FileWind turbine diagram.svg Wikimedia Commons
Explore a Wind Turbine To see how a wind turbine works, click on the image for a demonstration. Types of Wind Turbines Sizes of Wind Turbines Learn More Wind is a form of solar energy caused by a combination of three concurrent events: The sun unevenly heating the atmosphere Irregularities of the earth's surface The rotation of the earth.
Wind turbine work principle with mechanical inner structure outline diagram. Labeled educational
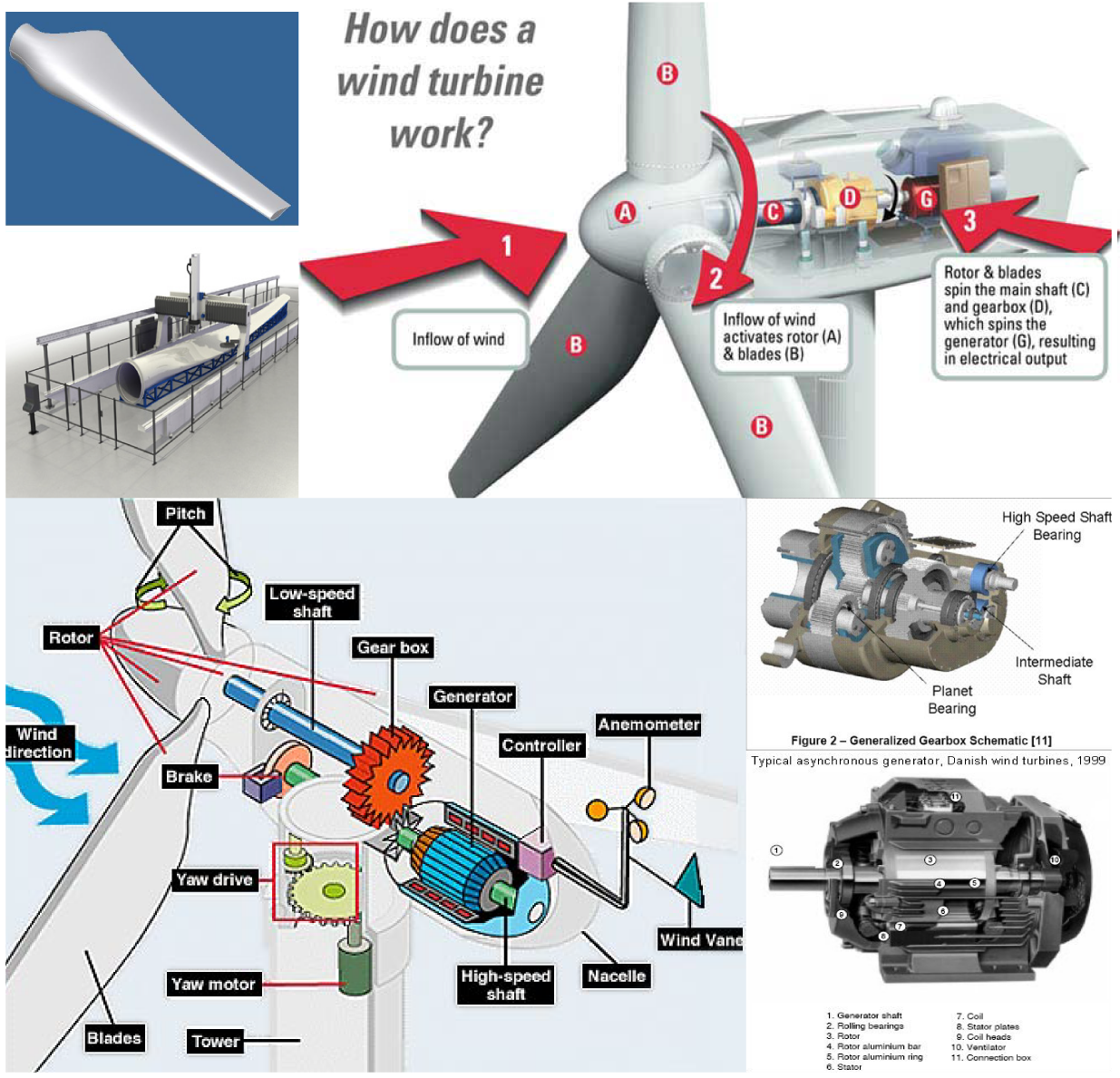
Step-by-step look at each piece of a wind turbine from diagram above: (1) Notice from the figure that the wind direction is blowing to the right and the nose of the wind turbine faces the wind. (2) The nose of the wind turbine is constructed with an aerodynamic design and faces the wind.

