What are sin cos tan? SOHCAHTOA With Examples Teachoo Finding
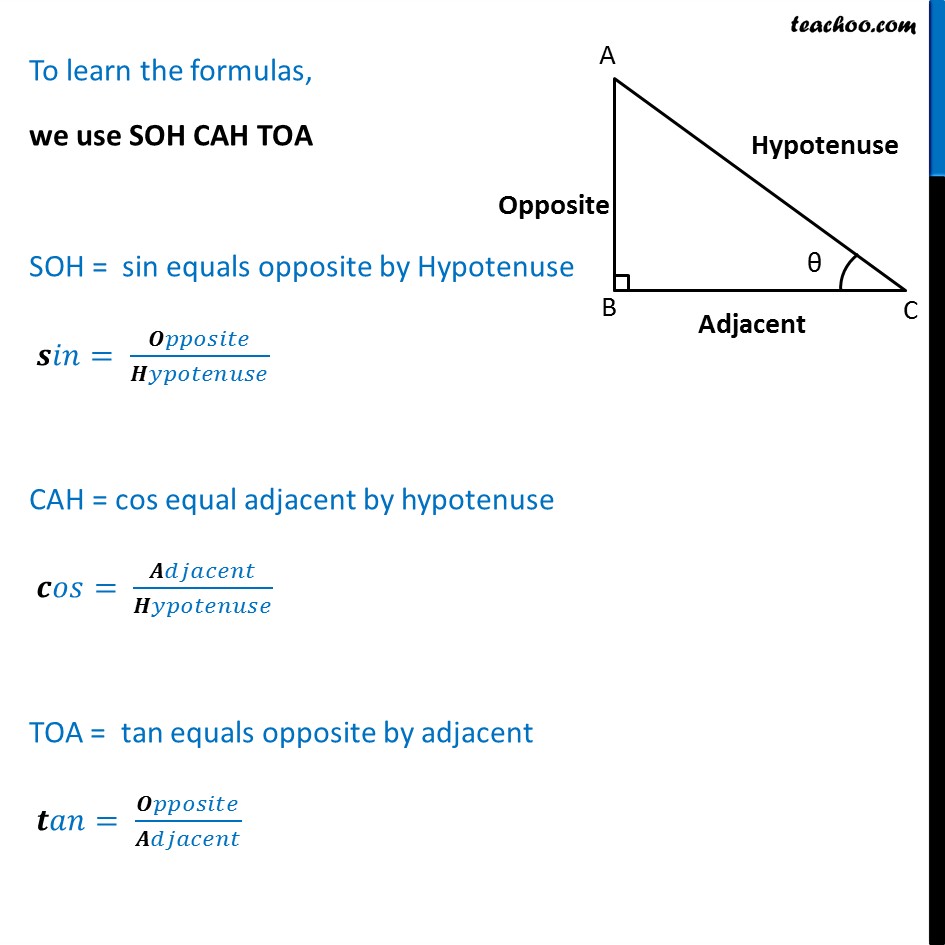
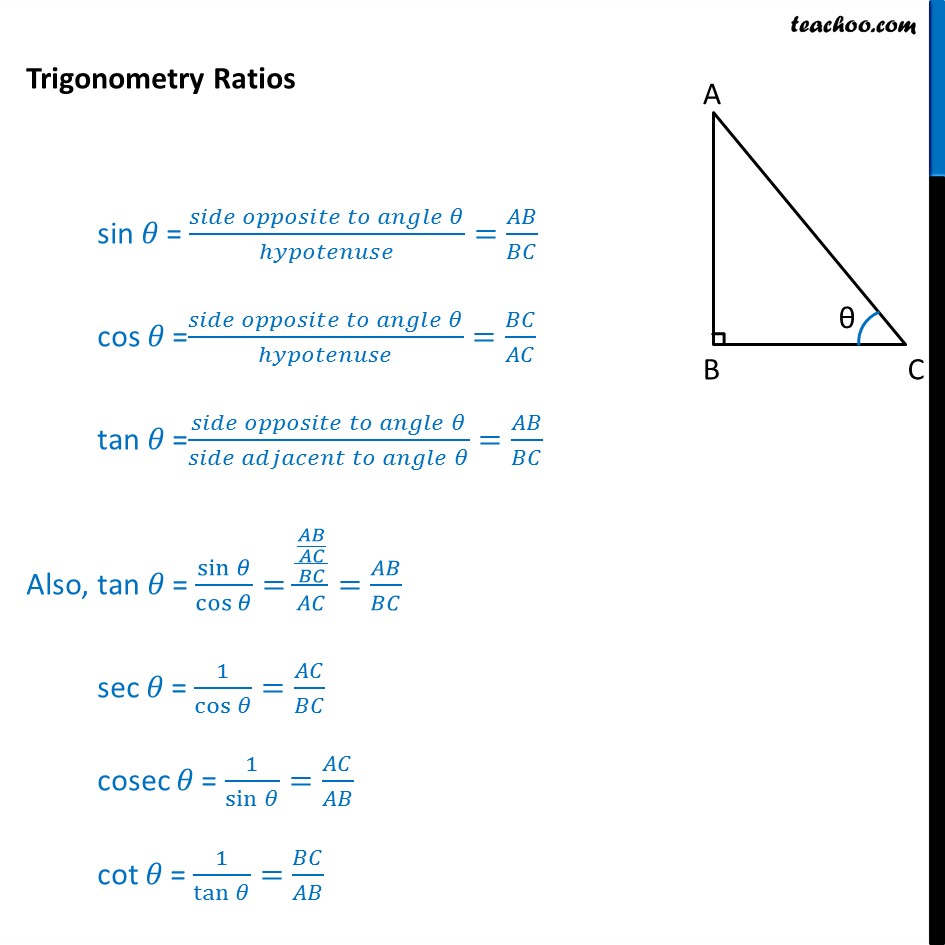
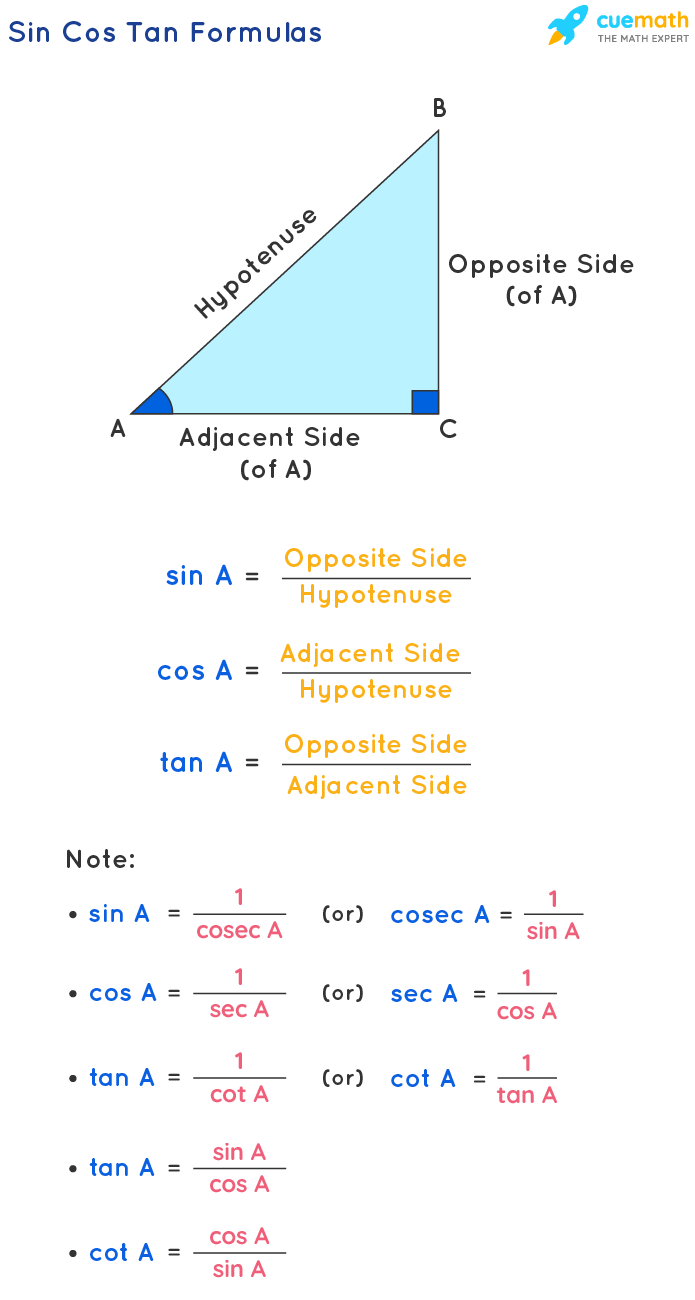
The formulas of any angle θ sin, cos, and tan are: sin θ = Opposite/Hypotenuse. cos θ = Adjacent/Hypotenuse. tan θ = Opposite/Adjacent. There are three more trigonometric functions that are reciprocal of sin, cos, and tan which are cosec, sec, and cot respectively, thus. cosec θ = 1 / sin θ = Hypotenuse / Opposite.

