1. Topographic Surface Anatomy
Larynx. Salivary glands. Motor and sensory innervation of face and oral cavity. Lymphoid system of face and neck. Coniotomy, tracheotomy. Term ANATOMY from Greek anatomé = „a cutting up" SYSTEMATIC ANATOMY As a science deals with morphology and structures of the human body.
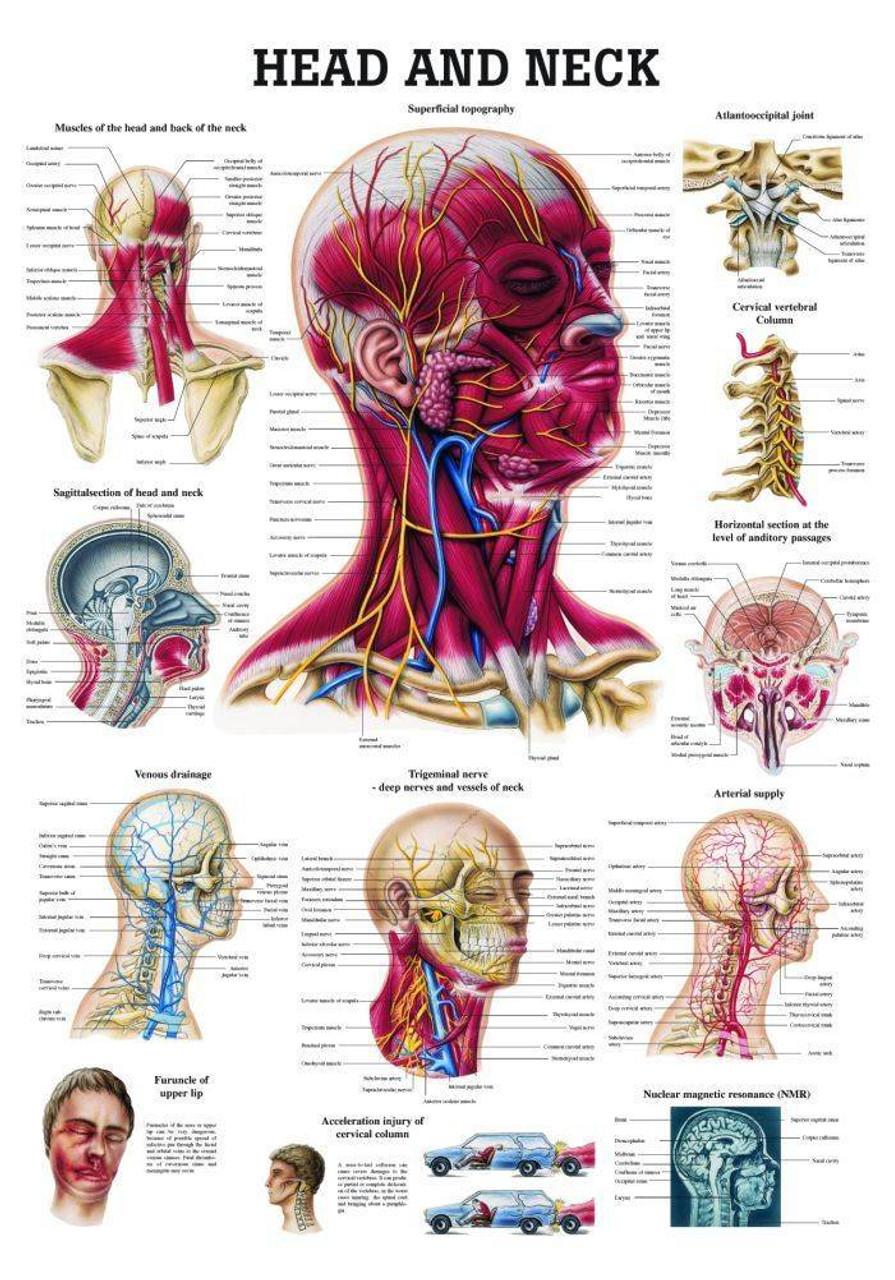
Head and Neck Laminated Anatomy Chart
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright.

