8.2 Solids and Liquids The Basics of General, Organic, and Biological
A typical phase diagram. The solid green line shows the behaviour of the melting point for most substances; the dotted green line shows the anomalous behavior of water. The red lines show the sublimation temperature and the blue line the boiling point, showing how they vary with pressure.

Solid, Liquid, & Gas Triple Venn Diagram Activity Middle School
A phase diagram lets you work out exactly what phases are present at any given temperature and pressure. In the cases we'll be looking at on this page, the phases will simply be the solid, liquid or vapor (gas) states of a pure substance. This is the phase diagram for a typical pure substance. These diagrams (including this one) are nearly.

IGCSE Edexcel Chemistry Help 1.1 understand the arrangement, movement
Solids Liquids Gases The particle model What are models? Working scientifically Variables Test your knowledge Key points Almost everything is made of particles. Particles can be atoms,.
Different states of matter solid, liquid, gas vector diagram By
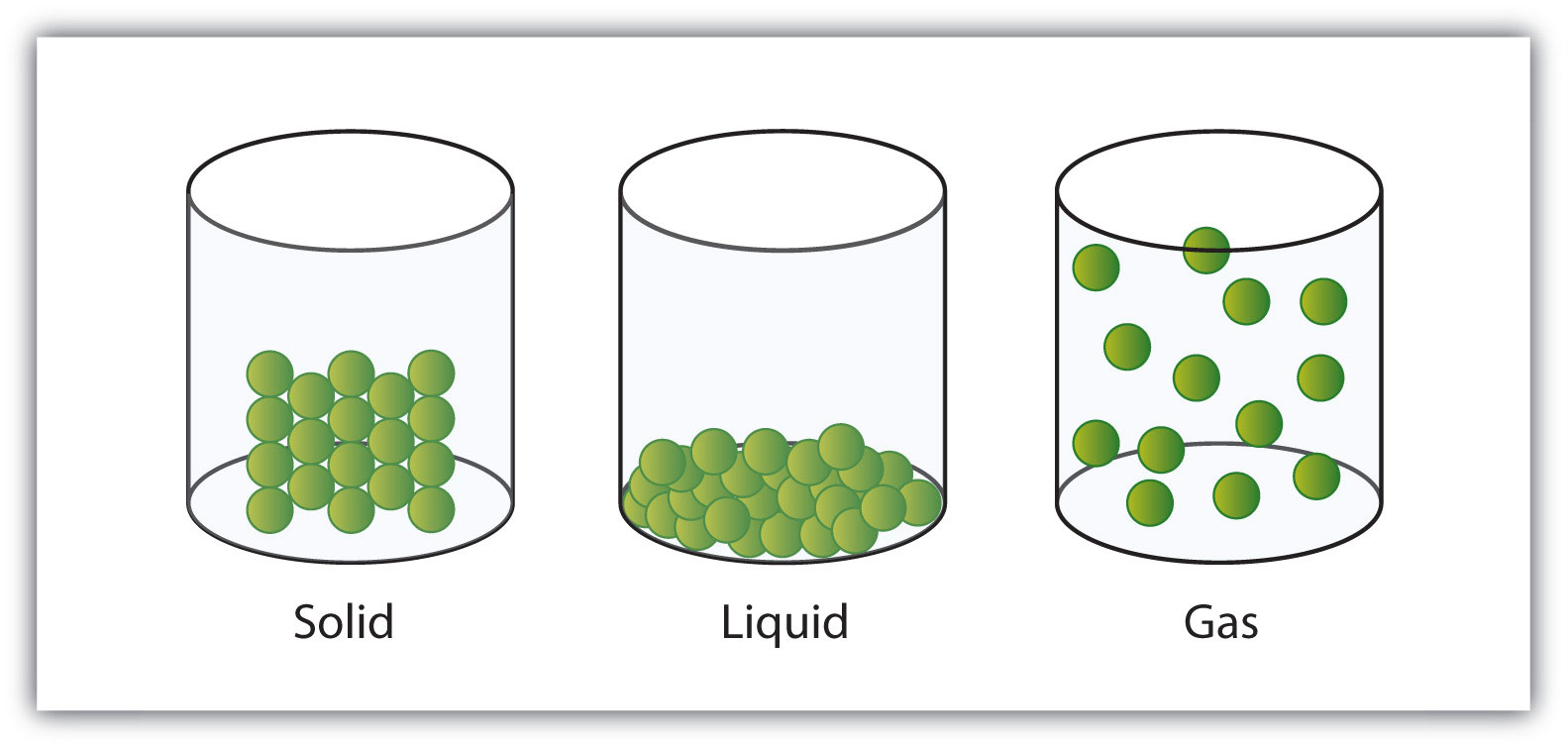