Trigonometry, Tangent, Math methods
Here are the formulas of sin, cos, and tan. sin θ = Opposite/Hypotenuse. cos θ = Adjacent/Hypotenuse. tan θ = Opposite/Adjacent. Apart from these three trigonometric ratios, we have another three ratios called csc, sec, and cot which are the reciprocals of sin, cos, and tan respectively. Let us understand these sin, cos, and tan formulas.

Sin,Cos,Tan adjacent, cos, en, geometry, hypotenuse, math, sin, tan, trigonometry Glogster
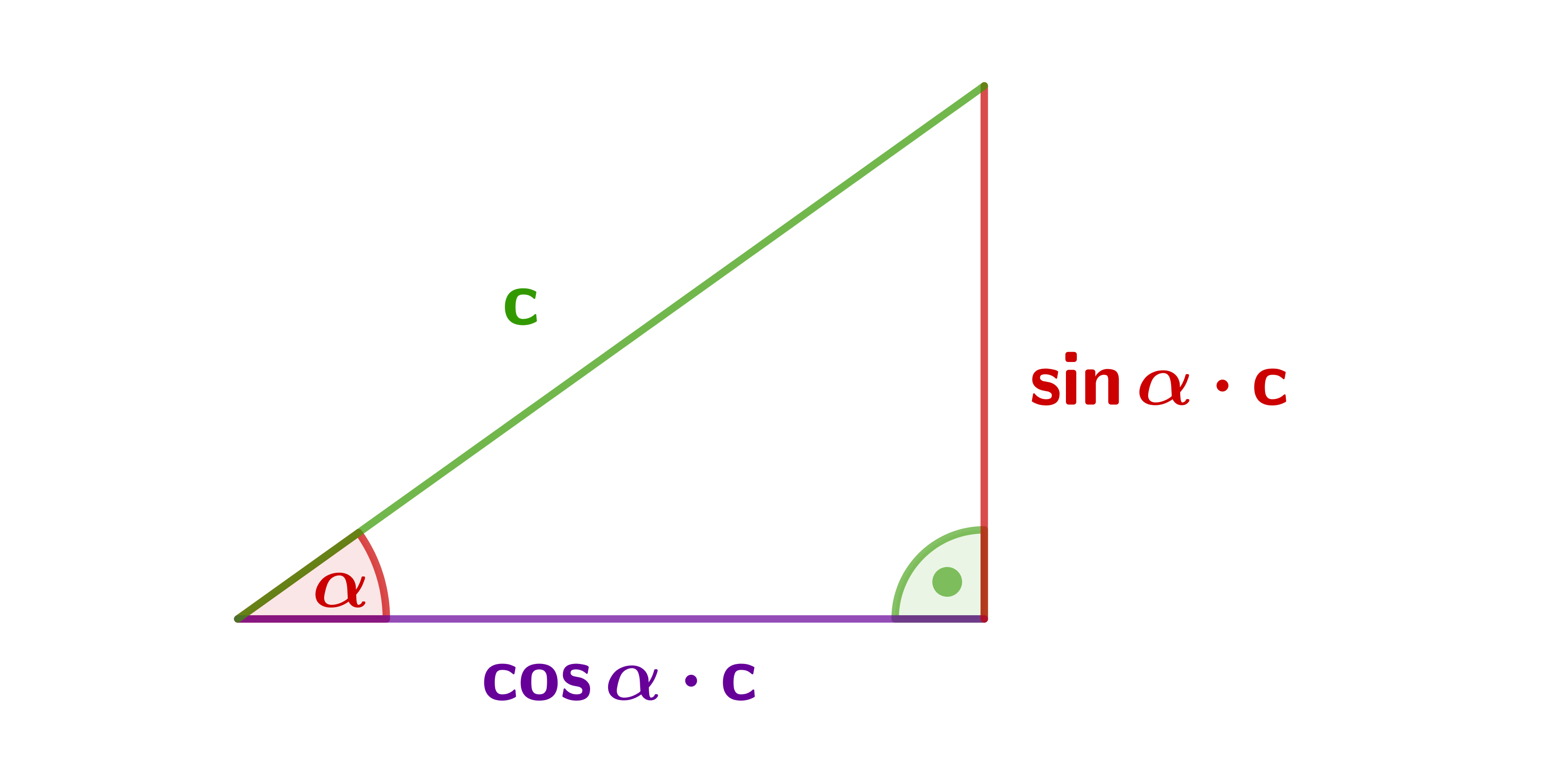
To calculate sine, cosine, and tangent in a 3-4-5 triangle, follow these easy steps: Place the triangle in a trigonometric circle with an acute angle in the center. Identify the adjacent and opposite catheti to the angle. Compute the results of the trigonometric functions for that angle using the following formulas: sin (α) = opposite.
Trudiogmor Sinus Cosinus Tangens Tabelle Formelsammlung
A: The Sin Cos Tan formula is a set of three trigonometric ratios used to solve problems involving right triangles. The three ratios are: Sine (sin): Opposite/Hypotenuse. Cosine (cos): Adjacent/Hypotenuse. Tangent (tan): Opposite/Adjacent. What is the Trigonometry Formula Chart? A: The Trigonometry Formula Chart is a chart that shows all of the.

