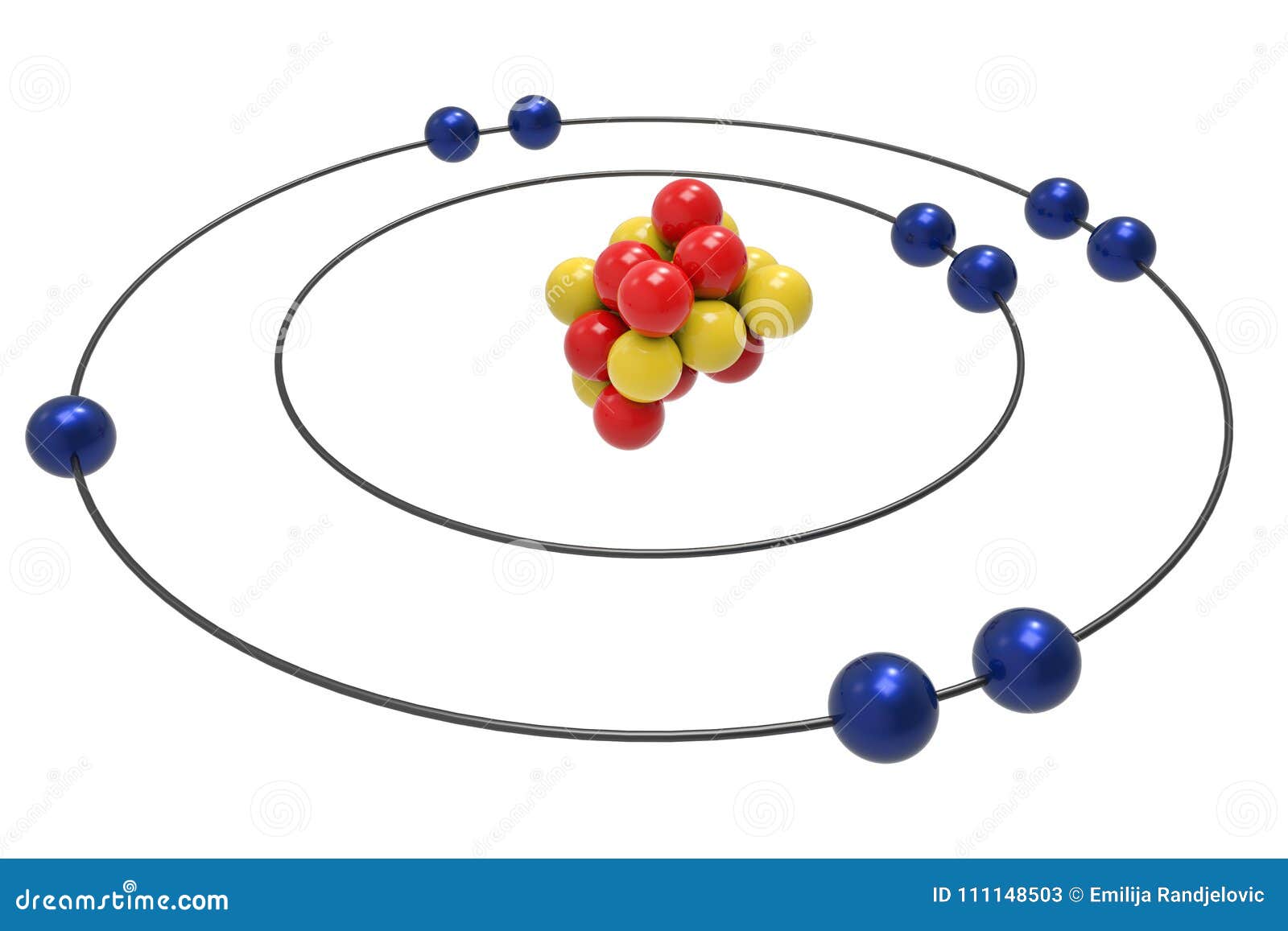
Bohr Model Of Fluorine Atom With Proton, Neutron And Electron Royalty
Bohr Diagram: The First Element In order to make a Bohr diagram, you need to know the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons the element has. In this section, we'll show a sample Bohr diagram for hydrogen. H —Hydrogen 1 proton 1 electron 0 neutrons

Grade 9 BohrRutherford Diagram Fluorine YouTube
Knowing this information allows us to set up our Bohr-Rutherford Diagram. Let's create one using Lithium. First determine the number of protons, neutrons and electrons. Lithium. Atomic Number = 3 #p = 3 (since atomic number is 3) Atomic Mass = 7 #n = 4 (since 7 - 3 = 4) #e = 3 (since same as #p) The Bohr-Rutherford Diagram for Lithium would.