A solid is a state of matter in which atoms or molecules do not have enough energy to move. They are constantly in contact and in fixed positions relative to one another. Figure 6.1. 1: States of Matter. All three containers contain a substance with the same mass, but the substances are in different states.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/phase-changes-56a12ddd3df78cf772682e07.png)
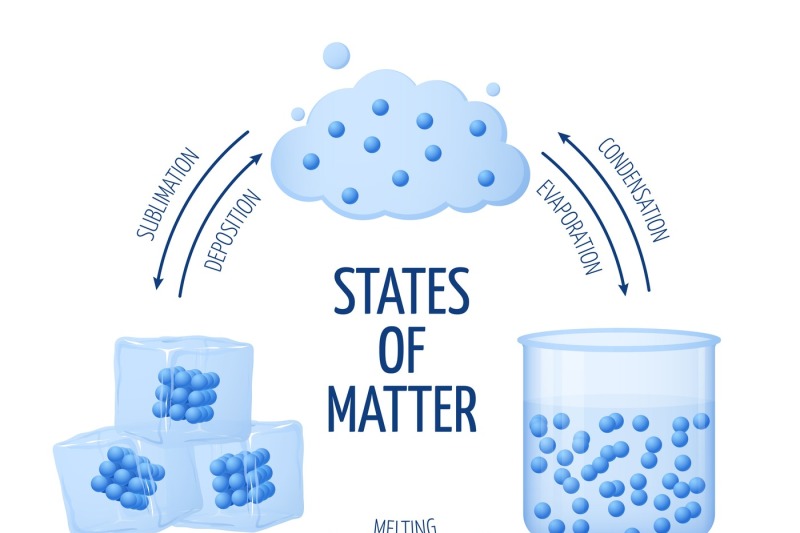
List of Phase Changes Between States of Matter
A phase diagram combines plots of pressure versus temperature for the liquid-gas, solid-liquid, and solid-gas phase-transition equilibria of a substance.
Changing the state of matter from solid, liquid and gas due to
In the video here, Sal uses a horizontal line through the phase diagram. But, it doesn't have to be horizontal. Imagine a vertical line through this diagram-- for water, choose 100 degrees C. As long as you are at 100 C, you can change the phase by changing the pressure on the system.

States of matter A simple introduction to solids, liquids, gases
Liquids and solids are often referred to as condensed phases because the particles are very close together. The following table summarizes properties of gases, liquids, and solids and identifies the microscopic behavior responsible for each property.