Trigonometrie Sinus, Kosinus & Tangens Mehr Spicker und Erklärungen auf studes.de
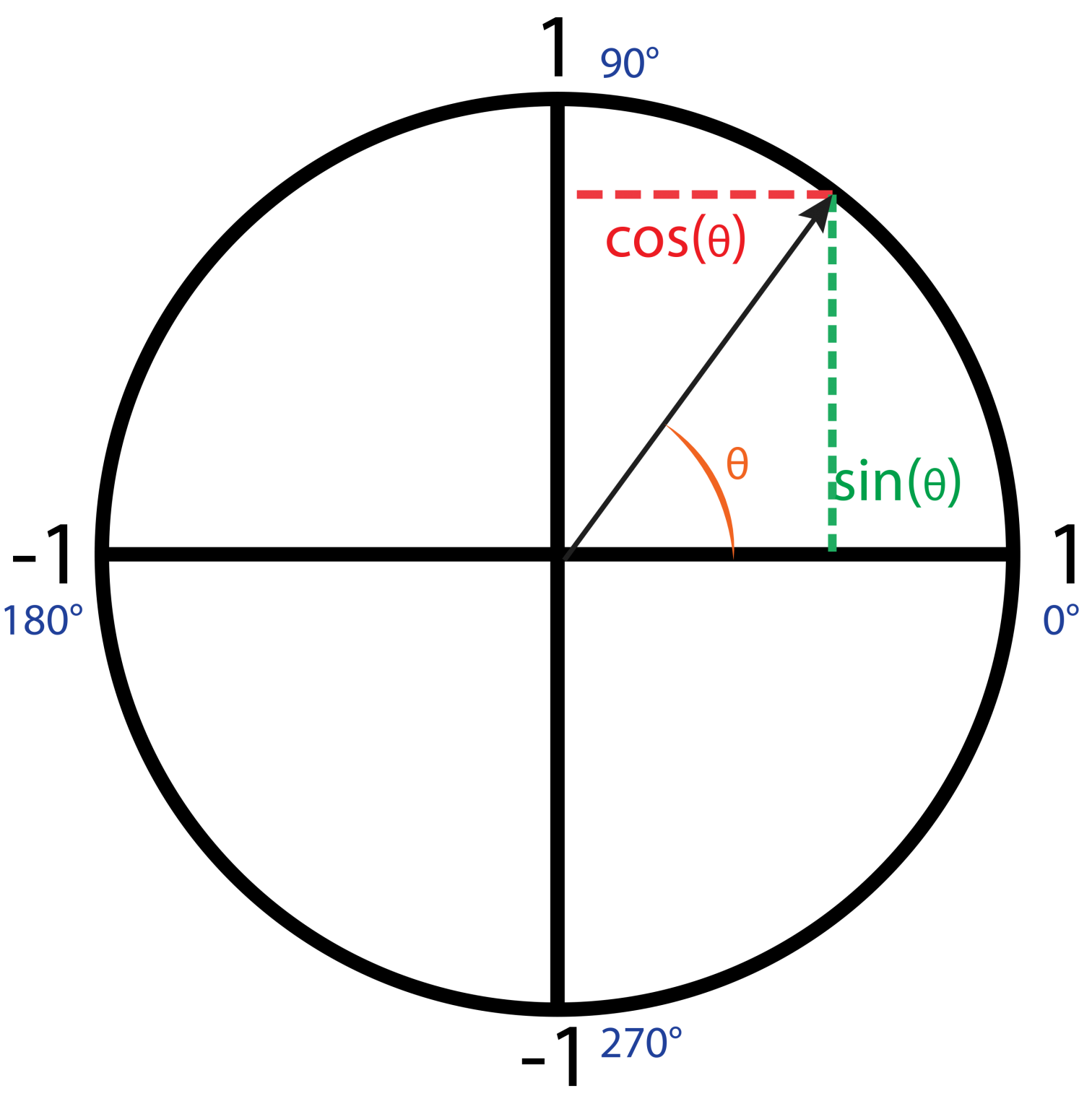
Remember: When we use the words 'opposite' and 'adjacent,' we always have to have a specific angle in mind. Range of Values of Sine. For those comfortable in "Math Speak", the domain and range of Sine is as follows. Domain of Sine = all real numbers; Range of Sine = {-1 ≤ y ≤ 1}; The sine of an angle has a range of values from -1 to 1 inclusive.
Sin Cos Tan Graphs / Graphs of Hyperbolic functions Sin, Cos and Tan YouTube / The following
Learn the basics of trigonometry in this video math tutorial by Mario's Math Tutoring. We discuss how to work with the trigonometric ratios: sine, cosine, a.

Sine, Cosine and Tangent Trigonometry, Tangent, Physics
Unit 4: Trigonometric equations and identities. 0/700 Mastery points. Inverse trigonometric functions Sinusoidal equations Sinusoidal models. Angle addition identities Using trigonometric identities Challenging trigonometry problems. Learn trigonometry—right triangles, the unit circle, graphs, identities, and more.