6. Draw a BohrRutherford diagram for each of the following molecules
Bohr's model of the atom can be combined with Rutherford's model in diagrams that summarize the numbers and positions of all three subatomic particles. For example, consider the following diagram for Phosphorous: There are certain rules to follow when drawing these diagrams: A circle is drawn in the center to represent the nucleus of the atom.
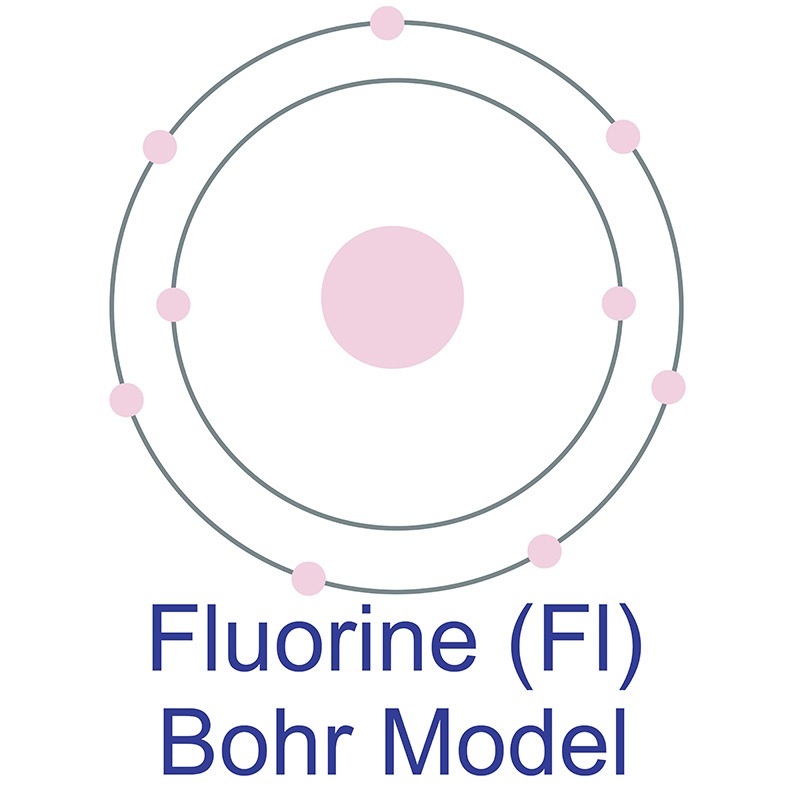
Fluorine Bohr Model
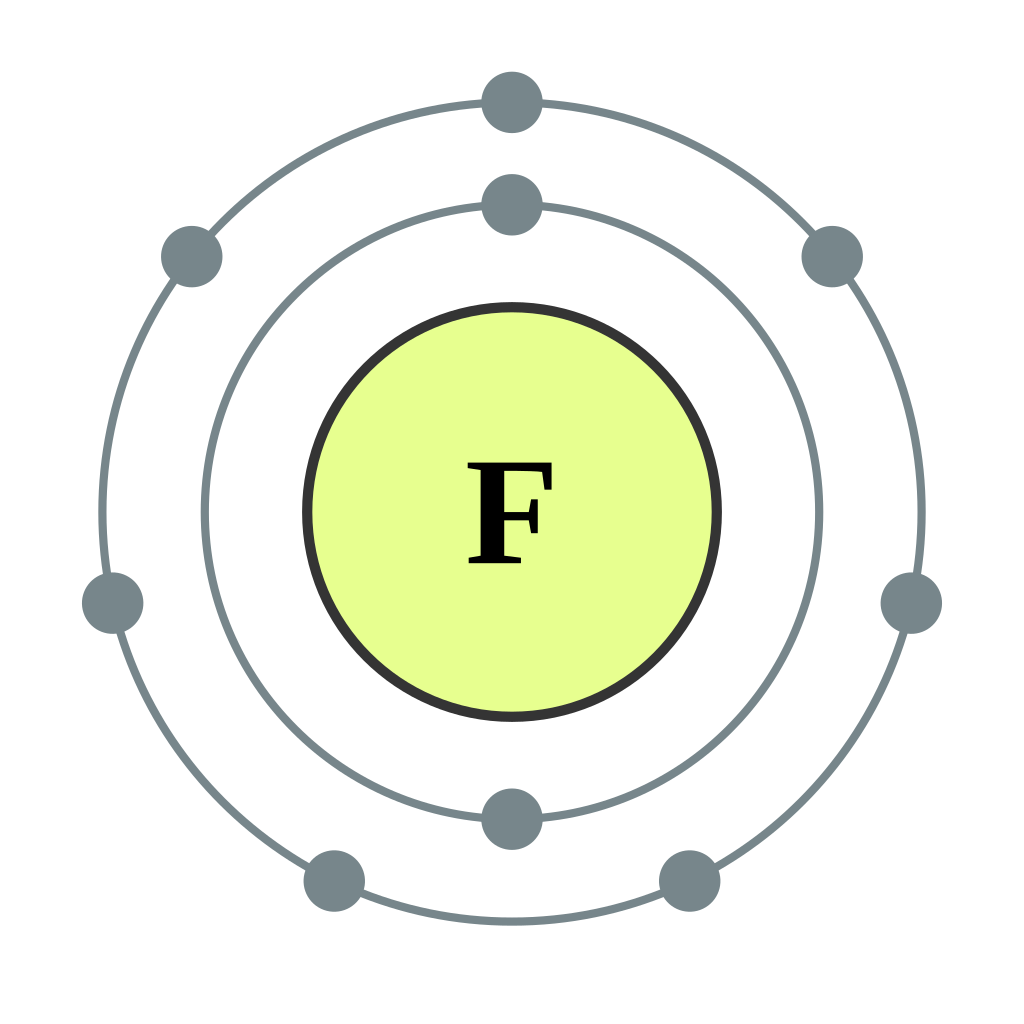
Bohr diagram is very interesting and easy to draw. Here, we will draw the Bohr diagram of the Fluorine atom with some simple steps. Steps to draw the Bohr Model of Fluorine atom 1. Find the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in the Fluorine atom