KS2 Science Year 4 3 States of Matter Solids Liquids and Gases
Watch different types of molecules form a solid, liquid, or gas. Add or remove heat and watch the phase change. Change the temperature or volume of a container and see a pressure-temperature diagram respond in real time. Relate the interaction potential to the forces between molecules.
Changing the state of matter from solid, liquid and gas due to
Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in Figure 5 as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating that carbon dioxide cannot exist as a liquid.
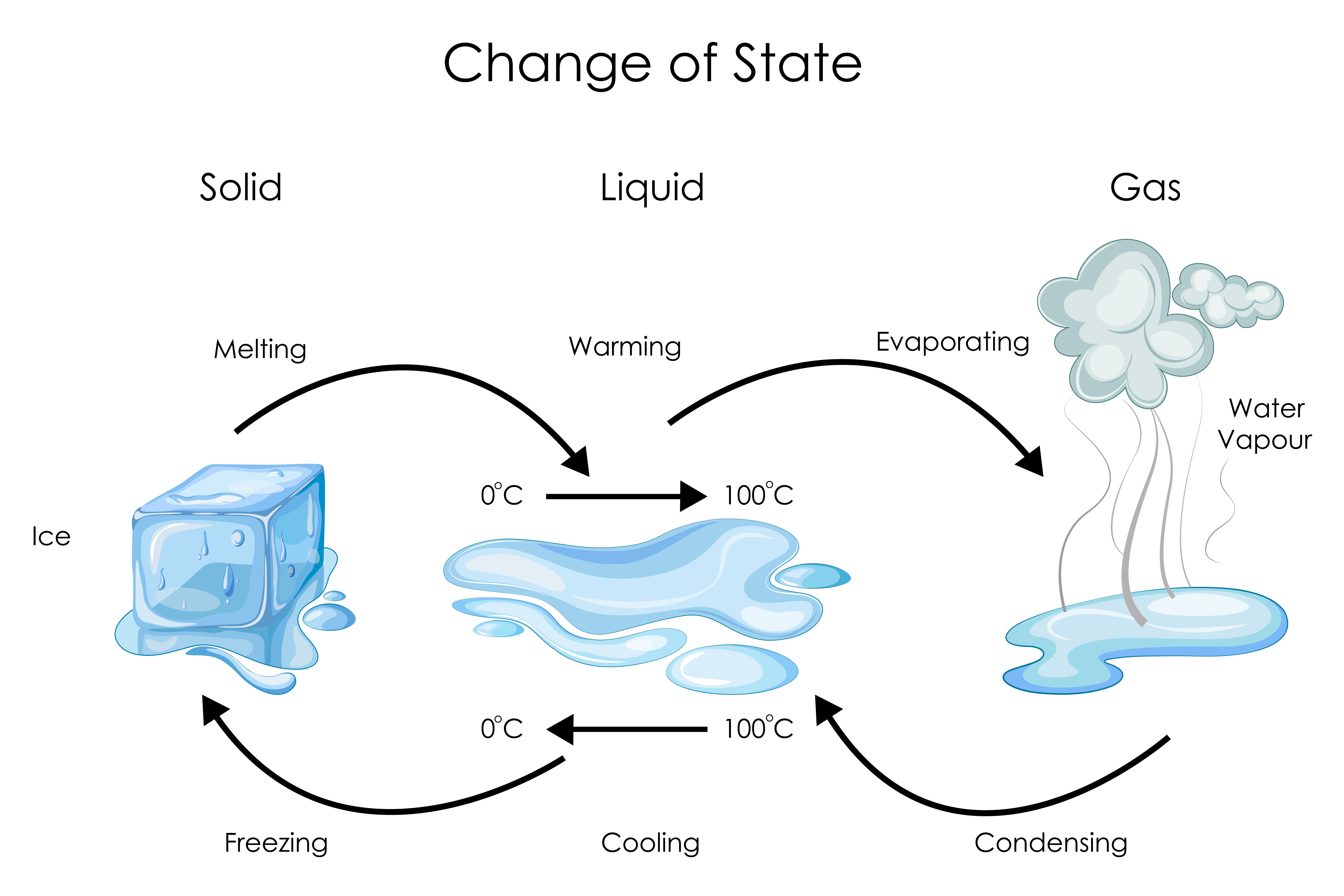
Chemistry States Of Matter Level 2 activity for kids PrimaryLeap.co.uk
Figure 13.5.1 13.5. 1: A sketch of volume versus temperature for a real gas at constant pressure. The linear (straight line) part of the graph represents ideal gas behavior—volume and temperature are directly and positively related and the line extrapolates to zero volume at 273.15oC 273.15 o C, or absolute zero.

Pin de tintinwin en nilar Estados de agregación de la materia
12.4: Phase Diagrams. To understand the basics of a one-component phase diagram as a function of temperature and pressure in a closed system. To be able to identify the triple point, the critical point, and four regions: solid, liquid, gas, and a supercritical fluid. The state exhibited by a given sample of matter depends on the identity.
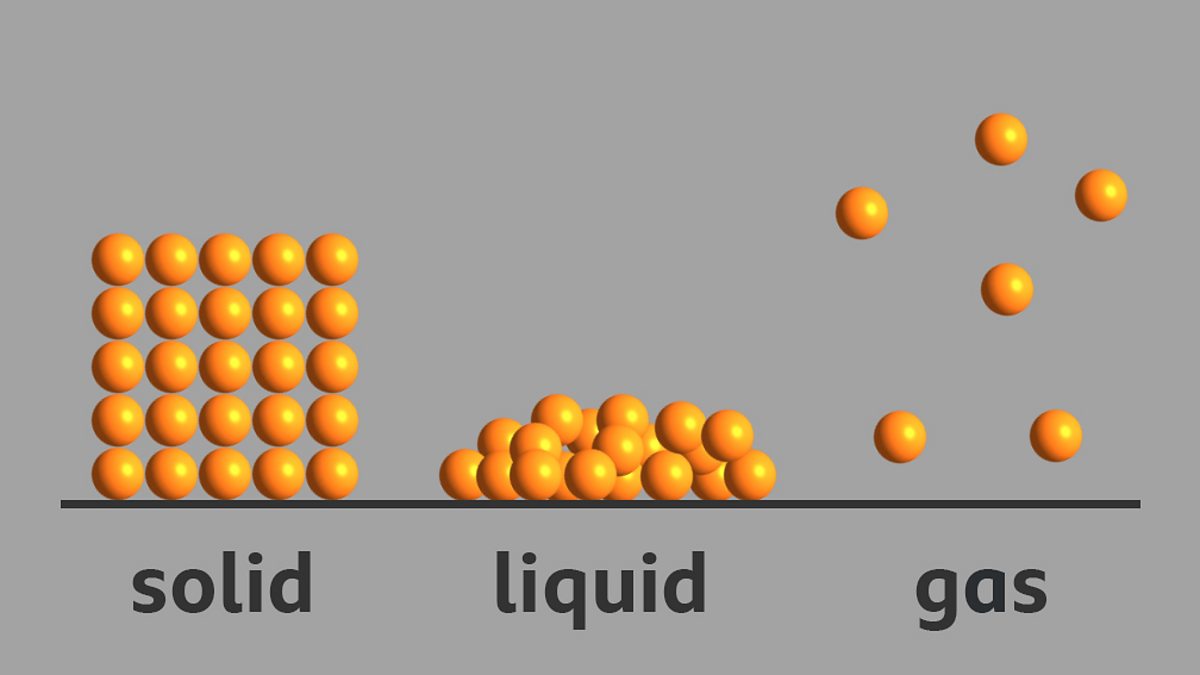
What is the arrangement of particles in a solid, liquid and gas? BBC
AboutTranscript. In this video, we'll learn how to represent solids, liquids, and gases using particulate models. The particles in a solid are either highly ordered (if the solid is crystalline) or have no regular arrangement (if the solid is amorphous). In both cases, the motion of the particles is limited. The particles in a liquid are close.
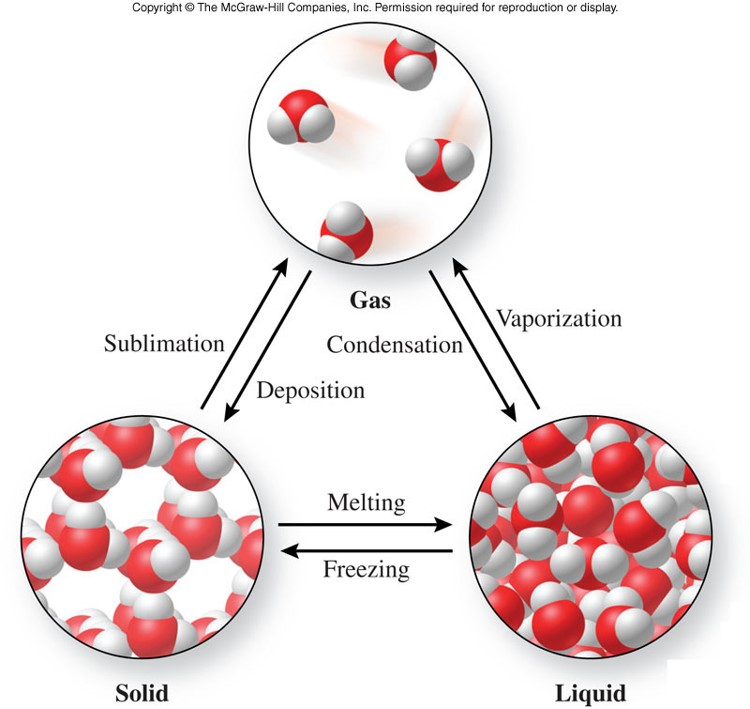
Chapter 1 Presentation
The solid-liquid curve labeled BD shows the temperatures and pressures at which ice and liquid water are in equilibrium, representing the melting/freezing points for water. Note that this curve exhibits a slight negative slope (greatly exaggerated for clarity), indicating that the melting point for water decreases slightly as pressure increases.
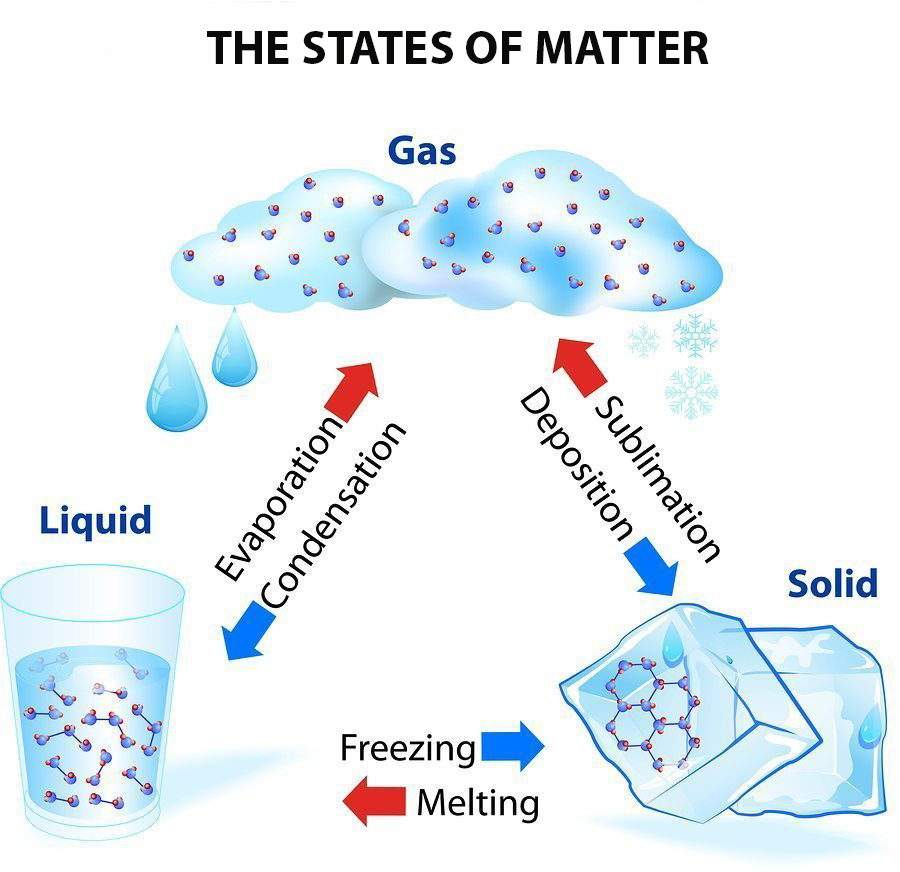
Itinerant Mission 3 Physical States of Matter Solid Liquid Gas
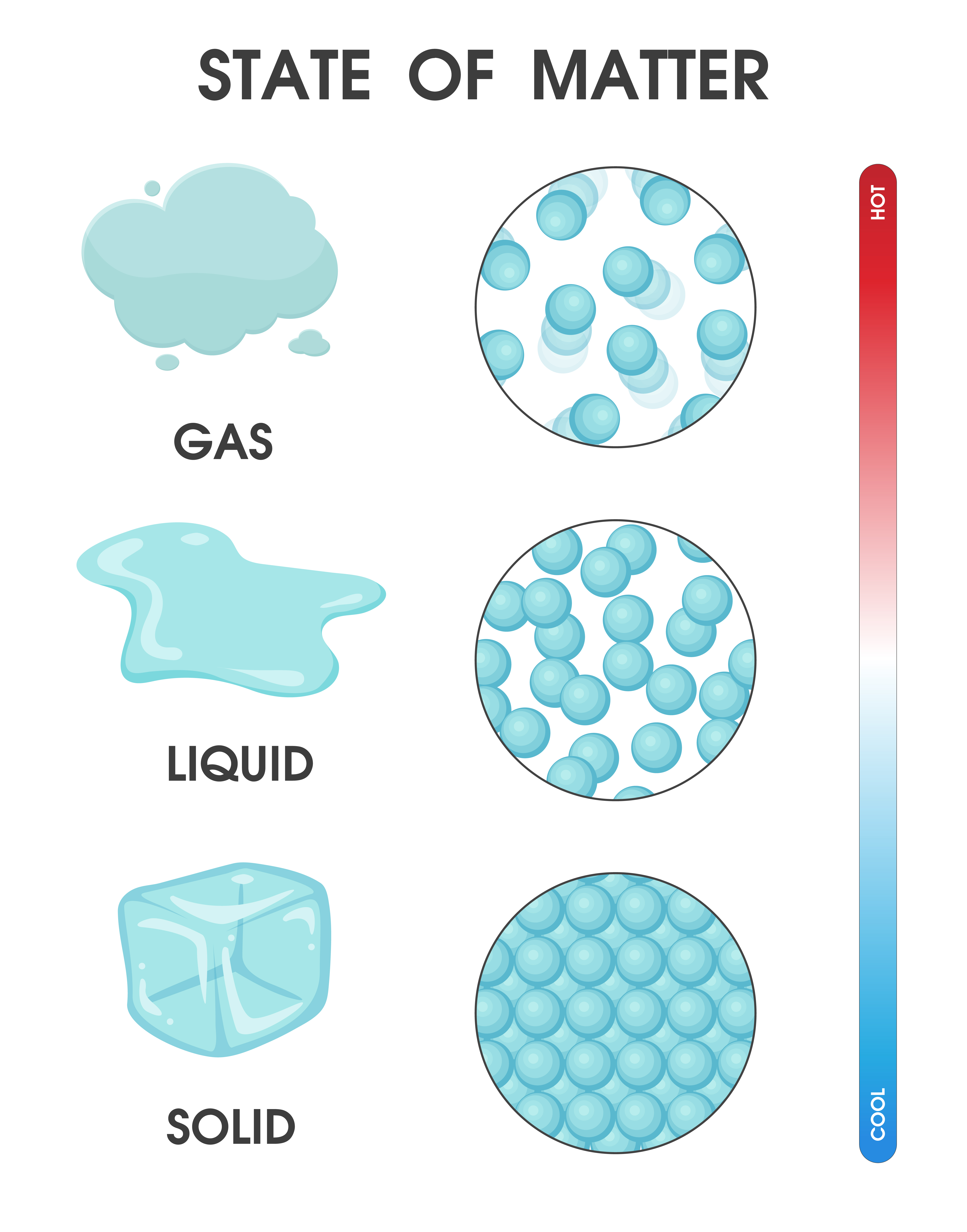
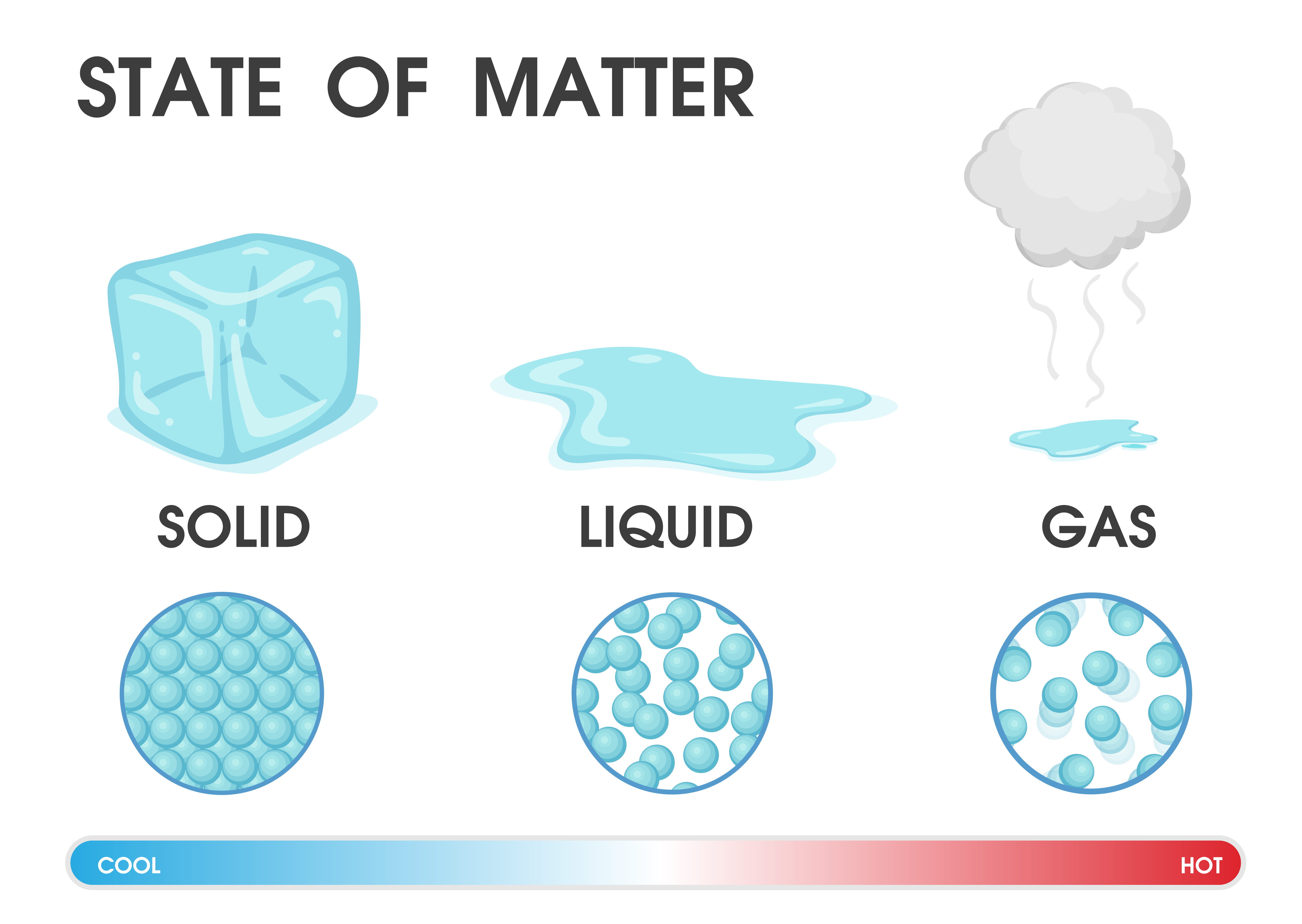
Gas. The atoms and molecules in gases are much more spread out than in solids or liquids. They vibrate and move freely at high speeds. A gas will fill any container, but if the container is not sealed, the gas will escape. Gas can be compressed much more easily than a liquid or solid.