The muscles of the anterior neck. Human anatomy and physiology, Human body anatomy, Thyroid
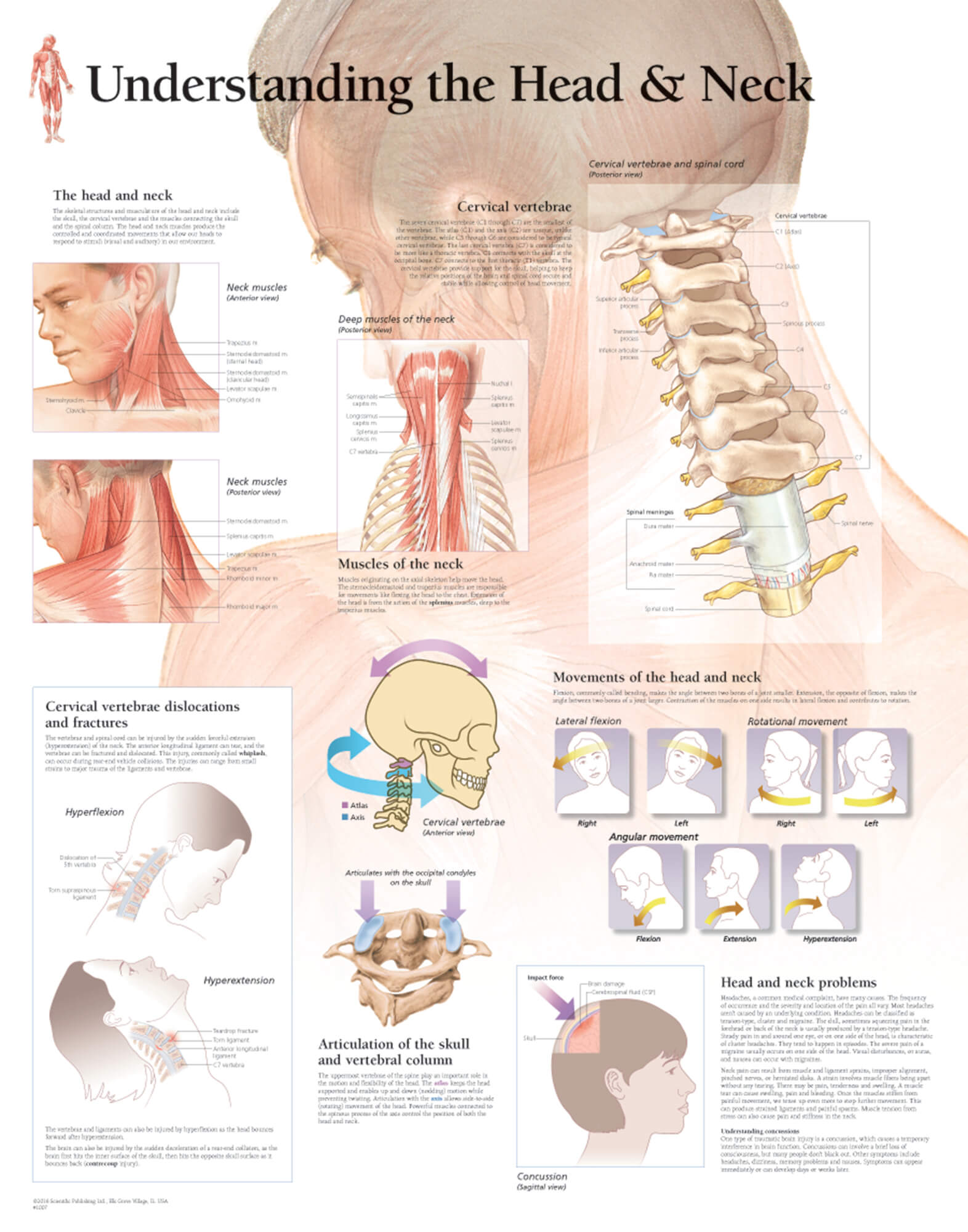
The movement of the head is mostly owing to its articulation with the neck. It acts as a bridge between the body and the head. Due to their proximity and directly linked functions, the head and neck regions are mentioned together. The head and neck areas are crucial to swallowing function. Therefore, the head provides the realization of many.
