
Bacterial Cell Diagrams 101 Diagrams
Size of Bacteria. Bacteria are single-celled organisms. This means that each bacterium is made up of only one cell. This is very different from humans. Our bodies are made up of trillions of cells . Bacteria are much smaller than human cells. Bacterial cells are between about 1 and 10 μm long.
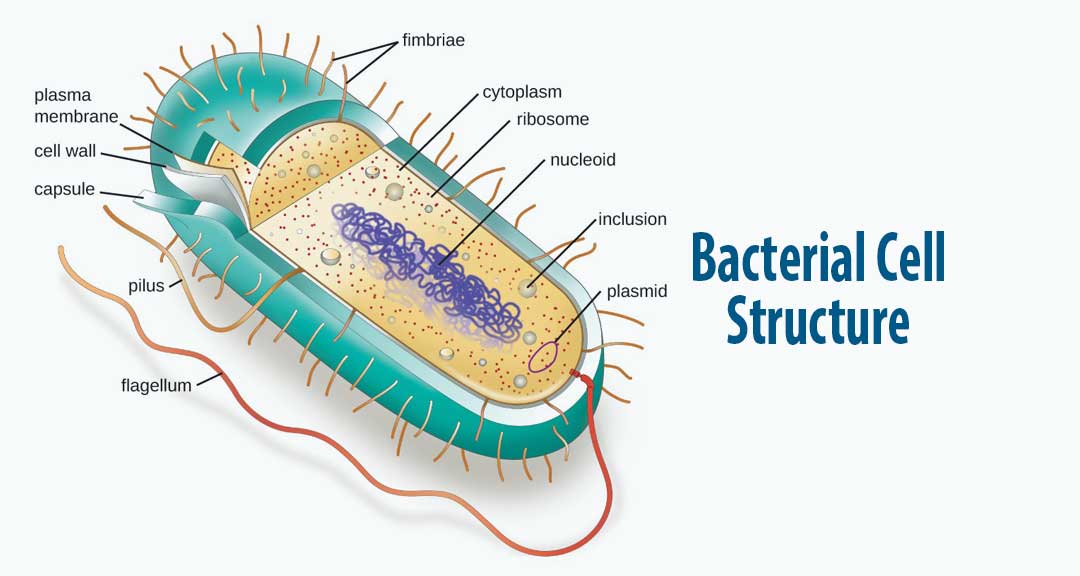
A Bacterial Cell With Flagella That Cover The Surface Is Called About
August 14, 2021 Bacteria are unicellular. Their structure is a very simple type. Bacteria are prokaryotes because they do not have a well-formed nucleus. A typical bacterial cell is structurally very similar to a plant cell. The cell structure of a bacterial cell consists of a complex membrane and membrane-bound protoplast.
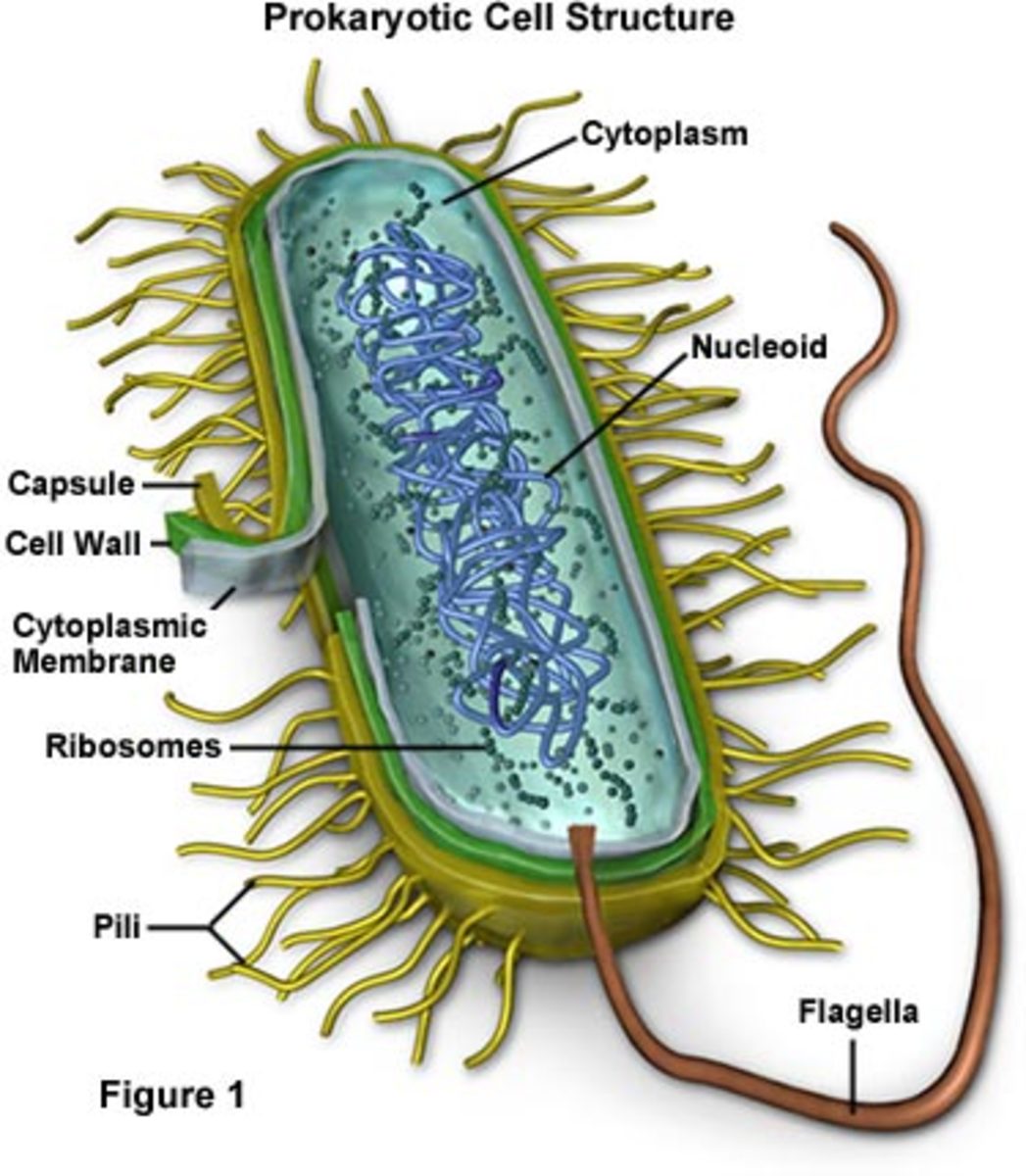
Bacterial Intracellular Structures That Give Bacteria/Prokaryotes an
In gram-negative bacteria, the cell wall is thin and releases the dye readily when washed with an alcohol or acetone solution. Cytoplasm - The cytoplasm, or protoplasm, of bacterial cells is where the functions for cell growth, metabolism, and replication are carried out. It is a gel-like matrix composed of water, enzymes, nutrients, wastes.