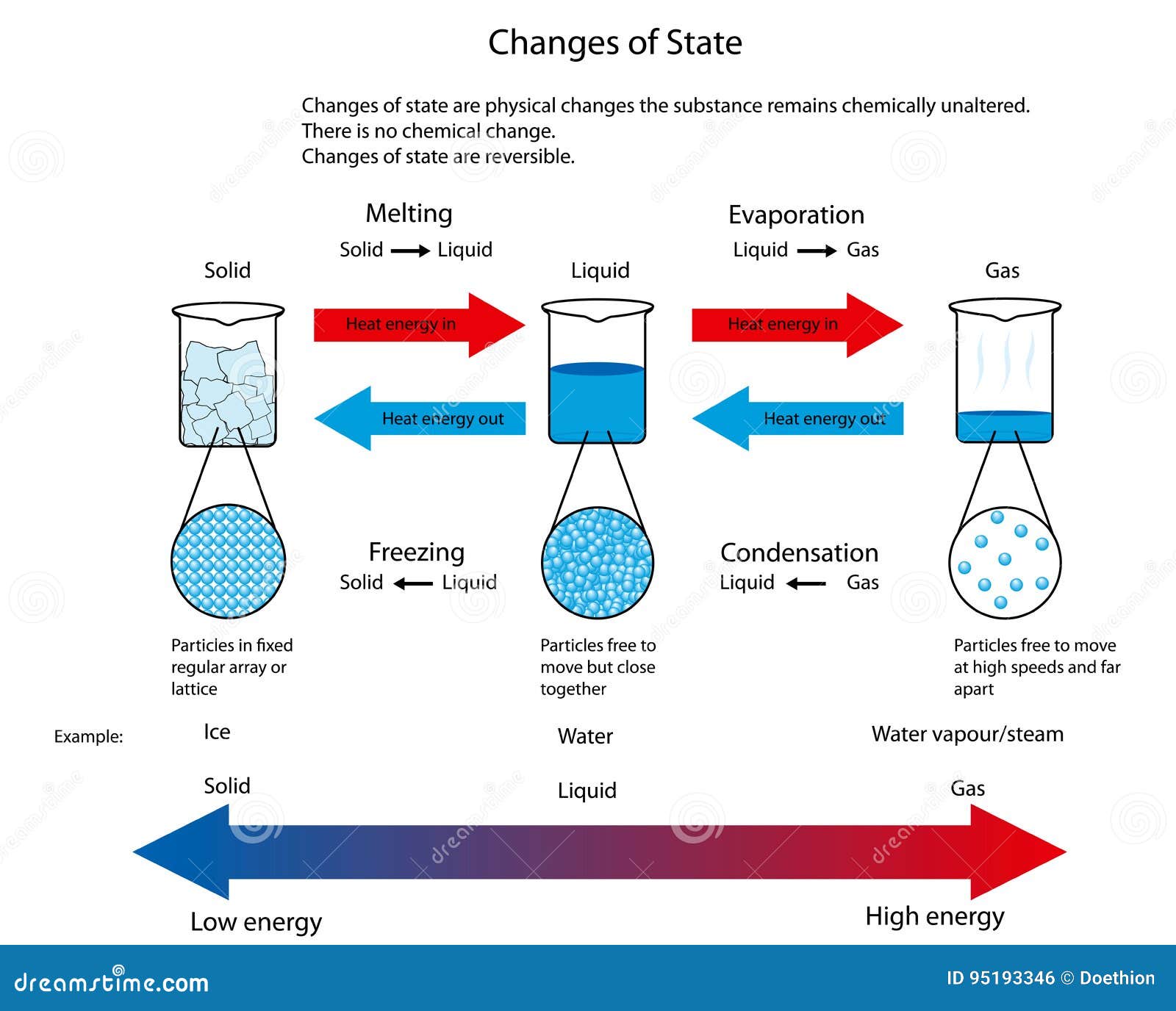
Illustration for Changes of State between Solid, Liquid and Gas Stock
A phase diagram combines plots of pressure versus temperature for the liquid-gas, solid-liquid, and solid-gas phase-transition equilibria of a substance. These diagrams indicate the physical states that exist under specific conditions of pressure and temperature, and also provide the pressure dependence of the phase-transition temperatures (melting points, sublimation points, boiling points).