Fluorine atom diagram concept Stock Vector Image & Art Alamy
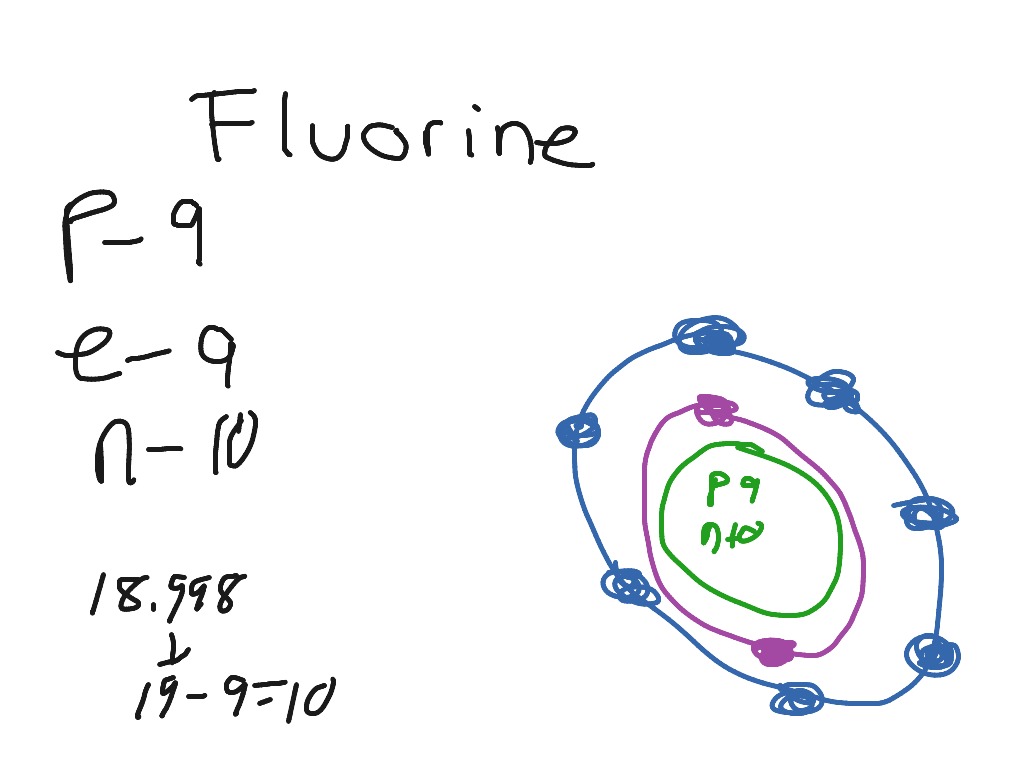
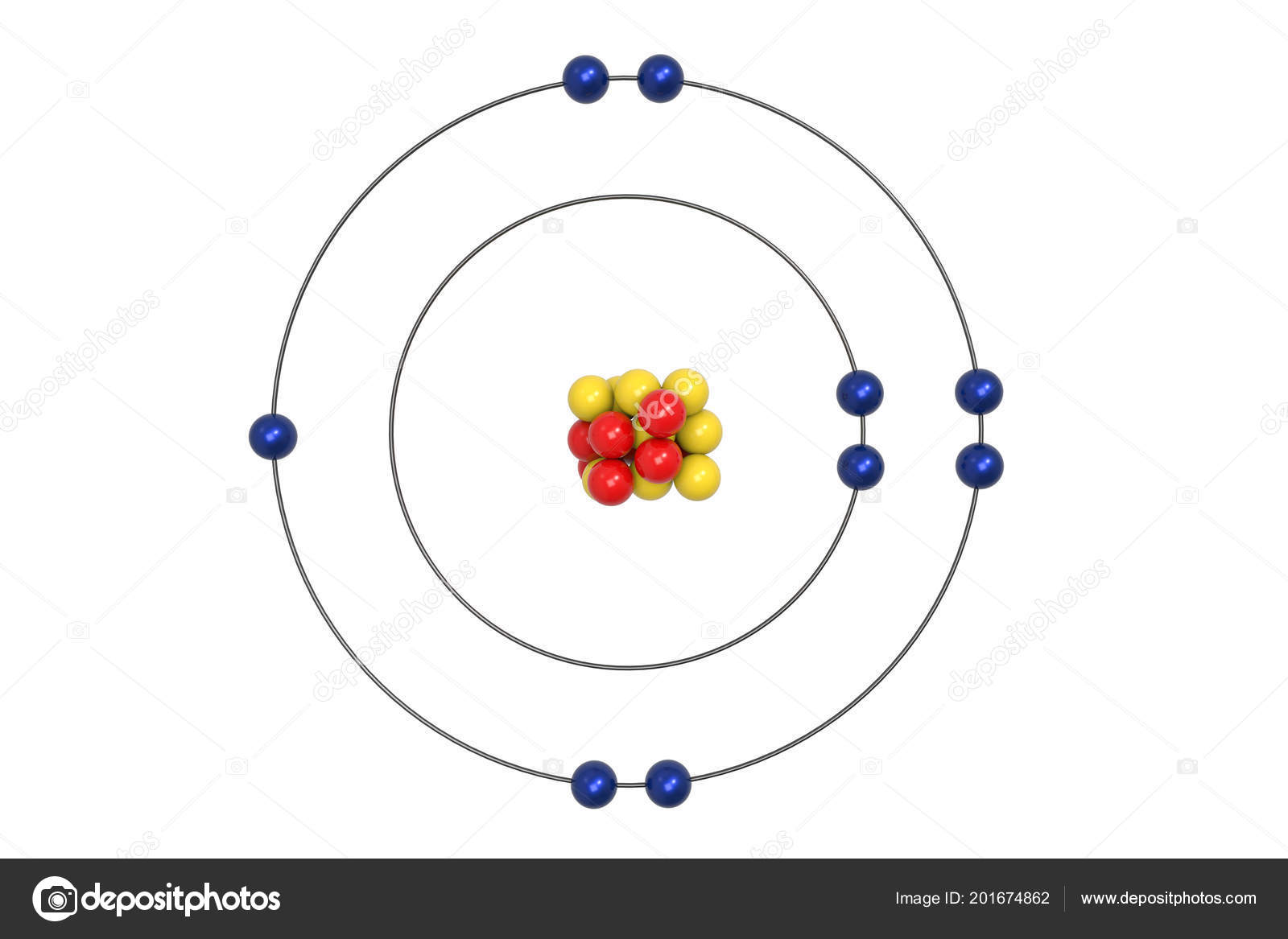
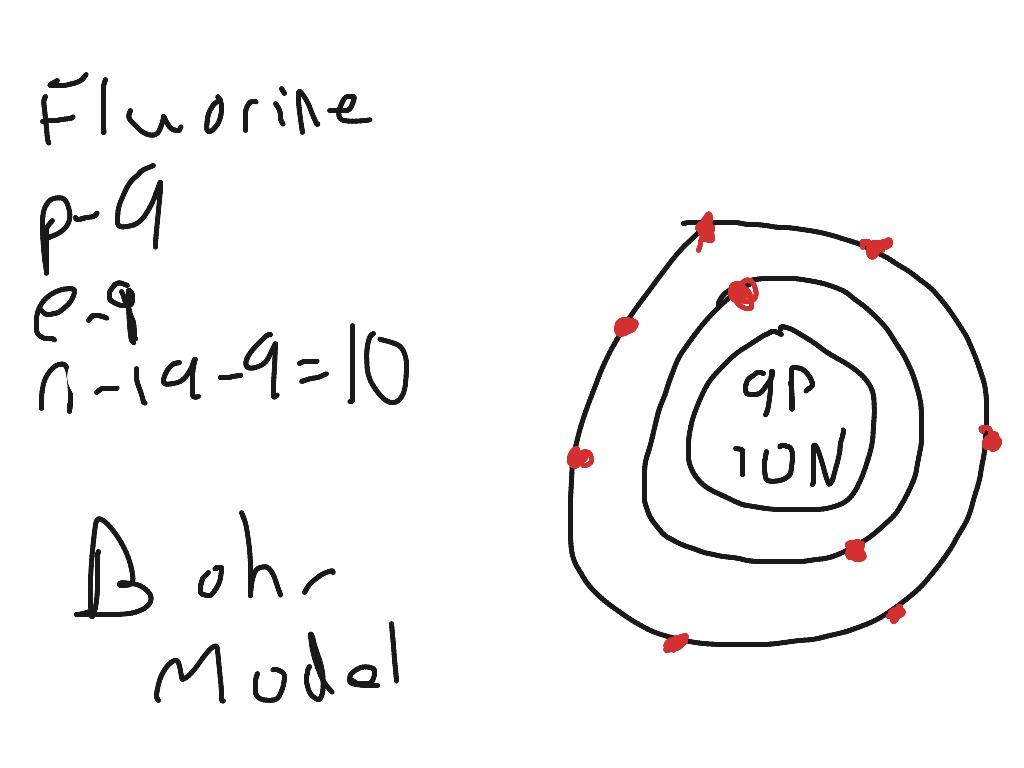
Example 2: Fluorine This is the Bohr -Rutherford Diagram for Fluorine (Atomic Number 9). Fluorine is the ninth element of the Periodic Table. As shown, Fluorine has nine protons (i.e., 9p) and ten neutrons (i.e., 10n). Thus, its Atomic Mass is 19. Fluorine also has nine total electrons -- two electrons in Orbit 1, seven electrons in Orbit 2 .
bohr rutherford diagrams lithium
This video expectation is to understand how the Bohr-Rutherford was designed and effectively use a template to draw the Bohr-Rutherford diagram of the first.