Sine, Cosine, Tangent, explained and with Examples and practice identifying opposite, adjacent
Sin, Cos and Tan are the basic trigonometric ratios used to examine the relationship between the angles and sides of a triangle (especially of a right-angled triangle). Sin, Cos and Tan are the abbreviated forms of Sine, Cosine and Tangent respectively. These can be represented in terms of the sides (opposite side, adjacent side and hypotenuse) respective to the angle of a right-angled triangle.

Section 4 Sine And Cosine Rule
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics. The word itself comes from the Greek trigōnon (which means "triangle") and metron ("measure"). As the name suggests, trigonometry deals primarily with angles and triangles; in particular, it defines and uses the relationships and ratios between angles and sides in triangles.The primary application is thus solving triangles, precisely right triangles.
Sin Cos Tan Triangle Calculator Cheapest Wholesalers, Save 52 jlcatj.gob.mx
The trigonometric functions most widely used in modern mathematics are the sine, the cosine, and the tangent functions. Their reciprocals are respectively the cosecant, the secant, and the cotangent functions, which are less used.

sin cos tan formulas
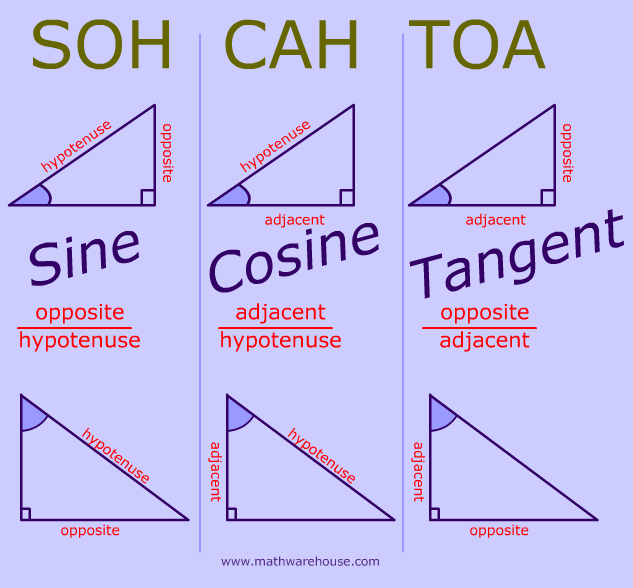
The sine of the angle = the length of the opposite side. the length of the hypotenuse. The cosine of the angle = the length of the adjacent side. the length of the hypotenuse. The tangent of the angle = the length of the opposite side. the length of the adjacent side. So in shorthand notation: sin = o/h cos = a/h tan = o/a.

Trigonometry
Exercise. Try this paper-based exercise where you can calculate the sine functionfor all angles from 0° to 360°, and then graph the result. It will help you to understand these relativelysimple functions. You can also see Graphs of Sine, Cosine and Tangent.. And play with a spring that makes a sine wave.. Less Common Functions. To complete the picture, there are 3 other functions where we.
