothoraces unless complex; Radiographic features Plain radiograph. A pneumothorax is seen as a region of lucency (dark) around the edge of the lung.
Pneumothorax, Xray Photograph by Science Photo Library
CLINICAL PRESENTATION. Pneumothorax should be suspected in patients who present with acute dyspnea and chest pain (classically pleuritic), particularly in those with an underlying risk factor ( table 1 ). The major competing diagnoses include acute pulmonary embolism, pleuritis, pneumonia, myocardial ischemia or infarction, pericarditis, and.
X Ray Diagnostics Of Pneumothorax Radiographic Representations Of The Lung Tissue In This
Figure 9.19A AP Chest x-ray, Pneumothorax, Small. Figure 9.19B Lateral Chest x-ray, Pneumothorax, Small. Image Assessment. Findings: The left lung was mildly hyperinflated. There was a visible pleural line in the apex of the left hemithorax. This line was convex outward. There were no visible lung markings beyond this pleural line. Diagnosis: