
PPT Economies of Scale PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2998684
Economies of scale - Wikipedia Economies of scale As quantity of production increases from Q to Q2, the average cost of each unit decreases from C to C1. LRAC is the long-run average cost. Part of a series on Economics History Outline Index Branches and classifications Concepts, theory and techniques By application Notable economists Lists

What Are Economies Of Scale And Why They Matter FourWeekMBA
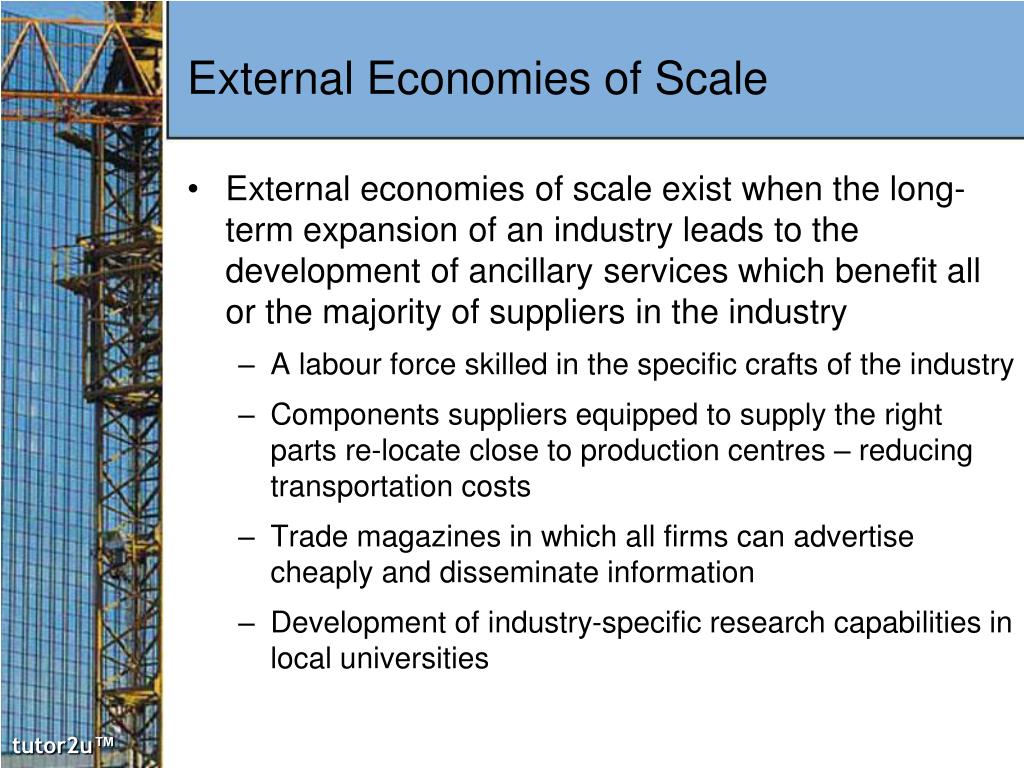
External economies of scale refer to the cost benefits that a company experiences as a result of factors external to the firm but within its industry or geographical area. These economies occur when an industry's output increases, leading to benefits for all companies within that industry.

What Are External Economies of Scale? External Economies of Scale In A Nutshell LaptrinhX
External economies of scale, or EEOS, are factors that help decrease production costs while simultaneously increasing output volume and financial gains. These factors are outside of the control of individual companies and organizations. Instead, these are industry-wide changes that relevant firms can inadvertently benefit from.
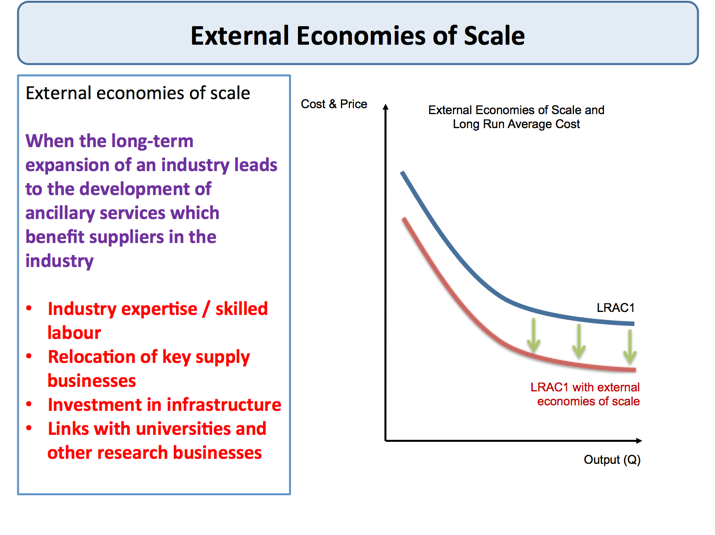
External Economies of Scale tutor2u Economics
External economies of scale refer to the cost advantages and productivity improvements that businesses can achieve by operating in an environment where the surrounding factors positively impact their operations. Unlike internal economies of scale, which result from a company's internal factors such as increased production levels or improved.