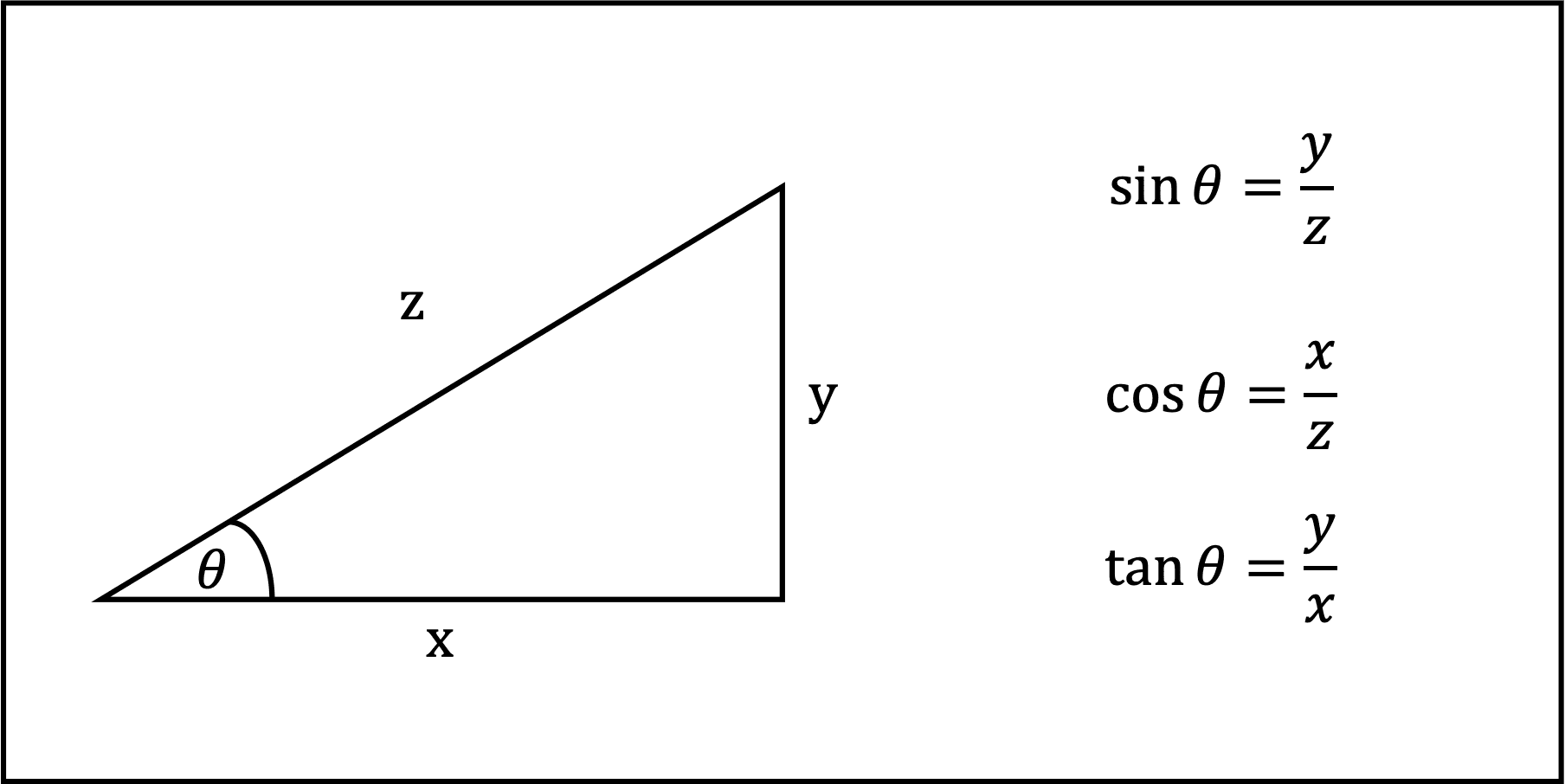
Trigonometric (Sin Cos Tan) Table 0360 Degrees (Downloadable) and How to Learn from It
Sin Cos Tan Formula. The three ratios, i.e. sine, cosine and tangent have their individual formulas. Suppose, ABC is a right triangle, right-angled at B, as shown in the figure below: Now as per sine, cosine and tangent formulas, we have here: Sine θ = Opposite side/Hypotenuse = BC/AC; Cos θ = Adjacent side/Hypotenuse = AB/AC

Trigonometry review Trigonometry, Math methods, Gcse math
Solved Examples. Question 1: Calculate the angle in a right triangle whose adjacent side and hypotenuse are 12 cm and 20 cm respectively? Solution: Given, Adjacent side = 12 cm. Hypotenuse = 20 cm. cos θ = Adjacent⁄Hypotenuse. cos θ = 12⁄20. θ = cos −1 (0.6)
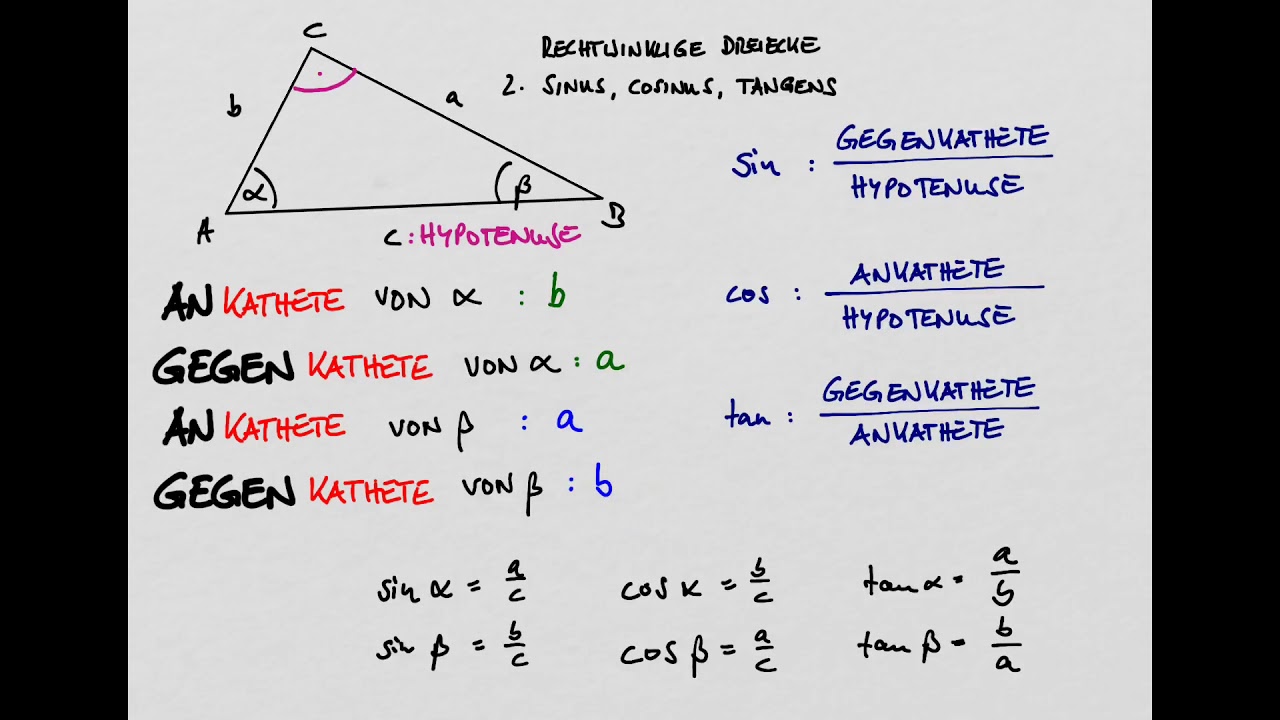
sinus cosinus tangens 2 formeln YouTube
In Trigonometry, different types of problems can be solved using trigonometry formulas. These problems may include trigonometric ratios (sin, cos, tan, sec, cosec and cot), Pythagorean identities, product identities, etc. Some formulas including the sign of ratios in different quadrants, involving co-function identities (shifting angles), sum & difference identities, double angle identities.
p5 Trigonometric functions and oscillation (sin, cos) EMS Interactivity
Sin, cos, and tan are trigonometric ratios that relate the angles and sides of right triangles. Sin is the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse, cos is the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse, and tan is the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side. They are often written as sin (x), cos (x), and tan (x), where x is an.