Bacterial Cell Diagrams 101 Diagrams
A prokaryote is a simple, single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
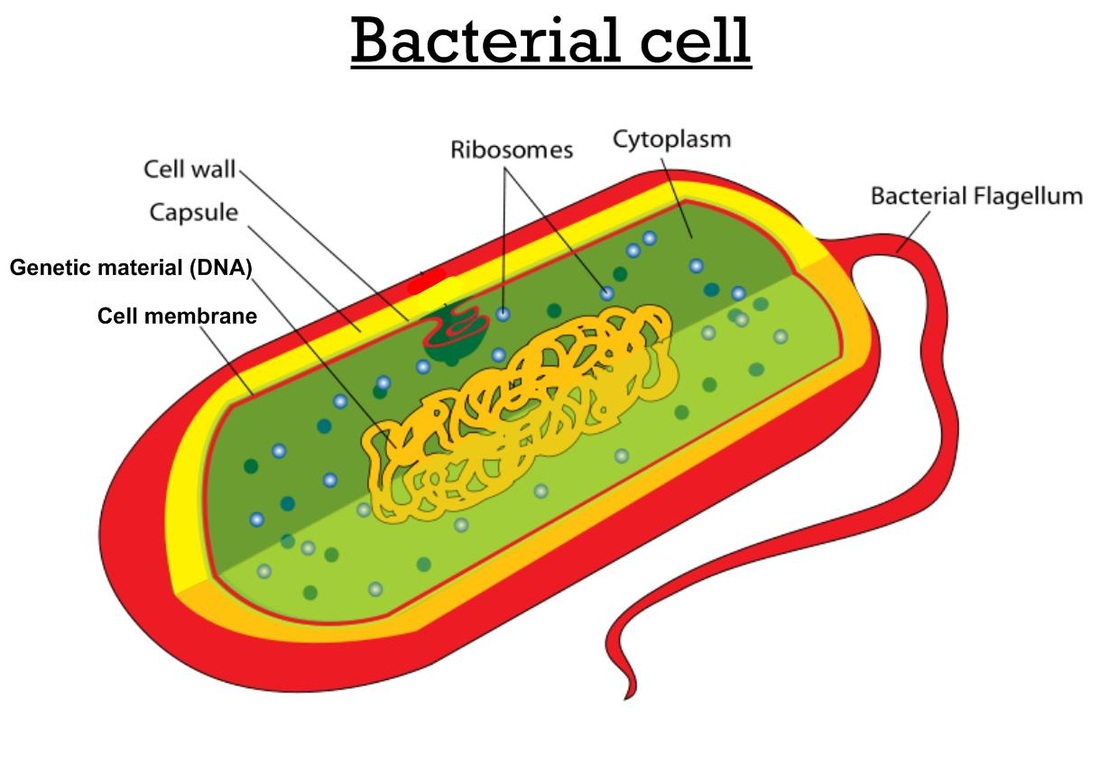
Bacteria Ms A Science Online
Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms belonging to the domains Bacteria and Archaea. Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells, have no nucleus, and lack organelles. All prokaryotic cells are encased by a cell wall. Many also have a capsule or slime layer made of polysaccharide.
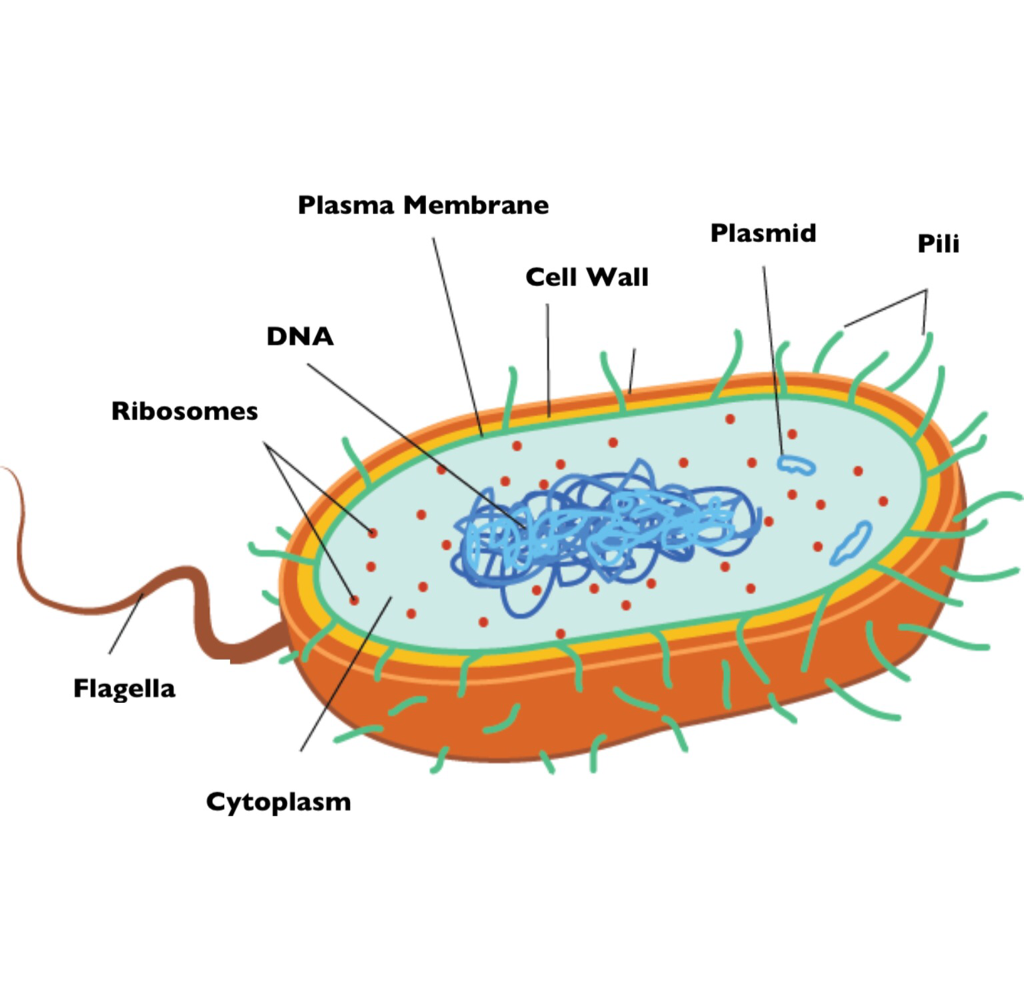
Bacteria Grade 11 Biology Study Guide
All bacteria, both pathogenic and saprophytic, are unicellular organisms that reproduce by