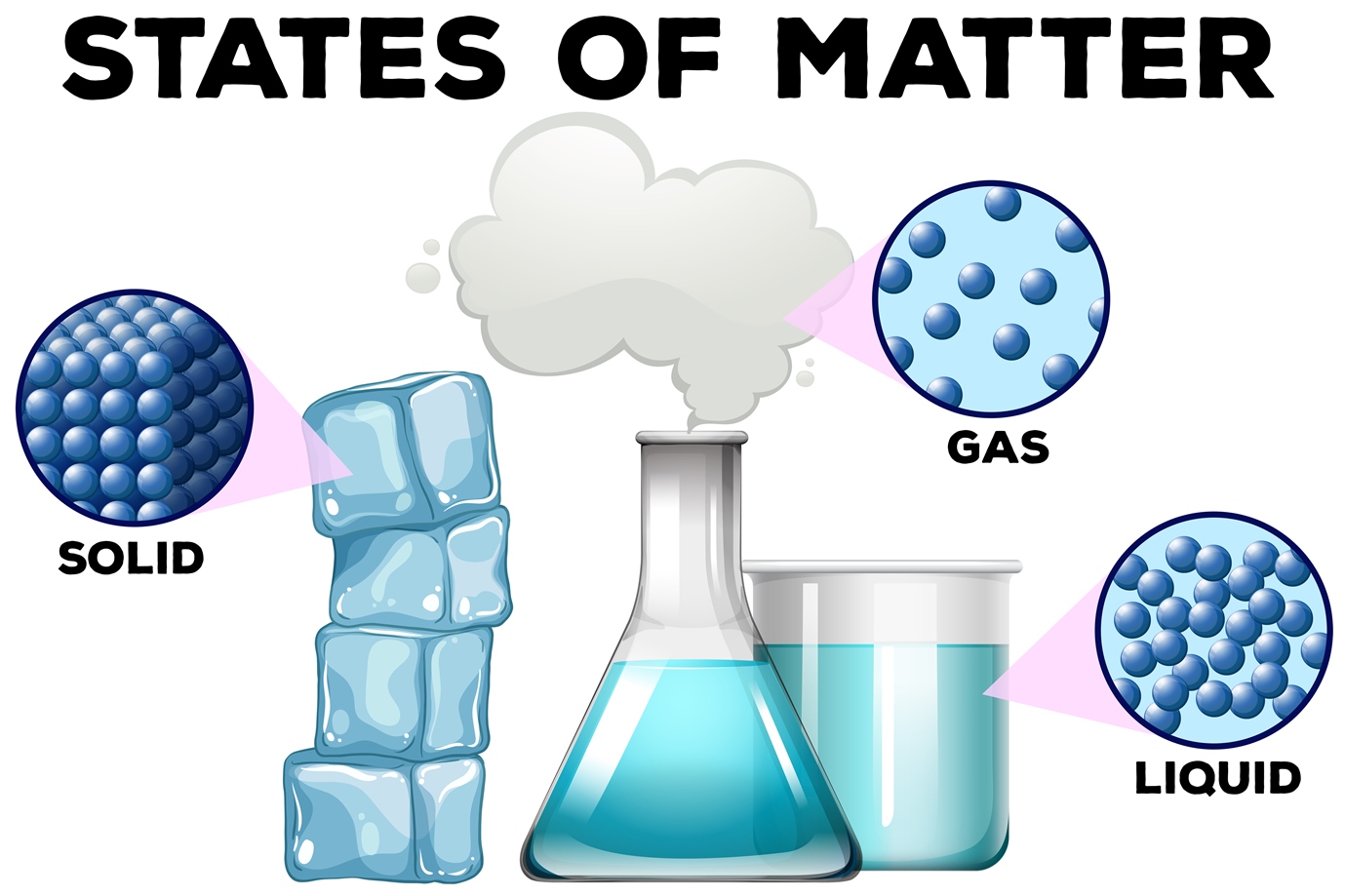
Solids, liquids and gases
A phase transition occurs when a substance changes from one state of matter to another state. There are three primary states of matter: liquid, solid, and gas. A phase diagram is a plot that illustrates the different phases of a substance across multiple variables, most often temperature and pressure. The diagram can help to demonstrate how.