Economies of Scale Meaning and Types Owlcation
External economies of scale refer to the cost advantages that a group of firms or an entire industry can achieve due to their collective actions and the industry's growth. Its purpose is to benefit from factors beyond the control of any single company.
PPT Economies and Diseconomies of Scale PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1063050
Some examples of external economies of scale include: Infrastructure: A firm may benefit from external economies of scale if it is located in an area with well-developed infrastructure, such as roads, ports, and airports, which can reduce the cost of transportation and logistics. Skilled labour: A firm may benefit from access to a pool of skilled labor in a particular region, which can reduce.
/GettyImages-917884918-f87fc37f7d2f4253b0173c2c23fb03e0.jpg)
External Economies of Scale Definition
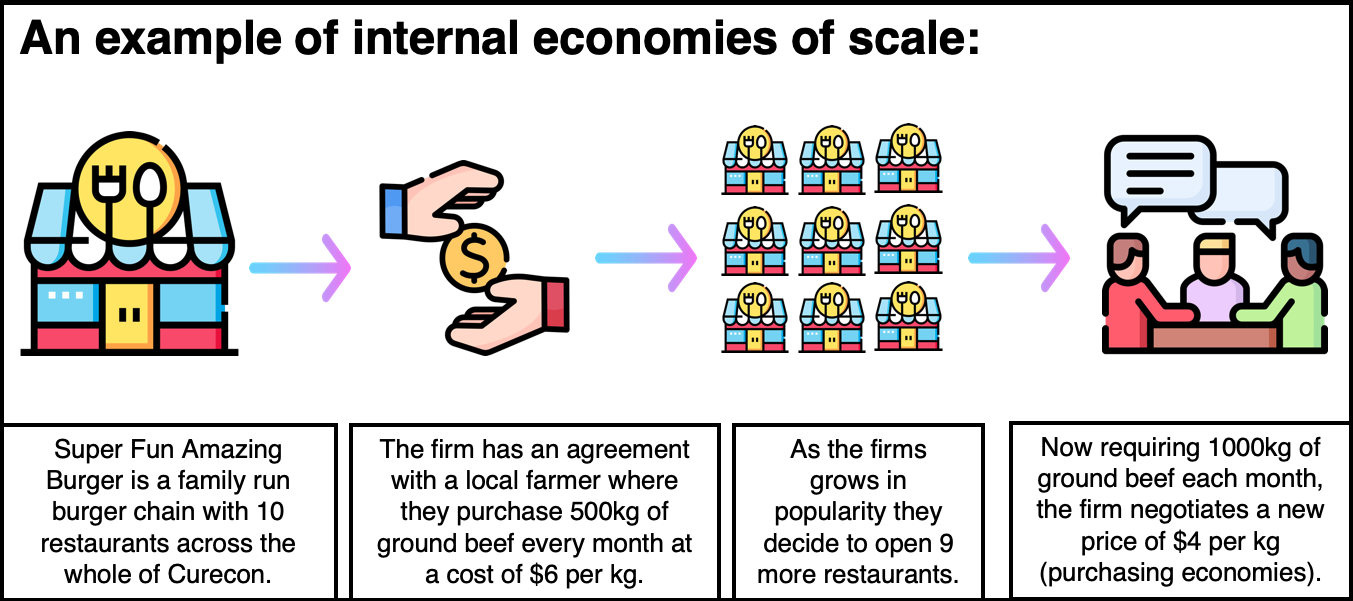
1. Internal Economies of Scale This refers to economies that are unique to a firm. For instance, a firm may hold a patent over a mass production machine, which allows it to lower its average cost of production more than other firms in the industry. 2. External Economies of Scale

Economies of Scale Example Best 4 Example of Economies of Scale
External economies of scale are generally described as having an effect on the whole industry. So when the industry grows, the average costs of business drop. External economies of scale can.