Fluorine Bohr Diagram
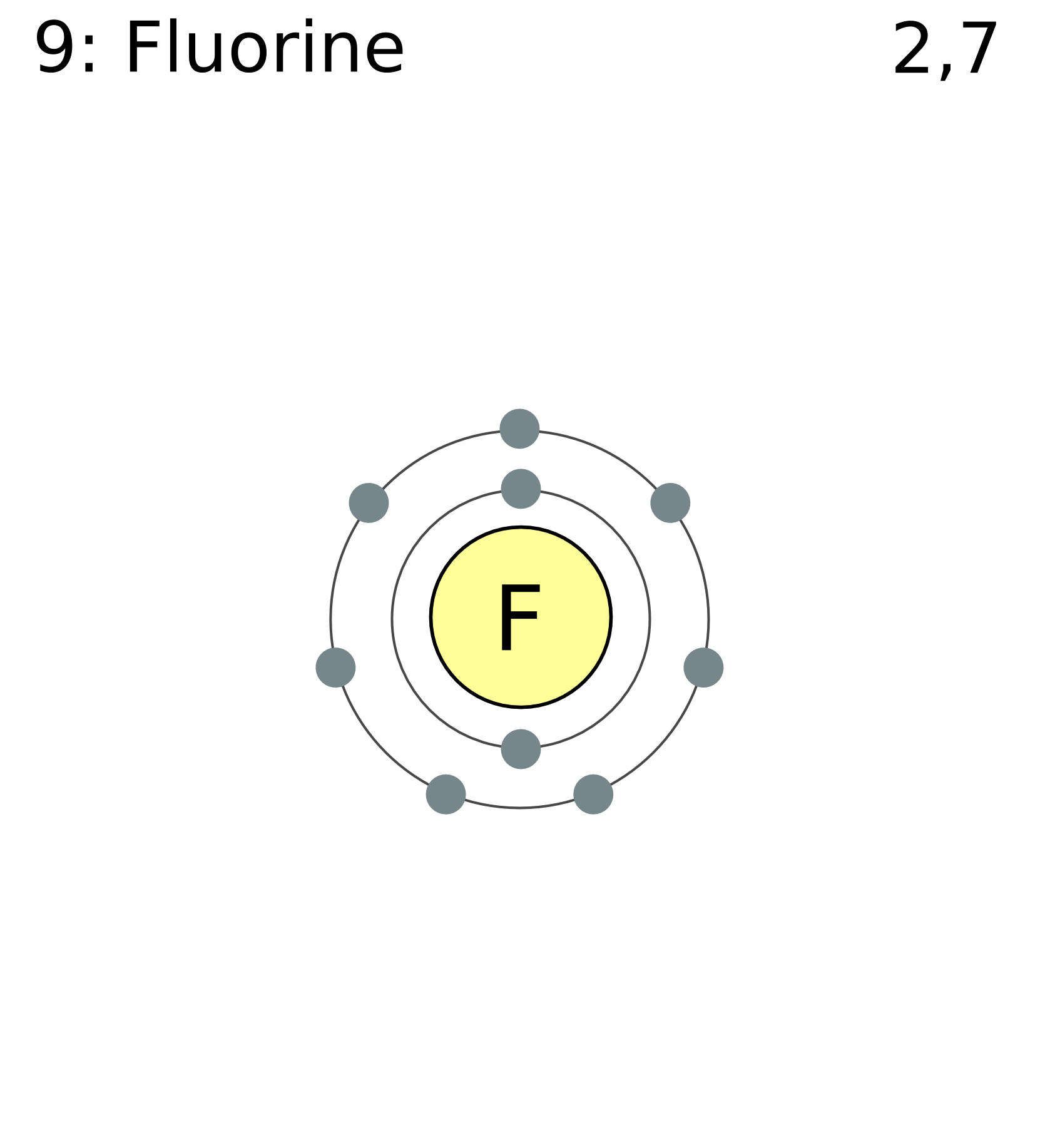
Fluorine has 2 electrons in its first shell and 7 in its second.Check me out: http://www.chemistnate.com
ShowMe fluorine
The simplest example of the Bohr Model is for the hydrogen atom (Z = 1) or for a hydrogen-like ion (Z > 1), in which a negatively charged electron orbits a small positively charged nucleus. Electromagnetic energy will be absorbed or emitted if an electron moves from one orbit to another. Only certain electron orbits are permitted.

Fluorine Molecule Diagram
Physical & Theoretical Chemistry Supplemental Modules (Physical and Theoretical Chemistry) Electronic Structure of Atoms and Molecules
Fluorine Atom Diagram
In this video we'll look at the atomic structure and Bohr model for the Fluorine atom (F). We'll use a Bohr diagram to visually represent where the electrons.