Wind turbine components [1]. Download Scientific Diagram
Small Wind turbines generally are defined as having a capacity output of less than 100 kilowatts (kW). These units comprise 30 to 80 parts; provide 120/240, single- or three-phase AC or DC output; and are used on a home, farm or small business.

Wind turbine technology Britannica
Explore a Wind Turbine The Power of Wind Wind turbines harness the wind—a clean, free, and widely available renewable energy source—to generate electric power. The animation below is interactive.
Schematic diagram of wind turbine system. Download Scientific Diagram
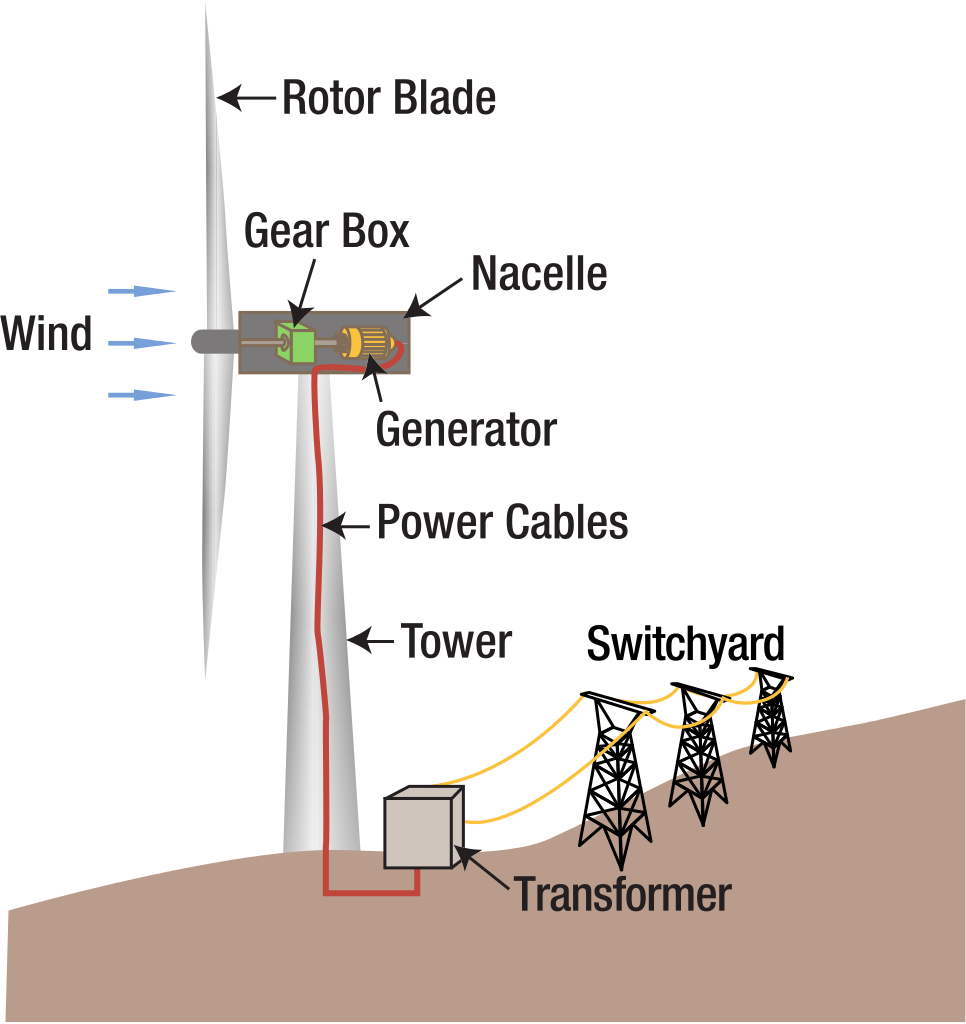
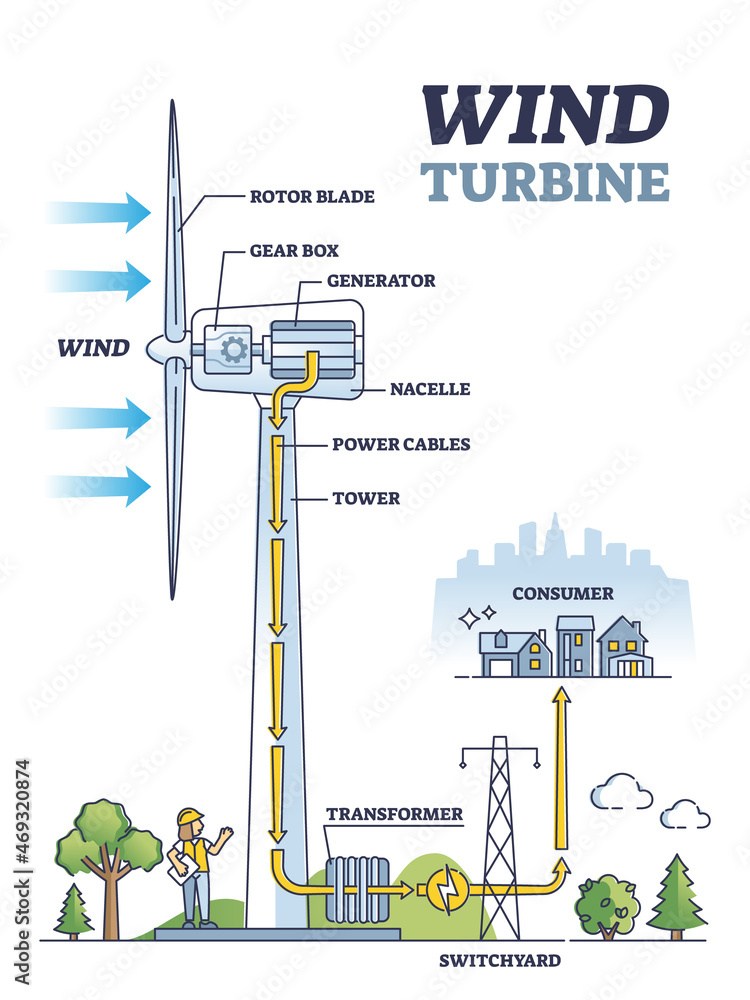