6.2 External Economies of Scale YouTube
Definition - External economies of scale occur when a whole industry grows larger and firms benefit from lower long-run average costs. External economies of scale can also be referred to as positive external benefits of industrial expansion. Individual firm experiencing economies of scale from a larger industry
Economies of scale là gì và cấu trúc Economies of scale trong Tiếng Anh
External Economies of Scale refer to benefits that come from external sources outside the control of the individual firm. Thus, they can lead to lower costs and increased productivity for all firms in the area. Example To illustrate external economies of scale, imagine a town that has multiple firms producing similar products.
What is economies of scale?
Investopedia / Mira Norian Understanding Economies of Scale The size of the business generally matters when it comes to economies of scale. The larger the business, the more the cost savings..
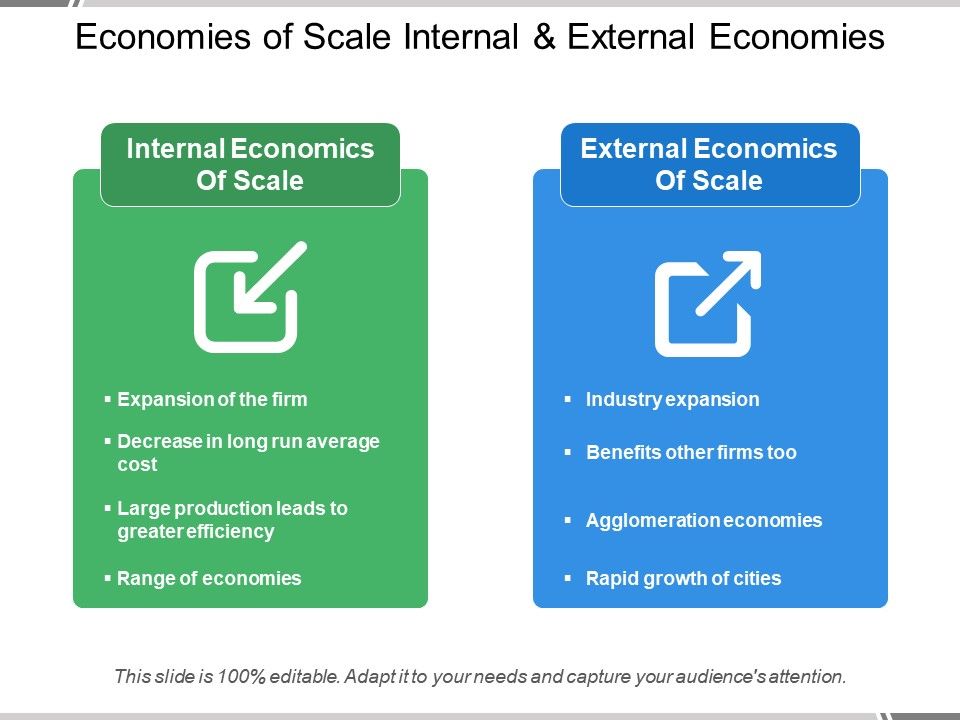
Economies Of Scale Internal And External Economies PowerPoint Slide Templates Download PPT
External economies of scale refer to factors that are beyond the control of an individual firm, but occur within the industry, and lead to a cost benefit. The prospect of external economies of scale often induces firms in the same industry to cluster together.
Differences between Internal and External Economies of Scale. YouTube
External economies of scale occur outside of a firm but within an industry. External Economies of Scale - revision video Here are five examples of industries that are clustered in a particular region and give rise to external economies of scale:

Economies of Scale tutor2u Business
External economies of scale describe factors beyond the control of a company that are present in the same industry and that lead to cost benefits. These factors may be positive or negative industry or economic trends. External economies of scale, therefore, are business-enhancing factors occurring outside a company but within the same industry.

What are economies of scale? Definition and meaning Market Business News
In economics of the firm, an external economy of scale refers to benefits that arise from general growth in the economy or a specific industry; external diseconomies are extra costs or.
Internal And External Economies Of Scale PowerPoint Design Template Sample Presentation PPT
External economies of scale are crucial as they drive industry growth, encourage regional development, reduce operational costs, and enhance competitiveness. Real-life examples such as Silicon Valley's transformation and the automotive industry in Germany exemplify the impact of these economies on innovation and international trade. The.