binary fission. Most bacteria are capable of independent metabolic existence and growth, but species of Chlamydia and Rickettsia are obligately intracellular organisms. Bacterial cells are extremely small and are most conveniently measured in microns (10-6 m). They range in size from large cells such as.

Bacterial Cell Diagrams 101 Diagrams
Bacteria are single-celled organisms. Key points to note when comparing and contrasting the structure of bacterial cells with animal and plant cells are that they:
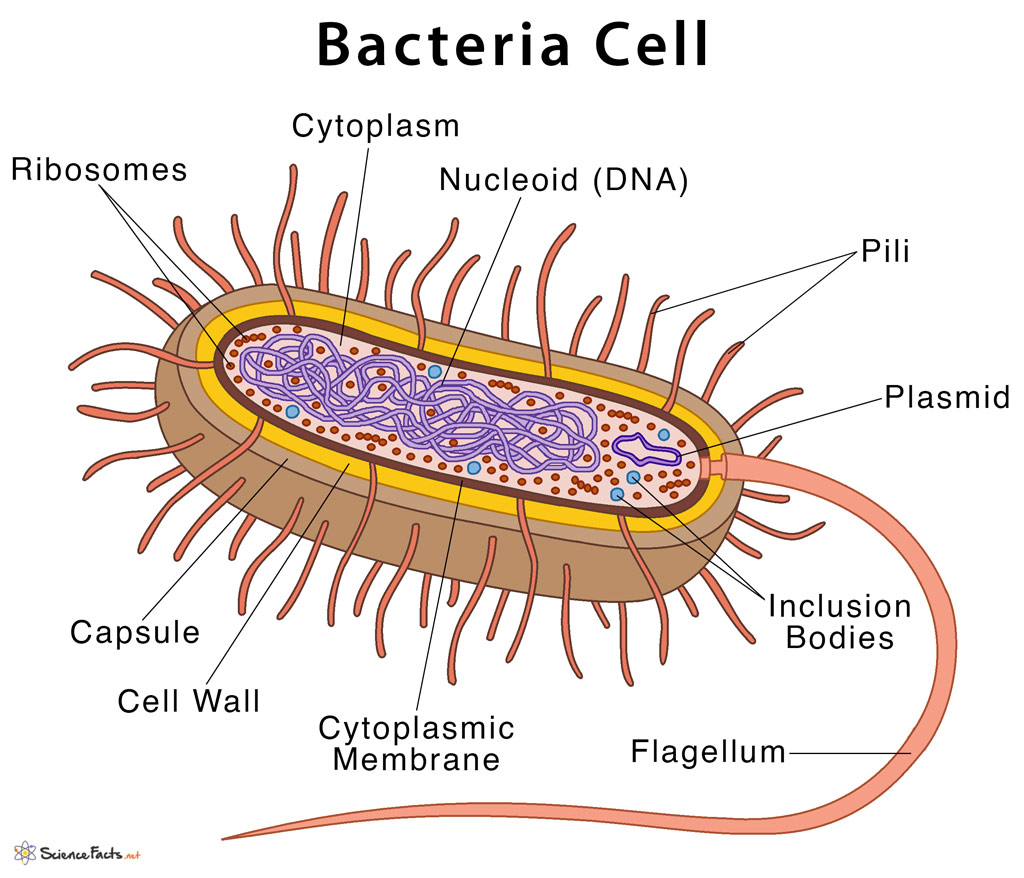
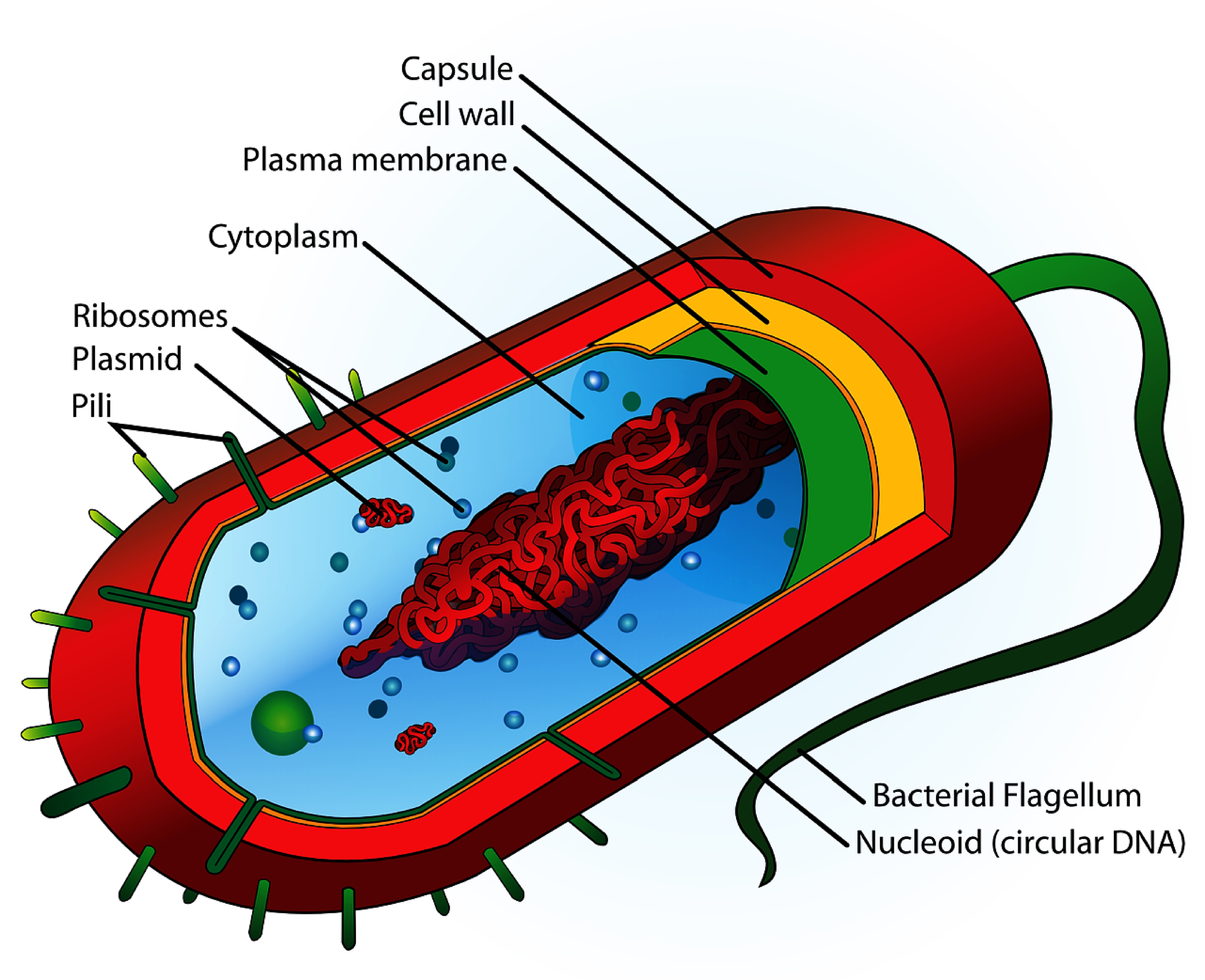
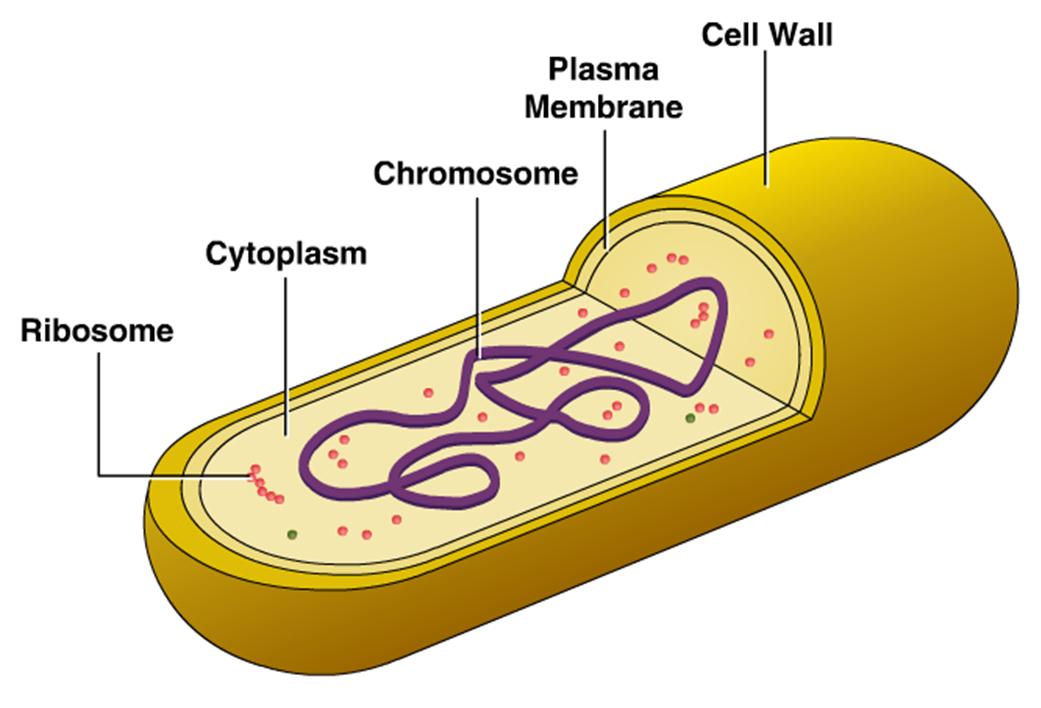
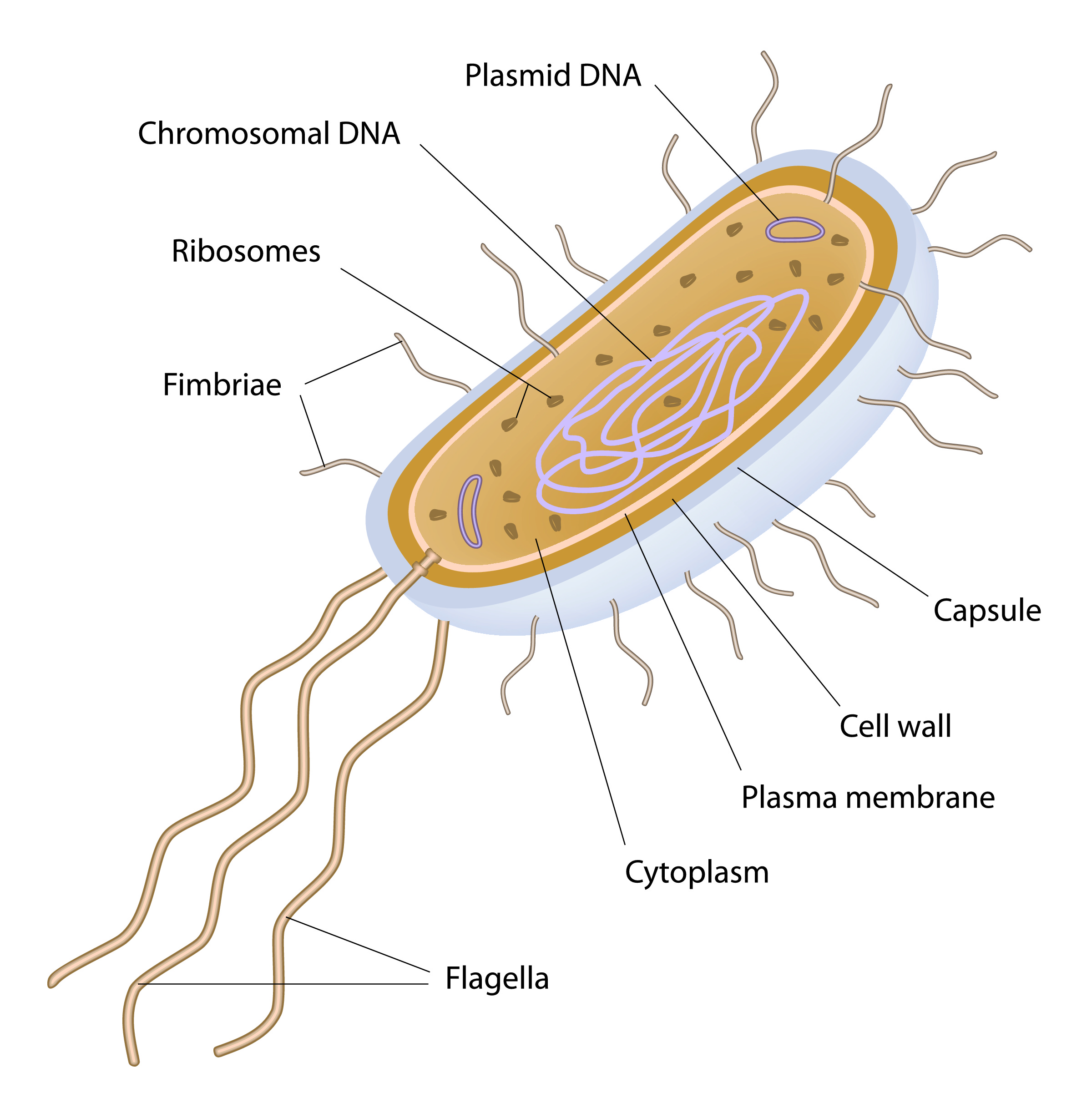
Bacteria Cell Structure
identify whether a bacterial cell is a prokaryotic cell or a eukaryotic cell;. but not animal cells; list the structure that are present in animal, but not plant cells. Draw a starfish egg with a diameter of approximately 2 cm. Label the cell membrane, chromatin, nucleolus, nuclear envelope, nucleus, and cytoplasm..