A modern wind turbine comprises many different parts, which can be broken down into three major components (see diagram below): Parts of a Wind Turbine 1. Support tower / mast 2. Nacelle 3. Rotor Blades 1. Support Tower / Mast

Components of a typical wind turbine as illustrated on NORDEX N80. Download Scientific Diagram
How a Wind Turbine Works - Text Version The Power of Wind Wind turbines harness the wind—a clean, free, and widely available renewable energy source—to generate electric power. This page offers a text version of the interactive animation: How a Wind Turbine Works. How a Wind Turbine Works
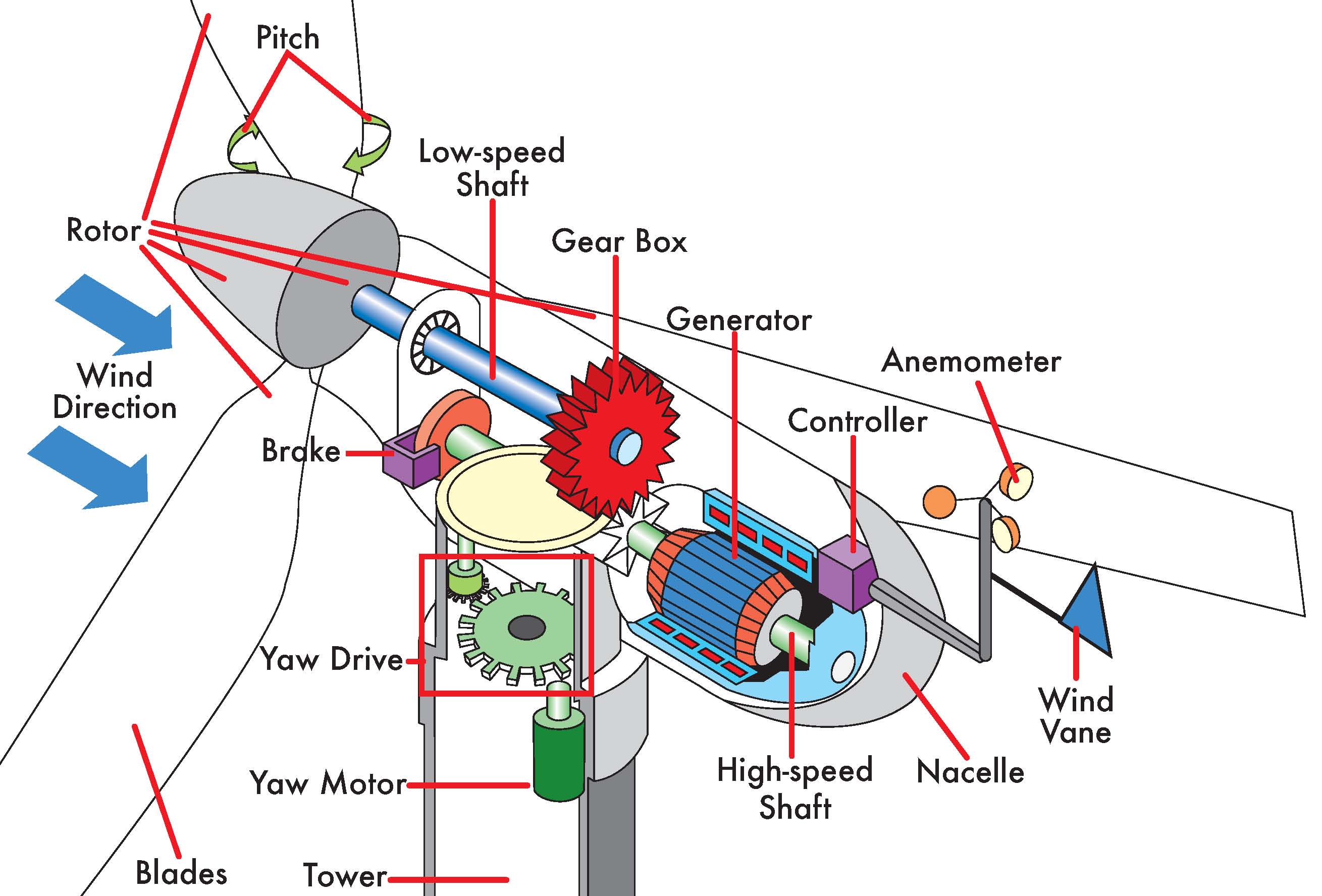
Diagram Of Wind Turbine How It Works
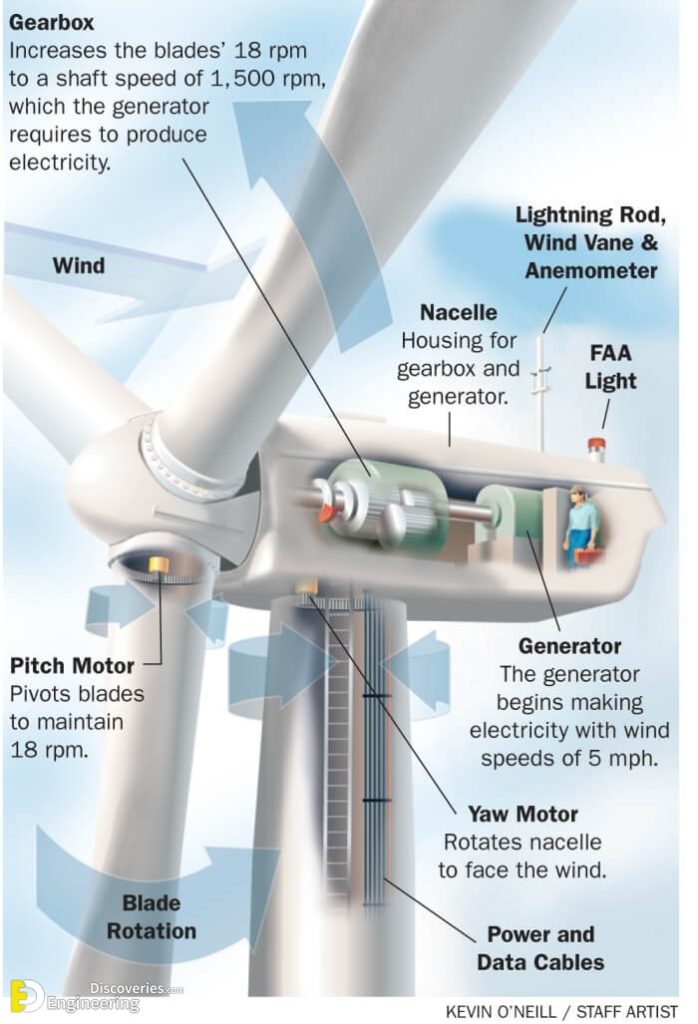
When the wind strikes the rotor blades, blades start rotating. The turbine rotor is connected to a high-speed gearbox. Gearbox transforms the rotor rotation from low speed to high speed. The high-speed shaft from the gearbox is coupled with the rotor of the generator and hence the electrical generator runs at a higher speed.

Inside of a wind turbine. Download Scientific Diagram
Figure 1. Wind turbine. Wind turbines operate by transforming the kinetic energy in wind into mechanical power which is used to generate electricity by spinning a generator. These turbines can be on land, or can be offshore wind turbines. [2] Turbine Components Figure 2. Illustration of Wind Turbine Components (click to enlarge). [3]

How Do Wind Turbines Work? EcoBatt Solutions
Jan. 3, 2024, 1:13 PM ET (AP) Two large offshore wind sites are sending power to the US grid for the first time wind turbine, apparatus used to convert the kinetic energy of wind into electricity.