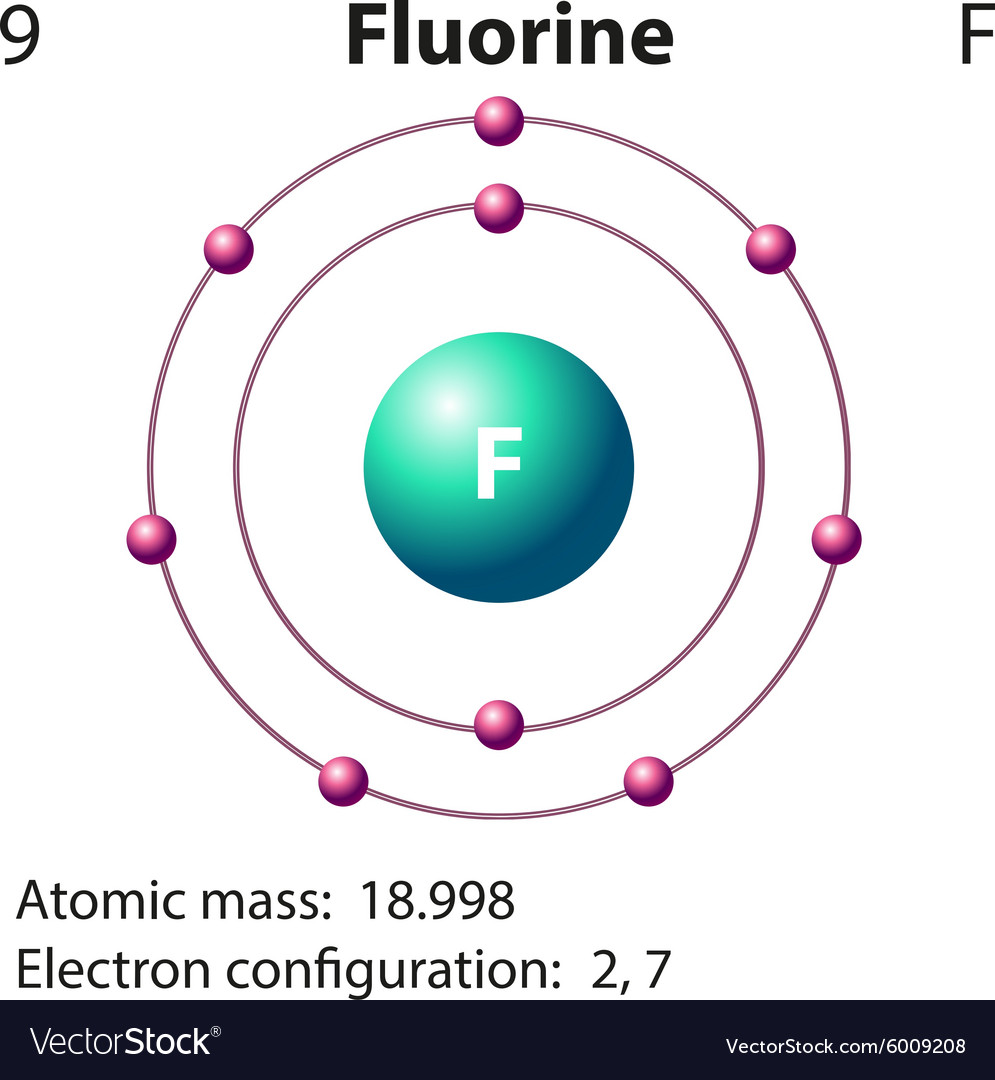
Diagram representation of the element fluorine Vector Image
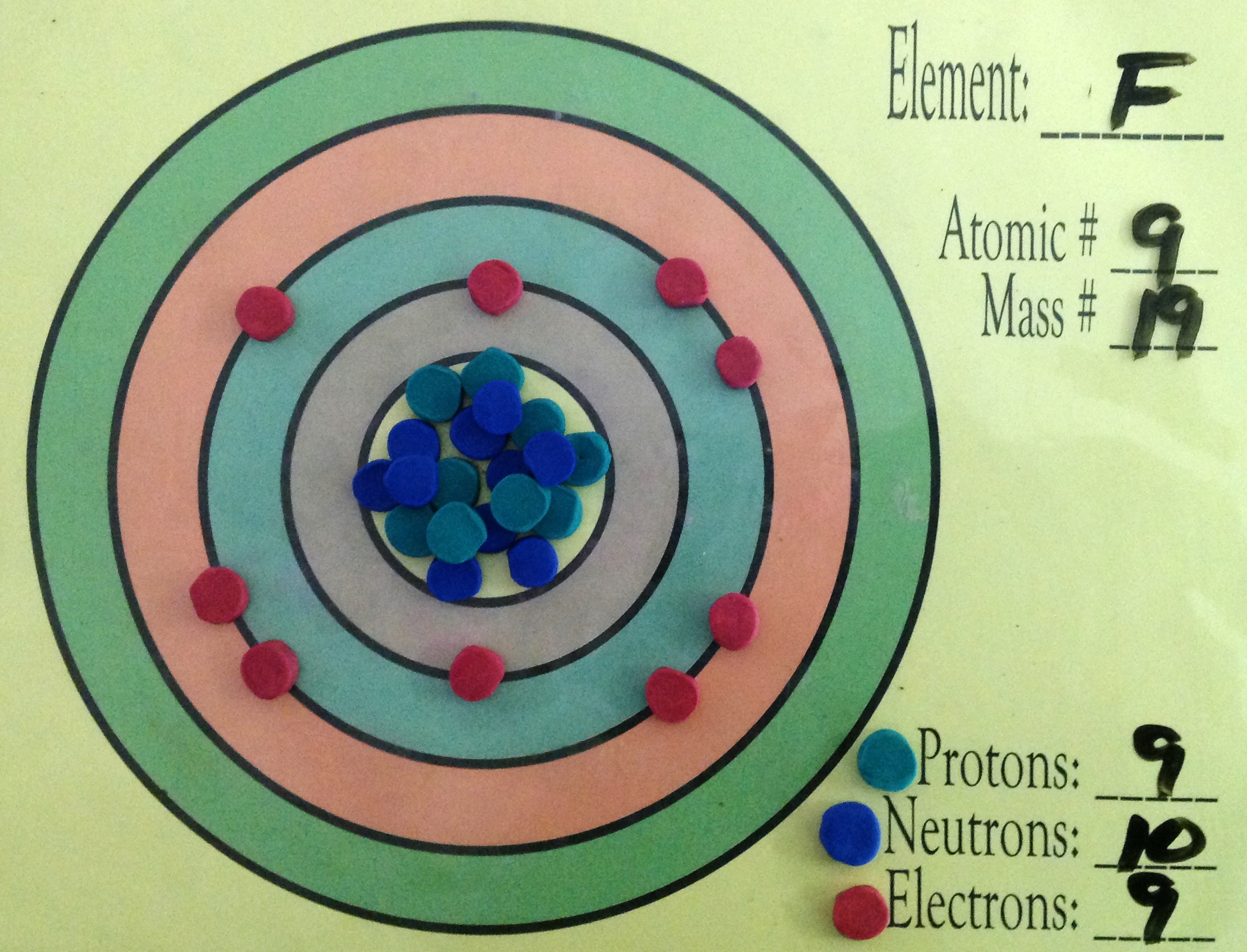
Set up the diagram. To set up the diagram, you will need a circle in the middle. This will represent the nucleus. Here you will write the number of protons and neutrons as shown below in this example using sodium (Na) Add in orbitals and electrons. In the last step you will need to draw circles around the nucleus.
Bohr Diagram Of Flourine
Schematic diagram of the Rutherford-Bohr atomic model with one orbital electron of mass m e and a finite nucleus of mass M. Both the orbital electron and the nucleus revolve about their common center-of-mass. Full size image. The following relationships will be useful in our calculations.

Fluorine Atom Diagram
How to draw a Bohr-Rutherford Diagram? Draw a nucleus -write the number of protons and neutrons inside the nucleus. Draw orbitals around the nucleus. Represent electrons as pairs of dots in the orbitals. Draw electrons as dots on the rings that represent the energy levels. Each ring has a maximum number of electrons that it can hold.
Fluorine Atom Bohr Model Proton Neutron Electron Illustration Stock
This page contains materials for the session on the atomic models of Rutherford and Bohr. It features a 1-hour lecture video, and also presents the prerequisites, learning objectives, reading assignment, lecture slides, homework with solutions, and resources for further study.

Fluorine Bohr Model
In 1913 Niels Bohr combined Rutherford's concept of the nuclear atom with Planck's idea of the quantized nature of the radiative process and developed, from first principles, an atomic model that successfully deals with one-electron structures like the hydrogen atom and one-electron ions such as singly ionized helium, doubly ionized lithium, etc. forming a hydrogen-like or hydrogenic.
Fluorine Bohr model Science ShowMe
This is the Bohr-Rutherford Diagram for Fluorine (Atomic Number 9). Fluorine is the ninth element of the Periodic Table. As shown, Fluorine has nine protons (i.e., 9p) and ten neutrons (i.e., 10n). Thus, its Atomic Mass is 19. Fluorine also has nine total electrons -- two electrons in Orbit 1, seven electrons in Orbit 2.