Label the Bacterial Cell Key New Unit 1 Cells and Cell Processes Ppt
Flagella 7. Pili and Fimbriae. Bacterial Cell: Component # 1. Cell Envelope: It is the outer covering of protoplasm of bacterial cell. Cell envelope consists of 3 components— glycocalyx, cell wall and cell membrane. (i) Glycocalyx (Mucilage Sheath): ADVERTISEMENTS:

Bacterial Cell Diagrams 101 Diagrams
Bacteria (sing. bacterium) are unicellular prokaryotic microorganisms which divide by binary fission. They do not possess nuclear membrane and the nucleus consists of a single chromosome of circular double-stranded DNA helix (Fig. 1.1). Flagella: ADVERTISEMENTS:
Effective use of alcohol for aromatic blending Tisserand Institute
Cell Structure of Bacteria (With Diagram) Article Shared by ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the cell structure of bacteria with the help of diagrams. A bacterial cell (Fig. 2.5) shows a typical prokaryotic structure.
Cellular Structure of Bacteria ZeroInfections
coccus (circle or spherical) bacillus (rod-like) coccobacillus (between a sphere and a rod) spiral (corkscrew-like) filamentous (elongated) Cell shape is generally characteristic of a given bacterial species, but can vary depending on growth conditions.

Unique Characteristics of Prokaryotic Cells Microbiology
bacteria, any of a group of microscopic single-celled organisms that live in enormous numbers in almost every environment on Earth, from deep-sea vents to deep below Earth's surface to the digestive tracts of humans. Bacteria lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other internal structures and are therefore ranked among the unicellular life-forms.
Cells worksheet from Times Tutorials
3.3 Bacterial Plasma Membranes. Describe the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure and identify the types of lipids typically found in bacterial membranes. Distinguish macroelements (macronutrients) from micronutrients (trace elements) and provide examples of each. Provide examples of growth factors needed by some microorganisms.

Page 1
1.11: Prokaryotic Cells. Distinguish between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells in terms of structure, size, and the types of organisms that have these cell types. Identify structures of bacterial cells in models and diagrams, including details of Gram-positive and Gram-negative cell walls and flagella.
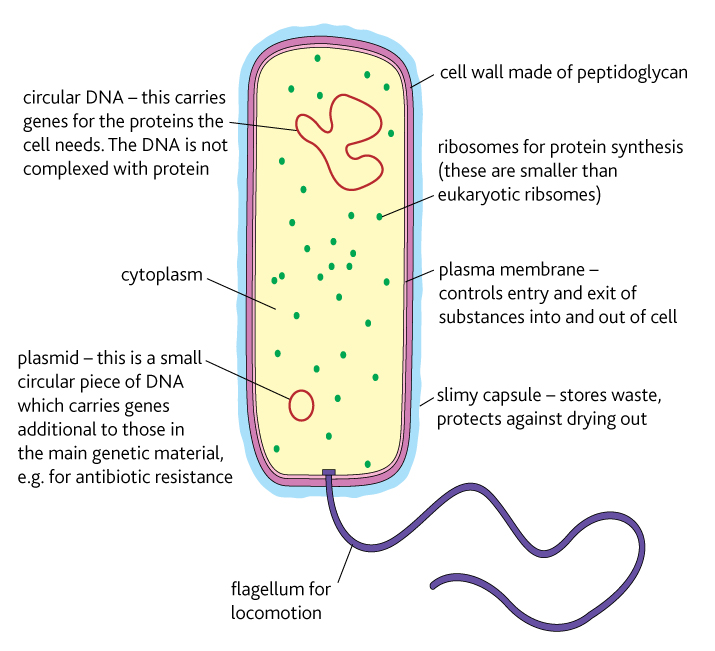
Bacterial cell structure Year 12 Human Biology
Capsule. A bacterial capsule is a polysaccharide layer that completely envelopes the cell. It is well organized and tightly packed, which explains its resistance to staining under the microscope. The capsule offers protection from a variety of different threats to the cell, such as desiccation, hydrophobic toxic materials (i.e. detergents), and bacterial viruses.