What are Turbines ? Types of turbines & their applications MechStuff
A major turbine part among these components is the generator and the turbine shaft that transfers the harvested power from wind to the generator through a gearbox. The gearbox is a vital component of wind turbines; it resides in the nacelle. A gearbox increases the main shaft speed from around 12-25 rpm* (for most of today's turbines) to a.

Wind Energy Diagram Sustainable Energy
How wind turbines work Wind turbines use blades to collect the wind's kinetic energy. Wind flows over the blades creating lift (similar to the effect on airplane wings), which causes the blades to turn. The blades are connected to a drive shaft that turns an electric generator, which produces (generates) electricity.
A Fundamental Introduction To How Wind Turbines Work How To Make Turbine & Go Green With It
Wind turbine components : 1- Foundation, 2- Connection to the electric grid, 3- Tower, 4-Access ladder, 5- Wind orientation control (Yaw control), 6- Nacelle, 7- Generator, 8- Anemometer, 9- Electric or Mechanical Brake, 10- Gearbox, 11- Rotor blade, 12- Blade pitch control, 13- Rotor hub
MEC&F Expert Engineers DIAGRAM OF TYPICAL WIND TURBINE
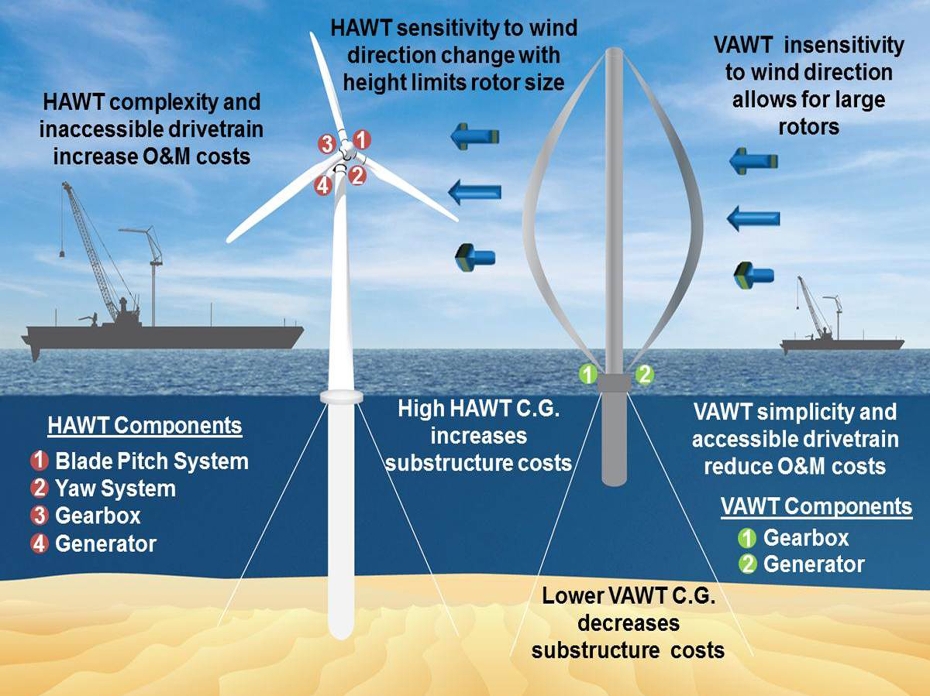
Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine or HAWT The most common type of wind turbine is the 'Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine' (HAWT). It is referred to as a horizontal axis as the rotating axis lies horizontally (see diagram, below).

major components wind turbine Skillwind
Equations for Wind Turbines: Wind Shear An important consideration for turbine siting and operation is wind shear when the blade is at the top position. Wind shear is calculated as: V — Wind speed at height H above ground level. Vref — Reference speed.
A Fundamental Introduction To How Wind Turbines Work How To Make Turbine & Go Green With It
The fraction of the year the turbine generator is operating at rated (peak) power. Capacity Factor = Average Output / Peak Output ≈ 30%. CF is based on both the characteristics of the turbine and the site characteristics (typically 0.3 or above for a good site) Power Curve of 1500 kW Turbine. wind speed (m/s)
What Is A Wind Turbine And How It Works? Engineering Discoveries
Thorntonbank Wind Farm, using 5 MW turbines REpower 5M in the North Sea off the coast of Belgium. A wind turbine is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy.As of 2020, hundreds of thousands of large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, were generating over 650 gigawatts of power, with 60 GW added each year. Wind turbines are an increasingly important.