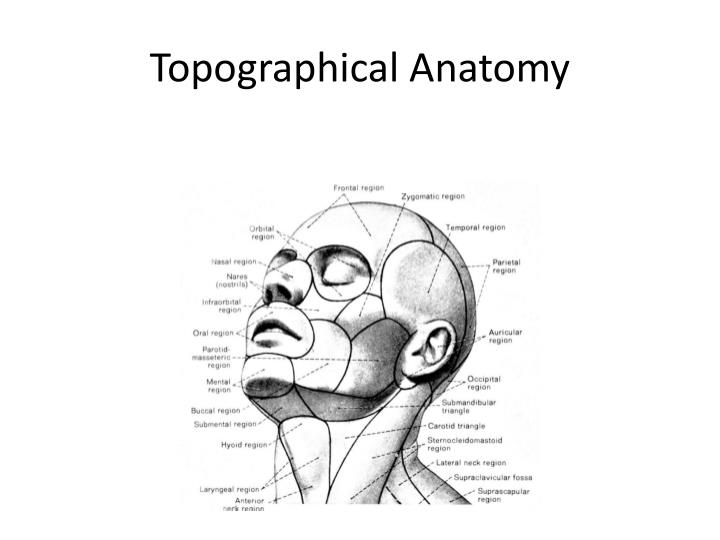
Topographic Anatomy of the Head DocsLib
This atlas of topographic and pathotopographic human anatomy is a fundamental and practically important book designed for doctors of all specializations and students of medical schools.

Topographische Anatomie des Menschen ‘Volume One Head & Neck’ Eduard Pernkopf [ed.] (Atlas of
Topographical Anatomy of the Head and Neck. Veins of the Head and Neck. Viscera of the Head and Neck. UAMS College of Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences. Mailing Address: 4301 West Markham Street, Little Rock, AR 72205. Phone: (501) 686-7000. Facebook; Twitter;
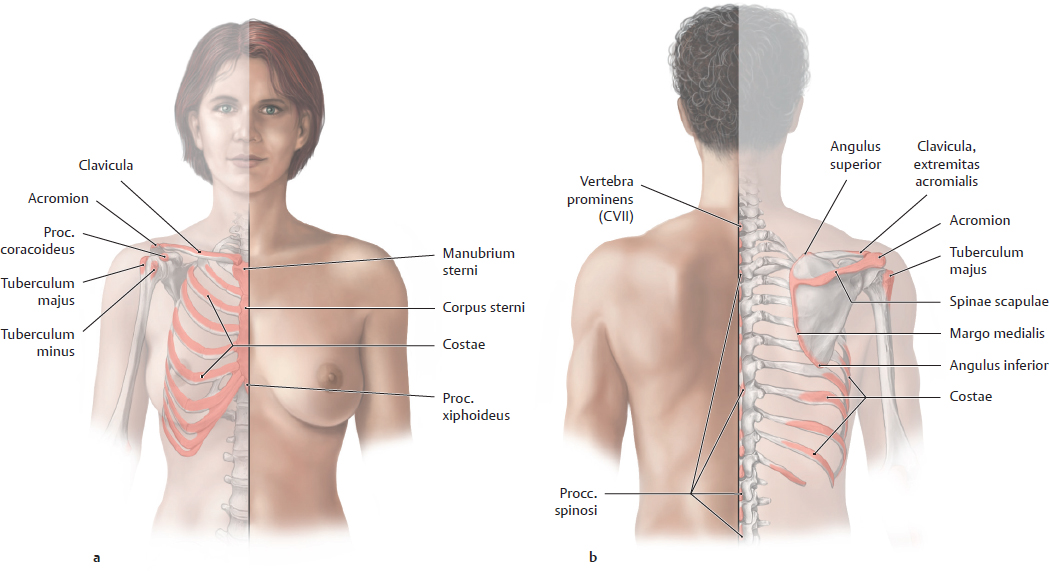
Topographical Anatomy Basicmedical Key
muscular triangle contains the strap muscles of the neck; larynx and thyroid gland lie deep to the strap muscles: omoclavicular triangle: boundaries: superior - inferior belly of the omohyoid m.; anterior - sternocleidomastoid m.; inferior - middle 1/3 of the clavicle: the external jugular vein courses deeply through the omoclavicular triangle
1 Head and Neck Basicmedical Key
First Online: 14 December 2022 423 Accesses Abstract In this chapter, we analyze the head's main anatomical challenges that are commonly related to injuries. There are specific regions discussed, such as the eyelids, nose, ears, and lips, besides the most common anatomical variants. In addition, the riskiest anatomical regions are also described.
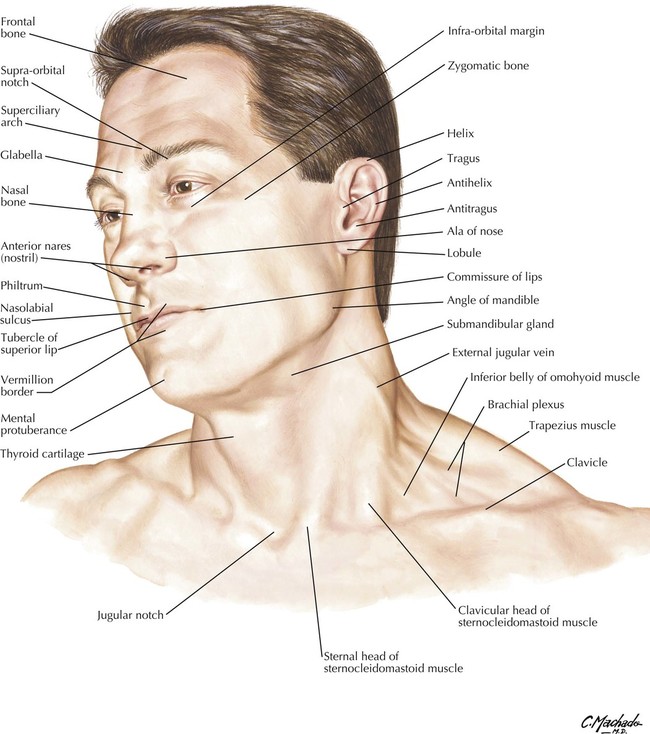
Understanding the Head & Neck Scientific Publishing
Written by an experienced and well-respected physician and professor, this new volume, building on the previous volume, Ultrasonic Topographical and Pathotopographical Anatomy, also available from Wiley-Scrivener, presents the ultrasonic topographical and pathotopographical anatomy of the head and neck, offering further detail into these important areas for use by medical professionals. This.

Pin on Acrylic painting techniques
Abstract This chapter contains sections titled: Topographic Anatomy of the Neck Fasciae, Superficial and Deep Cellular Spaces and their Relationship with Spaces Adjacent Regions (Fig. 37) Triangles.
Head and neck overview and surface anatomy Basicmedical Key
Introduction The neck is the bridge between the head and the rest of the body. It is located in between the mandible and the clavicle, connecting the head directly to the torso, and contains numerous vital structures.
Introduction to the Head and Neck Basicmedical Key
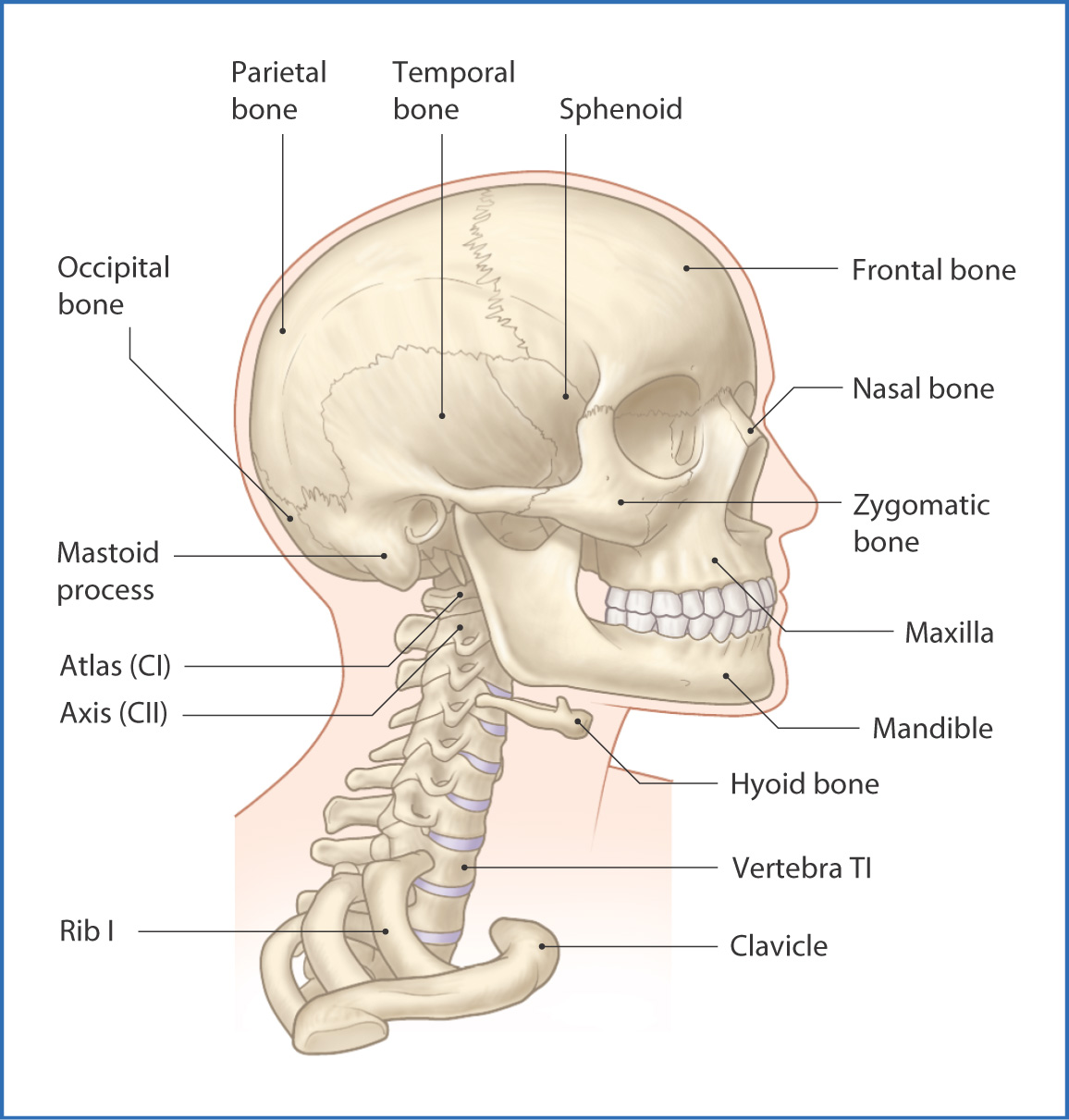
Skull Nose and nasal cavity Eye Ear Mouth Tooth Neck Sources Related articles + Show all Skull The skull is a strong, bony capsule that rests on the neck and encloses the brain. It consists of two major parts: the neurocranium (cranial vault) and the viscerocranium (facial skeleton).
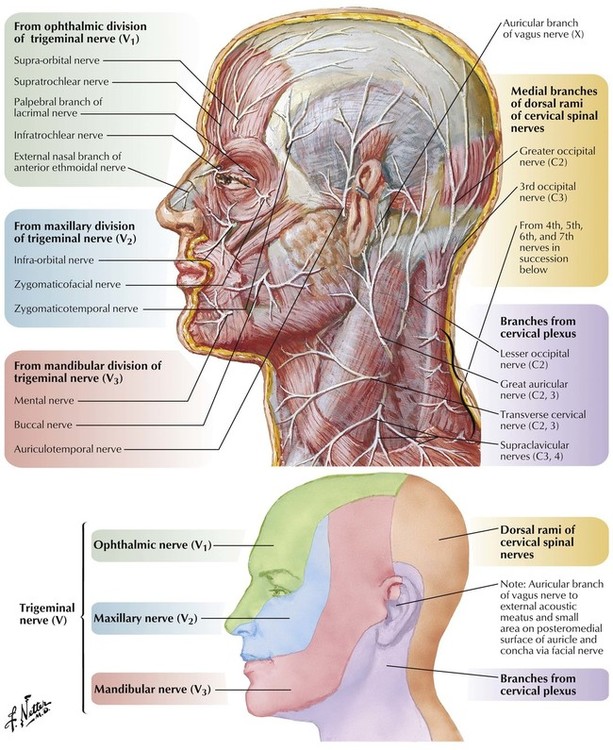
1 Head and Neck Basicmedical Key
The medical information on this site is provided as an information resource only, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes.
PPT Complex Odontogenic Infections PowerPoint Presentation ID1944812
The deep cervical fasciae of the neck, since its first description in the early 1800s, have been a source of considerable controversy amongst anatomists. Several different classification systems for these anatomic structures have been proposed based on topographic morphology, embryologic origin, and surgical approach. The most commonly accepted classification system found in the literature is.

Anatomy of the Neck TrialExhibits Inc.
Head Caput 1/2 Synonyms: none The head is the superior part of the body that is attached to the trunk by the neck. It is the control and communication center as well as the "loading dock" for the body. It houses the brain and therefore is the site of our consciousness: ideas, creativity, imagination, responses, decision making and memory.

Introduction into topographic anatomy of head & neck online presentation
Written by an experienced and well-respected physician and professor, this new volume, building on the previous volume, Ultrasonic Topographical and Pathotopographical Anatomy, also available from Wiley-Scrivener, presents the ultrasonic topographical and pathotopographical anatomy of the head and neck, offering further detail into these important areas for use by medical professionals.

Anatomy Of The Upper Chest Area / The Complete Human Body Anatomical Terminology Flashcards
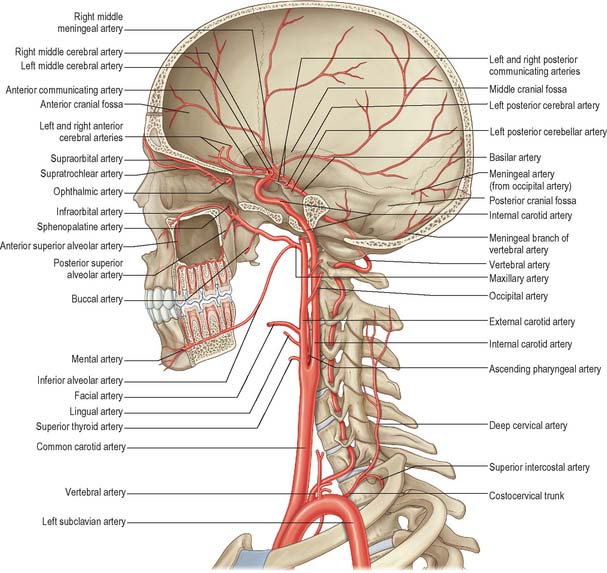
The roentgenograms of the skull and of the vertebral column of the head and neck skeleton and the arteriograms of the blood vessels of the neck and brain are vividly informative. The libraries of the medical schools will undoubtedly possess a copy of this book, yet it may be urged that all students. Spector B. Atlas of Topographical and.